一句话定义
袋式电池是一种可充电锂离子电池,其外壳采用柔性层压箔袋(而非刚性金属外壳),最大限度地提高了能量密度,减轻了重量,提高了设计灵活性,这些都是与棱柱式和圆柱形电池相比所具有的重要优势。
详细说明
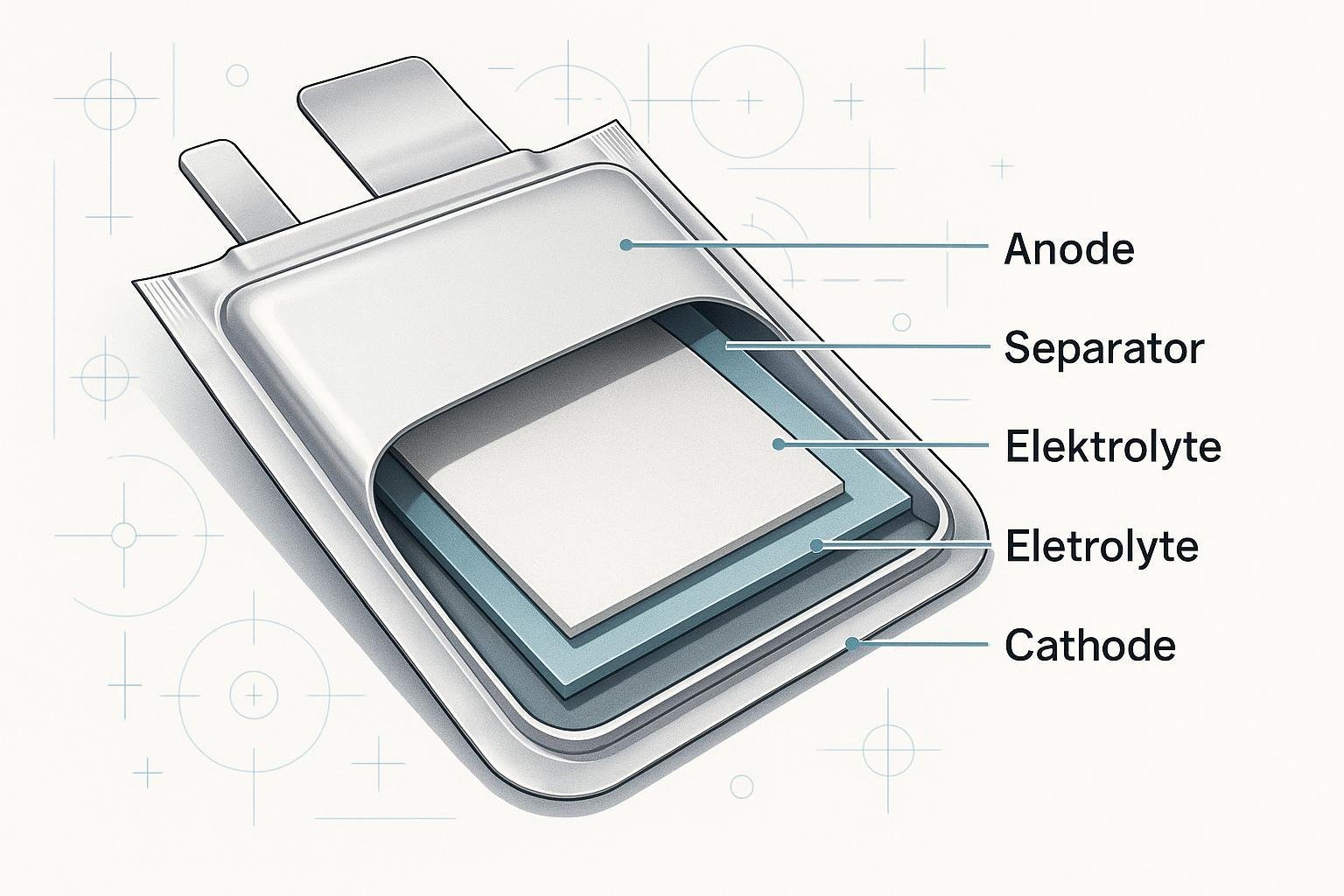
在软袋电池中,阳极(通常为石墨)、阴极(如氧化钴锂、锰或磷酸铁)、隔膜和液体或凝胶电解液层层叠加,密封在一个薄薄的热封铝箔塑料袋中。与圆柱形或棱柱形电池的硬罐不同,这种软袋可适应不同的尺寸和形状,最大限度地减少了未使用的空间,提高了 90-95% 的包装效率(见图 1)。 Grepow 比较).外袋只能提供最低限度的物理保护,因此,精心设计的外部支撑结构和电池管理(BMS)集成至关重要。
电池工作时,锂离子通过电解液在阳极和阴极之间穿梭,电子则通过外部电路在焊接在电池内部集流器上的薄片导电端子之间移动。
主要组件和功能
- 活性材料:石墨阳极、各种锂基阴极
- 分离器:微孔聚合物,防止短路
- 电解质:液体或凝胶,有时以聚合物为基础,安全性更高
- 层压袋外壳:多层铝箔/塑料层压板,精确热封
- 标签:铝/铜焊接连接器,用于电力传输
技术亮点:
- 高能量密度:典型值为 150-250 Wh/kg
- 卓越的包装效率:高达 95%
- 轻质、扁平或定制形状设计
- 需要谨慎的膨胀/热管理和强大的模块支持
视觉对比表
| 特点 | 邮袋电池 | 棱镜电池 | 圆柱形电池 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 外壳材料 | 柔性层压板 | 刚性金属/塑料外壳 | 硬质金属罐 |
| 形状 | 扁平/可定制 | 矩形/块状 | 圆形 |
| 典型能量密度(Wh/kg) | 150-250 | 120-200 | 110-180 |
| 包装效率 | 90-95% | 80-90% | 60-75% |
| 机械强度 | 低(需要支持) | 高 | 非常高 |
| 肿胀风险 | 中-高(需要管理) | 中度 | 低 |
| 常见应用 | 电动汽车、智能手机、无人机、ESS | 电动汽车、存储、工业 | 电动工具、消费设备 |
常见应用
- 消费电子产品:智能手机、平板电脑和笔记本电脑都青睐外形纤薄、能量密度高的袋装电池。
- 电动汽车(EV):用于日产聆风、雪佛兰 Bolt 等车型以及某些特斯拉和梅赛德斯-奔驰汽车的大规格电池组 (电池大学).
- 储能系统(ESS):家用和电网电池采用袋式电池,适用于空间有限的装置。
- 无人机和机器人:重量轻、效率高的电源。
相关和易混淆的概念
- 棱镜电池:硬质矩形电池,保护性强,但包装效率较低。
- 圆柱形电池:传统的圆形金属罐电池;成熟、可靠、成本效益高,但体积较大。
- 锂聚合物电池(LiPo):有时与袋式电池混淆;实际上是指使用聚合物电解液,而不考虑其形状。并非所有锂聚合物电池都使用袋状结构,也并非所有袋状电池都使用聚合物电解液。
- 电池管理系统 (BMS):对所有类型的细胞都是必要的,但由于肿胀和热量因素,对小袋细胞尤为重要。
为什么选择袋式电池?
袋式电池具有更高的能量密度、更大的设计自由度和更轻的重量,是现代设备和电动汽车的理想之选。不过,它们必须采用坚固的封装和先进的 BMS,以保证安全性和使用寿命。欲了解更多技术信息,请参阅 扫描技术分析.

