
You might wonder why some batteries last longer or can be reused while others cannot. The main difference between lithium batteries and lithium-ion batteries is rechargeability and chemistry. Lithium batteries are single-use, while lithium-ion batteries offer a rechargeable alternative. Knowing the difference helps you choose the right battery for your device and keeps you safe. Recent studies show that lithium-ion batteries power most smartphones, laptops, and even electric vehicles, which now make up over 60% of global lithium-ion demand. Using the right battery improves device performance and reduces safety risks.
主要区别
Rechargeability
When you choose between lithium batteries and lithium-ion batteries, rechargeability stands out as the most important difference. Lithium batteries are single-use. You cannot recharge them. Once they run out of power, you must replace them. These batteries work best in devices that need a long shelf life and low power, such as smoke alarms or remote controls.
Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, are rechargeable. You can use them hundreds of times before they wear out. This makes them ideal for devices you use every day, like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries have built-in management systems. These systems help control charging, temperature, and voltage, which keeps you safe and extends the battery’s life.
Key Points:
- Lithium batteries are non-rechargeable and meant for single use.
- Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable and support many charge cycles.
- Lithium batteries cost less and suit low-drain, single-use devices.
- Lithium-ion batteries cost more at first but save money over time in high-demand electronics.
- Lithium batteries have a longer shelf life, while lithium-ion batteries lose some charge each month even when not in use.
Chemistry
The chemistry inside each battery type also sets them apart. Lithium batteries use lithium metal as the anode. This gives them high energy and a long shelf life. However, lithium metal can form sharp crystals called dendrites, which may cause safety issues.
Lithium-ion batteries use a different approach. They have a graphite anode and a lithium cobalt oxide cathode. During charging and discharging, lithium ions move between these two materials. This process is called intercalation. The battery does not use pure lithium metal, which makes it safer and more stable for repeated use. Lithium-ion batteries also form a protective layer inside, which helps prevent damage and keeps the battery working longer.
You will find that these differences in battery chemistries affect how each battery performs, how long it lasts, and how safe it is to use.
Quick Comparison Table
Here is a simple table to help you see the main differences between lithium batteries and lithium-ion batteries:
| 特点 | Lithium Batteries | Lithium-ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Rechargeability | ❌ Single-use, not rechargeable | ✅ Rechargeable, hundreds of cycles |
| Chemistry | Lithium metal anode | Graphite anode, lithium-ion cathode |
| Structure | Simple, rigid casing | Complex, includes management system |
| Shelf Life | Up to 10-12 years | Loses ~5% charge per month unused |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher upfront, lower long-term cost |
| Common Uses | Smoke alarms, watches, cameras | Phones, laptops, electric vehicles |
| 安全 | Lower risk of overheating | Needs safety circuits for protection |
| Energy Density | High (single-use only) | High (rechargeable, repeated use) |
| Flexibility | Rigid shapes | Rigid or flexible (polymer types) |
📝 小贴士 Always check your device’s manual to see which battery technology it needs. Using the wrong type can damage your device or cause safety problems.
Lithium Batteries

Structure
You will find that lithium batteries have a simple but effective structure. Each battery contains a cathode made from lithium-metal oxides or polyanion oxides, which sits on a thin aluminum foil. The anode usually uses graphite or other materials that can hold lithium. Between the cathode and anode, there is an electrolyte. This part lets lithium ions move but blocks electrons. A separator keeps the two electrodes apart to prevent short circuits. The battery also includes binders and additives to keep everything stable and improve performance. The whole cell sits inside a strong casing to protect it from damage. You can see these parts in many shapes, such as button, cylindrical, or prismatic cells.
| 组件 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Cathode | Lithium-metal oxides on aluminum foil, with binders and additives |
| Anode | Graphite or other lithium-hosting materials |
| 电解质 | Moves lithium ions between electrodes |
| 分离器 | Prevents short circuits by keeping electrodes apart |
| Current Collectors | Aluminum for cathode, copper for anode |
| Cell Casing | Protects the battery |
它们如何工作
Lithium batteries generate power through a special electrochemical process. When you use the battery, lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte. At the same time, electrons flow through your device, creating electricity. This process only goes one way in lithium batteries, so you cannot recharge them. The design gives you high energy and long shelf life, but you must replace the battery when it runs out. The internal structure affects how much energy you get, how long the battery lasts, and how safe it is to use.
⚡ 小贴士 Using high-quality materials and good design can lower internal resistance, giving you better capacity and longer battery life.
Common Uses
You will see lithium batteries in many devices and industries. Their high energy and long shelf life make them perfect for smoke alarms, cameras, and watches. In aerospace, satellites and spacecraft use lithium batteries because they are lightweight and powerful. Environmental monitoring tools, like sensors and data loggers, rely on these batteries for long-term energy storage. Automotive electronics, wireless devices, and smart home products also use lithium batteries for reliable power. Even in emergency backup systems, lithium batteries provide steady energy when you need it most.
| Application Sector | Examples and Description |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Satellites, spacecraft, UAVs benefit from lightweight, high-capacity lithium batteries. |
| Environmental Monitoring | Sensors and data loggers in remote locations use lithium batteries for long life. |
| Home Appliances | Cordless vacuums, smart thermostats, and wireless speakers use lithium batteries for compact power. |
| Emergency Backup Power | Backup for lighting, communication, and medical equipment during outages. |
Lithium-ion Batteries

Structure
You will notice that lithium-ion batteries have a unique structure compared to other battery chemistries. Each lithium-ion battery contains an anode, cathode, separator, and electrolyte. The plates inside often appear tightly wound or laminated, which helps save space and improve performance. Manufacturers add special safety features like Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) devices, Circuit Interrupt Devices (CID), pressure vents, and gasket seals. These parts help prevent overheating, fire, or explosion, making lithium-ion batteries safer for everyday use.
You can find several types of lithium-ion batteries, such as cylindrical, rectangular, and pouch cells. Each type uses different packaging and internal designs. For example, cylindrical types use a steel shell and wound electrodes, while pouch cells use a flexible film and laminated plates. This flexibility allows lithium-ion batteries to fit many devices, from smartphones to electric vehicles.
| Type of Lithium-ion Battery | Shape & Packaging | 主要功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 圆柱形 | Steel shell | Stable, low cost, wound electrodes |
| Rectangular | Light housing | Customizable, higher energy density |
| Pouch Cell | Flexible film | Lightweight, flexible, thin separators |
它们如何工作
Lithium-ion batteries store and release energy by moving lithium ions between the anode and cathode. When you charge the battery, lithium ions travel from the cathode to the anode, storing energy. When you use the device, the ions move back to the cathode, releasing energy for your device to use. This process is called reversible intercalation. The electrolyte lets ions move but blocks electrons, which keeps the current under control. The separator keeps the anode and cathode apart to prevent short circuits. The battery management system (BMS) monitors temperature and charging, which helps keep the battery safe and extends its life.
🔋 请注意: The structure of lithium-ion batteries makes them rechargeable. The movement of ions between the electrodes allows you to use the battery again and again.
Common Uses
You will see lithium-ion batteries in many modern devices and industries. These batteries power smartphones, laptops, and tablets because they offer high energy density and long run times. Electric vehicles, such as cars, buses, and scooters, rely on lithium-ion batteries for lightweight, fast charging, and long lifespan. Many types of lithium-ion batteries, including those with lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide, appear in solar energy storage systems, helping store power from solar panels for later use.
Other common uses include:
- Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) systems for computers and medical devices
- Surveillance and alarm systems in remote locations
- Digital cameras and wearable devices like smartwatches
- Drones and personal mobility devices
- Data centers and backup systems
You can also find lithium-ion batteries in aerospace, military, and renewable energy projects. Their flexible design and high capacity make them a top choice for many applications.
Lithium vs. Lithium-ion Batteries
Energy Density
When you compare lithium batteries and lithium-ion batteries, you will notice a big difference in energy density. Energy density tells you how much energy a battery can store for its size or weight. Both types offer high energy density, but lithium-ion batteries have become the standard for most modern devices because they balance high energy density with long battery life and safety.
Recent research shows that lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles reach energy densities between 160 Wh/kg and 250 Wh/kg. Some advanced lithium-ion batteries, like solid-state types, can go even higher, up to 450 Wh/kg. This means you get more power in a smaller, lighter battery. Lithium-air and lithium-sulfur batteries, which are still in development, promise even higher specific energy and high energy density, possibly four times greater than current lithium-ion batteries. These new batteries could change how you use energy in the future.
Lithium batteries also provide high specific energy and high energy density, especially in single-use applications. You will find them in devices where you need a lot of power in a small space, such as cameras or medical equipment. However, you cannot recharge them, so you must replace them after use.
📊 请注意: If you want the best performance for portable electronics or electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries give you the highest energy density and specific energy available today.
Lifespan
You should always consider how long a battery will last before you need to replace it. The lifespan of a battery depends on how many times you can use and recharge it, known as cycle life, and how many years it will work well.
Here is a table that shows the typical lifespan and cycle life for different battery types:
| 电池类型 | Typical Cycle Life (cycles) | Typical Service Life (years) |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion (general) | 300-1000 | 2-10 |
| Lithium Polymer (LiPo) | 1500-2000 | 2-5 |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | 3000-6000+ | 15-20 |
| Lithium (primary, non-rechargeable) | 1 (single-use) | 5-15 |
Lithium-ion batteries stand out because you can recharge them many times. Some types, like lithium iron phosphate, last even longer and can handle thousands of cycles. Lithium batteries, on the other hand, are single-use. You get a long shelf life, sometimes up to 15 years, but you must replace them after one use. If you want long battery life and high performance, lithium-ion batteries are the better choice.
安全
Safety is a key factor when you choose between lithium and lithium-ion batteries. Both types can be dangerous if you do not handle them properly. You need to know the risks to keep yourself and your devices safe.
- Both lithium and lithium-ion batteries have a higher fire risk than other batteries because of their flammable parts.
- Common safety risks include:
- Fire hazards from overheating or thermal runaway.
- Battery cell breach, which can cause fire and gas release.
- Overcharging and overheating, which may lead to dangerous incidents.
- Mechanical damage, such as cracking or swelling, which can signal battery failure.
- Signs of trouble include swelling, heat, discoloration, noise, smoke, or strange smells.
Lithium batteries use a sealed design to protect the reactive lithium metal inside. If the seal breaks, the battery can catch fire quickly. Lithium-ion batteries use special safety circuits and management systems to lower the risk, but they still need careful handling. You should never use damaged batteries or charge them with the wrong charger.
⚠️ 小贴士 Always store and use batteries in cool, dry places. Watch for signs of damage, and recycle old batteries safely.
Cost
You will see a difference in cost when you compare lithium batteries and lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries cost more upfront, but they last much longer and need less maintenance. Over time, this makes them a better value for devices you use often.
| 电池类型 | Upfront Cost | Lifespan (cycles) | Maintenance | Total Cost Over Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 锂 | 低 | 1 (single-use) | None | High (needs frequent replacement) |
| Lithium-ion | 高 | 300-6000+ | 低 | Low (long-term savings) |
For example, lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles cost about $139 to $151 per kWh in 2024. This price has dropped over the years because of better technology and larger production. Even though you pay more at first, you save money because you do not need to replace the battery as often. Lithium batteries cost less to buy, but you must replace them every time they run out, which adds up if you use them a lot.
环境影响
You should think about the environment when you choose a battery. Both lithium and lithium-ion batteries have a big impact on the planet, from mining to disposal.
Producing lithium-ion batteries creates almost twice as much carbon emissions as making regular car engines. About 46% of electric vehicle emissions come from battery manufacturing. Mining lithium uses a lot of water—about 2 million tonnes for every tonne of lithium. This causes water shortages in dry regions like South America’s Lithium Triangle. Nickel and cobalt mining for lithium-ion batteries also pollutes land and water. Some countries have shut down mines because of this damage.
Most batteries, including lithium and lithium-ion, end up in landfills. Only about 5% get recycled because recycling is hard and expensive. Old batteries can leak toxic chemicals and start fires in landfills. Governments are pushing for better recycling, but progress is slow.
🌱 请注意: If you want to lower your impact, choose rechargeable lithium-ion batteries and recycle them when possible. This helps reduce waste and pollution.
Quick Comparison Table
Here is a side-by-side look at lithium vs. lithium-ion batteries:
| 特点 | Lithium Batteries | Lithium-ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Rechargeability | Single-use only | Rechargeable, many cycles |
| 高能量密度 | 是 | Yes (even higher in advanced types) |
| High Specific Energy | 是 | 是 |
| Lifespan | Long shelf life, single use | Long battery life, many recharges |
| 安全 | Lower risk if sealed, but fire risk if breached | Needs safety circuits, risk of fire if damaged |
| Cost | Low upfront, high over time | High upfront, low over time |
| 环境影响 | High (disposal, mining) | High (production, disposal, mining) |
| Performance | Good for low-drain devices | Best for high-drain, daily devices |
📝 小贴士 Always match the battery type to your device’s needs. Think about how often you use it, how long you want it to last, and how you will dispose of it.
Pros and Cons
Lithium Batteries
When you look at lithium batteries, you will see many strengths. These batteries store a lot of energy in a small, lightweight package. You can use them in portable electronics and devices that need compact power. Many people choose lithium batteries because they last a long time—sometimes up to 10 years if you take care of them. You do not need to do any maintenance, which saves you time and effort. Fast charging and long run times make them useful for many jobs. As technology improves, the cost of lithium batteries keeps dropping.
Advantages of lithium batteries:
- High energy density for more power in a small size
- Lightweight and easy to carry
- Long lifespan with proper care
- No maintenance needed
- Fast charging and longer run times
- Lower energy use during charging
However, you should also know the downsides. Lithium batteries can get damaged by high temperatures. You must store and use them carefully to avoid problems. Over time, their performance drops, and they hold less charge. Making and throwing away these batteries can hurt the environment. They cost more than lead-acid batteries, and you may need special equipment to use them safely. Battery Management Systems (BMS) are required for safety, but these can sometimes limit power or shut down the battery.
Disadvantages of lithium batteries:
- Sensitive to heat and need careful handling
- Performance drops as the battery ages
- Environmental concerns from mining and recycling
- Higher upfront cost
- Need for BMS and possible equipment changes
Lithium-ion Batteries
You will find that lithium-ion batteries power most of your modern devices. These batteries have a high energy density, so your phone or laptop can run longer without getting heavier. Each cell gives a higher voltage, which means you need fewer cells for the same job. Lithium-ion batteries charge quickly and last through many cycles. They have become the top choice for electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and even airplanes.
Pros of lithium-ion batteries:
- High energy density for lighter, longer-lasting devices
- Higher voltage per cell for efficient designs
- Fast charging and long cycle life
- Essential for modern technology and electric vehicles
You should also be aware of the risks. Lithium-ion batteries need careful charging and discharging. If you do not follow the right steps, the battery can overheat or even catch fire. Problems like thermal runaway can happen if the battery gets damaged or has a defect. Fires from lithium-ion batteries are hard to put out. Some safety issues have made headlines, such as the Boeing 787 Dreamliner battery fires. You must use proper chargers and avoid damaging the battery to stay safe.
Cons of lithium-ion batteries:
- Need precise charging and handling
- Risk of overheating, fire, or explosion
- Fires are hard to control
- Manufacturing defects can cause sudden failure
- Confusing terms and types can make choosing the right battery harder
📝 小贴士 Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging and storing lithium-ion batteries. This helps you stay safe and get the best performance.
Choosing the Right Battery
Application Guide
You need to match the battery to your device or project for the best results. Start by thinking about how you will use the battery. If you need power for a long time without recharging, like in smoke alarms or medical devices, lithium batteries work well. These batteries last for years and have a long shelf life. For devices you use every day, such as smartphones, laptops, or electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries are the better choice. They recharge quickly and handle many charge cycles.
If you work with high-energy applications, like power tools or drones, you should look for batteries with 高能量密度. Lithium-ion batteries fit these needs because they store more energy in a small space. For renewable energy storage, such as solar panel systems, lithium iron phosphate batteries offer safety and long life. Vehicles and electric vehicles also rely on lithium-ion batteries for their balance of power and rechargeability.
📝 小贴士 Always check the battery’s voltage and size to make sure it fits your device. Using the wrong battery can damage your equipment or cause safety problems.
Key Factors
When you choose a battery, you should look at more than just the type. Many factors affect performance, safety, and cost. Here is a table to help you compare:
| Factor | Description & Impact on Selection |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | Affects compatibility and performance in your device. |
| Capacity (Specific Energy & Power) | Shows how much energy and power the battery can deliver for its weight. |
| Lifespan (Cycle Life) | Tells you how many times you can use and recharge the battery. |
| Charging & Discharging Rates | High rates can shorten battery life; some batteries handle fast charging better. |
| Cost (Acquisition & Maintenance) | Upfront price and long-term expenses both matter. |
| Safety & Environmental Impact | Some batteries are safer and better for the environment. |
| Operating Temperature | Batteries work best within certain temperature ranges. |
| Depth of Discharge (DoD) | Deeper discharges can shorten battery life unless the chemistry allows it. |
| Battery Management System Optimization | Helps maximize performance and lifespan. |
You should also consider the company that makes the battery. A reliable manufacturer offers better support and safer products. Look for batteries with UN38.3 certification to ensure safe transport and use. Product variety and expert customer support also help you find the best fit for your needs.
⚡ 请注意: Battery aging affects both performance and safety. Over time, batteries lose capacity and may become less safe. Regular checks and proper storage help extend battery life.
Misconceptions
Common Myths
Many people believe things about lithium and lithium-ion batteries that are not true. Surveys show that almost one in four people do not know what a lithium-ion battery is. Most people do not realize these batteries can catch fire or explode if handled the wrong way. Only 40% know not to charge e-bike or scooter batteries overnight or when no one is watching. Less than half know how to recycle or handle damaged batteries safely.
Here are some of the most common myths:
- You can throw lithium-ion batteries in the trash or regular recycling bins. In fact, 33% of Americans think this is safe, but it can cause fires.
- Many people believe electric vehicle (EV) batteries cannot be recycled. Almost half of those surveyed think this is true, but battery materials can be reused.
- Some think lithium-ion batteries are more dangerous than gasoline. About 40% of people believe this, but both have risks if not handled properly.
- Many people worry that EV batteries will fill landfills with toxic waste. In reality, recycling programs can recover valuable materials.
- Some believe EVs are always slow, small, or hard to charge. Over 50% think EV batteries do not last as long as gas engines.
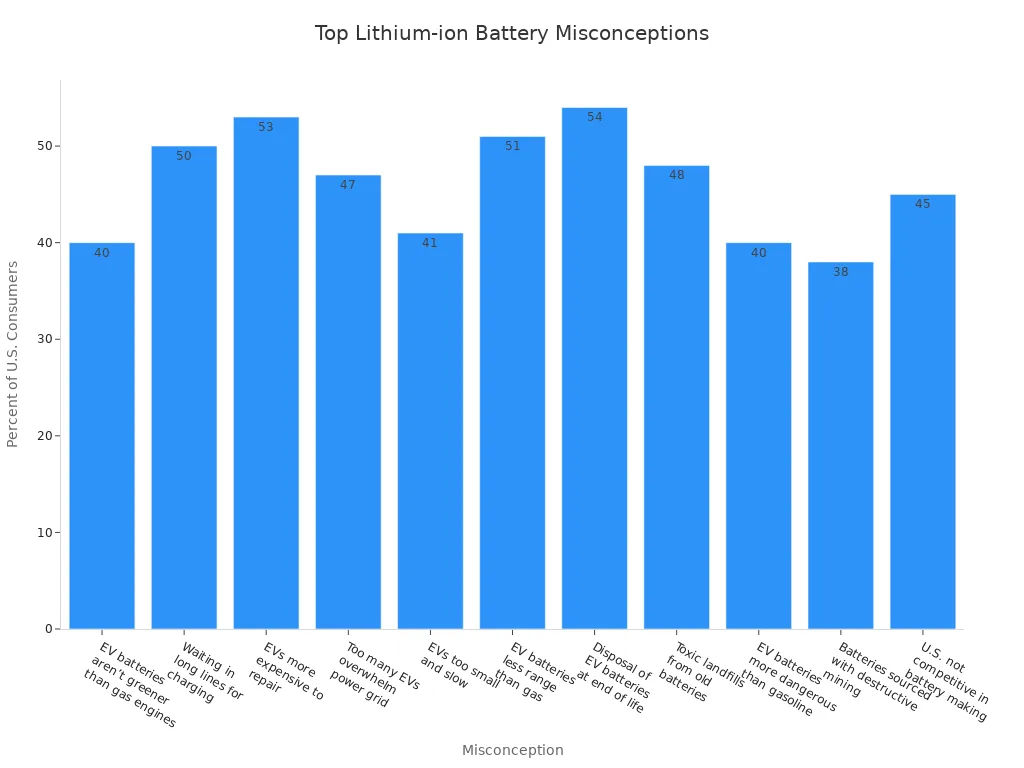
| Misconception | Percentage of U.S. Consumers |
|---|---|
| EV batteries cannot be recycled | 47% |
| EVs are more expensive to repair | 53% |
| Lithium-ion batteries are more dangerous | 40% |
| EV batteries do not offer enough range | 51% |
| EVs will cause toxic landfills | 48% |
📝 请注意: Never put lithium-ion batteries in household trash or recycling bins. Always use a battery recycling center.
Safety Tips
You can keep yourself and your devices safe by following simple rules. Always use the charger that comes with your device. Do not use chargers that do not match your battery. Handle batteries gently. If you drop or damage a battery, stop using it right away. If you see swelling, leaks, or strange smells, unplug the device and call for help.
Here are some important safety tips:
- Follow the instructions from the manufacturer for charging and storage.
- Charge batteries in open areas, away from things that can burn.
- Do not leave batteries charging overnight or when you are not home.
- Store batteries in cool, dry places, between 68°F and 77°F.
- Cover battery terminals with tape before recycling, or use a plastic bag.
- Never throw batteries in the trash or regular recycling bins.
- If a battery gets wet or damaged, keep it away from your home and call a professional.
- Unplug devices when fully charged to prevent overheating.
⚠️ 小贴士 If you notice a battery getting hot, swelling, or leaking, stop using it and move it to a safe place. Call 9-1-1 if you see smoke or fire.
You now know that lithium batteries work best for single-use, low-drain devices, while lithium-ion batteries suit high-demand, rechargeable applications. Choosing the right battery keeps you safe, saves money, and boosts performance. Always check these points before you decide:
- Device power needs and usage pattern
- Battery type (rechargeable or single-use)
- Safety certifications like UL or UN38.3
- Expected lifespan and maintenance
- Size, weight, and temperature limits
📝 Remember: Match your battery to your device and environment for the best results.
常见问题
What is the main difference between lithium and lithium-ion batteries?
You can recharge lithium-ion batteries many times. Lithium batteries are single-use. You must replace them when empty. Lithium-ion batteries use a different chemistry that makes them safer for repeated charging.
Can you use lithium-ion batteries in any device?
You should only use lithium-ion batteries in devices designed for them. Using the wrong battery can damage your device or cause safety problems. Always check your device’s manual before choosing a battery.
How do you store lithium and lithium-ion batteries safely?
Store batteries in a cool, dry place. Keep them away from heat, water, and direct sunlight. Do not store batteries in metal containers. Use the original packaging or a battery case for extra safety.
What should you do if a battery leaks or swells?
Stop using the battery right away. Move it to a safe area. Do not touch leaking material. Contact a recycling center or local waste service for help. Never throw damaged batteries in the trash.
Are lithium-ion batteries better for the environment?
Lithium-ion batteries reduce waste because you can recharge them many times. However, making and recycling them uses energy and resources. Always recycle old batteries to help protect the environment.

