
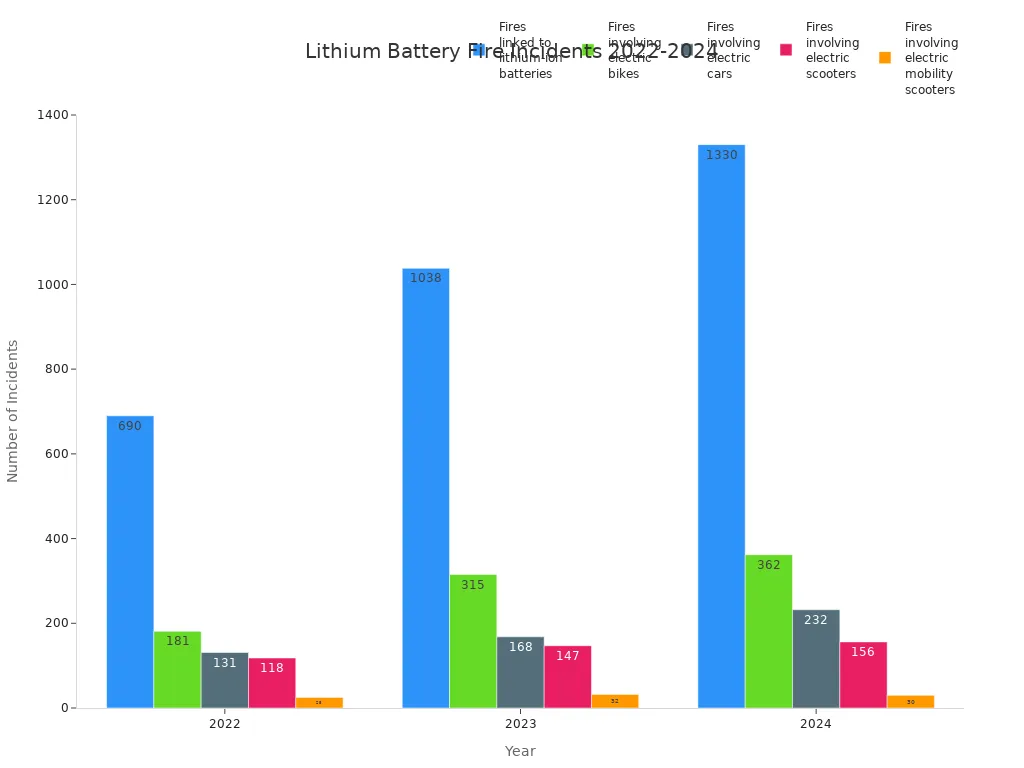
You face more lithium battery explosion risks in 2025 than ever before. Lithium battery use in phones, e-bikes, and electric vehicles keeps rising. The number of fires linked to lithium battery explosion has nearly doubled since 2022, as shown below:
| Incident Type | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | % Change 2022-2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fires linked to lithium-ion batteries | 690 | 1038 | 1330 | +93% |
| Fires involving electric bikes | 181 | 315 | 362 | +100% |
| Fires involving electric cars | 131 | 168 | 232 | +77% |
| Fires involving electric scooters | 118 | 147 | 156 | +32% |
| Fires involving electric mobility scooters | 25 | 32 | 30 | +20% |
Recognizing warning signs and acting fast can improve your safety. You need up-to-date safety knowledge to lower your risk and respond to lithium battery explosion risks in daily life.
Lithium Battery Explosion Risks

Lithium battery explosion risks have become a major concern in 2025. You see these risks in many devices, from smartphones to electric vehicles. Understanding the causes of lithium battery explosion helps you stay safe and avoid serious hazards. Let’s look at the main causes, the dangers of thermal runaway, and how физический ущерб increases explosion risks.
Main Causes
You face several causes of lithium battery explosion in daily life. These causes often work together, making the risks even greater. Here are the most common causes:
- Microscopic defects in the separator: Tiny flaws inside the battery can cause short circuits between the anode and cathode.
- Welding flaws and electrode damage: Mistakes during manufacturing can create weak spots that lead to internal shorts.
- Metal microparticle contamination: Small metal pieces inside the battery can trigger shorts and overheating.
- Thermal runaway process: Rapid heating and chemical reactions inside the battery can cause sudden explosions.
- Overcharging and fast charging: Charging the battery too quickly or past its safe limit can deposit lithium metal on the anode, increasing explosion risks.
- Large local currents after fast charging: Recent studies show that fast charging can create high local currents inside the battery, even when it is not in use. These currents can lead to dangerous reactions and thermal runaway.
- State of Charge (SOC) influence: Batteries with a high charge level release more hazardous gases during thermal runaway.
⚠️ Note: Manufacturing defects remain a recognized risk factor for lithium battery explosion. Some manufacturers, especially those selling online, may use thinner separators to cut costs. This choice increases the risk of battery fires and explosions, but experts do not have exact numbers for how often these defects cause incidents in 2025.
Вот summary table of the main causes and their effects:
| Cause/Factor | Описание |
|---|---|
| Microscopic defects in separator | Flaws cause internal short circuits between anode and cathode |
| Welding flaws and electrode damage | Производственные дефекты create weak spots and shorts |
| Metal microparticle contamination | Contaminants inside battery lead to shorts and overheating |
| Overcharging and fast charging | Excessive charging deposits lithium metal, raising explosion risks |
| Large local currents after fast charging | High currents inside battery at rest trigger dangerous reactions |
| State of Charge (SOC) influence | High SOC leads to more hazardous gas emissions during thermal runaway |
Thermal Runaway
Thermal runaway is one of the most dangerous causes of lithium battery explosion. You need to know how this process works to understand the risks:
- Thermal runaway is a chain reaction inside a lithium-ion battery. A rapid temperature increase triggers chemical reactions that produce even more heat.
- Causes include internal short circuits from physical damage or poor maintenance, overcharging, fast charging, and exposure to unsafe temperatures.
- The temperature can rise extremely fast, reaching up to 752°F (400°C) in milliseconds. This sudden heat causes the battery to vent flammable gases, catch fire, or explode.
- The electrolyte inside the battery is flammable. If the battery gets damaged, the electrolyte can leak and ignite.
- Once thermal runaway starts, it is very hard to stop. You may see smoke, fire, or even a violent explosion.
🔥 Tip: Most battery fires and explosions happen because of thermal runaway. Overcharging, using the wrong charger, or exposing the battery to heat can all trigger this chain reaction.
Here is a quick list of what can trigger thermal runaway:
- Mechanical abuse: Dropping, crushing, or puncturing the battery.
- Electrical abuse: Overcharging, short circuits, or faulty battery management systems.
- Thermal abuse: Leaving the battery near heat sources or in hot environments.
- Manufacturing defects: Poor assembly, impurities, or low-quality parts.
Физический ущерб
Physical damage is a leading cause of lithium battery explosion. You might drop your device or crush the battery by accident. Even small impacts can harm the battery’s internal parts. Here’s how physical damage increases explosion risks:
- Impacts, punctures, or crushing can break the separator inside the battery. This damage causes internal short circuits.
- Internal shorts lead to overheating. Overheating can trigger thermal runaway, which quickly leads to fire or explosion.
- The battery’s electrolyte is highly flammable. If the casing cracks, the electrolyte can leak and catch fire when exposed to air.
- Physical damage can also break down the thin protective layer on the anode, called the SEI layer. This breakdown causes uncontrolled reactions and speeds up battery failure.
| Type of Physical Damage | Описание | Consequence on Battery Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical deformation or abuse | Dropping, mishandling, or stress during use or assembly | Breakage of components, separator damage, short circuits, thermal runaway |
| Separator damage | Damage from abuse or dendrite growth | Loss of separation, internal shorts, temperature spikes, thermal runaway |
| SEI layer breakdown | Penetration or overheating breaks the protective layer | Uncontrolled reactions, rapid failure |
| Dendrite growth | Lithium filaments puncture separator during fast charging | Internal shorts, possible thermal runaway |
🚨 Alert: Physical damage is not always visible. Even if your device looks fine, internal damage can still cause a lithium battery explosion later. Always handle batteries with care to avoid these hazards.
Warning Signs of Lithium Battery Explosion
Recognizing the warning signs of failure can help you avoid a dangerous lithium battery explosion. You should always watch for changes in your device, listen for odd sounds, and notice any strange smells. These clues often appear before an explosion and give you a chance to act quickly.
Физические изменения
You may notice several physical changes before a lithium battery explosion. These changes often signal that the battery is close to failing:
- Swelling or bulging of the battery casing
- Discoloration of the battery or device
- Excessive heat generation, making the device hot to touch
- Leakage of fluid or venting of smoke
- Rapid temperature increase, sometimes reaching over 150°C inside the cell
Swelling is a common sign that the battery’s life is ending. If you see your device’s case bulge or change shape, stop using it right away. Smoke or vapor coming from the battery means gases are building up inside. This can lead to a sudden explosion, especially if the battery ruptures. In enclosed spaces, these gases can form explosive clouds.
⚠️ If you notice any of these physical changes, move the device to a safe area and do not use it again.
Unusual Sounds or Odors
Strange sounds or smells are important warning signs of failure. You might hear:
- Hissing, popping, or cracking noises from the battery
- Sudden loud pops or small explosions
- Hissing that sounds like escaping gas
You may also smell:
- Strong chemical or burning plastic odors
- A metallic taste or burning sensation in your nose or throat
These sensory warnings mean the battery is leaking toxic fumes or reacting inside. Not all explosions give you these clues, but when you notice them, stop using the device immediately.
Device Malfunction
Device malfunctions often happen before a lithium battery explosion. Watch for:
- Overheating or the device becoming unusually hot
- Sudden shutdowns or restarts
- Failure to charge or hold a charge
- Visible smoke or sparks
Many incidents start with overheating or smoking, especially in devices like e-cigarettes, power banks, and laptops. Mechanical abuse, thermal abuse, or electrical problems can all cause these malfunctions. If your device acts strangely, treat it as a sign of lithium battery explosion risk.
🚨 Always treat warning signs of failure seriously. Quick action can prevent injury or property damage from an explosion.
How to Respond to Lithium Battery Explosion Risks
Emergency Actions
When you notice warning signs of a lithium battery explosion, you must act quickly. Your first goal is to protect yourself and others from harm. Follow these steps to handle battery fires and prevent injuries:
- Move everyone away from the device showing signs of overheating, swelling, or smoke.
- Do not touch, move, or cover the device. Picking up a smoking or burning battery can cause serious injury.
- If you see flames, use a proper fire extinguisher if you have one nearby.
- After putting out the fire, cool the device with water or a non-alcoholic liquid for at least 15 minutes. This helps stop further thermal runaway.
- Never use ice or burn bags to cool the battery. These can make the situation worse.
- Wear personal protective equipment, such as gloves and a mask, if you need to be near the device.
- Call emergency services right away if you cannot control the fire or if toxic fumes fill the area.
⚠️ Always use extreme caution near an overheating or burning battery. Toxic gases can escape quickly and may not have a strong smell or color.
Evacuation and Safety
Your safety comes first during a lithium battery fire. Toxic fumes from burning batteries can harm your lungs and body. These fumes may contain hydrogen fluoride, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen cyanide. Even a small fire can release enough gas to cause coughing, headaches, or worse.
To stay safe, follow these evacuation steps:
- Leave the area immediately if you see smoke, fire, or smell chemicals.
- Move to fresh air and open windows or doors to help ventilate the space.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a cloth or mask to reduce inhaling toxic fumes.
- Help others evacuate, especially children, elderly people, or anyone with breathing problems.
- Call emergency services and report the fire.
- Do not return to the area until firefighters say it is safe.
- Remove and bag any clothing that may have absorbed smoke or chemicals.
- Wash your skin with soap and water if you think you touched battery chemicals.
- Seek medical help if you feel dizzy, have trouble breathing, or notice any symptoms after exposure.
🛑 Remember, even after the fire is out, battery fires can reignite. Firefighters may need to monitor the area for hours or days.
Fire Extinguishers and Help
You must use the right fire extinguisher to fight a lithium battery fire. Water is not always safe for these fires. Using the wrong extinguisher can make the fire worse or put you in danger.
- For small lithium-ion battery fires, use a Class D dry powder extinguisher. These are made for metal fires and work well on battery fires.
- Dry chemical extinguishers, such as those with sodium bicarbonate or potassium bicarbonate, can help stop the fire by breaking the chemical reaction.
- Clean agent systems, like halon or halon replacements, are good for electrical fires and do not leave a mess.
- CO2 extinguishers may help with small fires in tight spaces but do not cool the battery enough to stop reignition.
- Foam extinguishers and water mist systems are sometimes used in large storage areas or electric vehicles, but you should not use regular foam or water on a battery fire at home.
🚒 Always call for professional help if you cannot control the fire. Firefighters have special training and equipment for battery fires. They know the best countermeasures for lithium battery fire and can keep everyone safe.
Fire prevention starts with knowing the right tools and steps. Keep a suitable extinguisher in your home or workplace if you use devices with lithium batteries. Regular fire safety training and emergency drills help you and your family stay prepared.
Measures to Prevent Lithium Battery Explosion
Safe Charging and Storage
You can lower the risk of lithium battery explosions by following the latest safety practices for charging and storage. Always use lab-certified batteries and chargers. Remove batteries from chargers once they reach full charge. Avoid overcharging and never leave devices charging near flammable materials. Store batteries at room temperature, away from sunlight and heat. Keep them in their original packaging and protect the terminals to prevent short circuits. Inspect batteries often for signs of damage like swelling, heat, or leaking. If you notice any warning signs, move the battery to a safe area and contact emergency services.
⚠️ Tip: Charging lithium batteries with non-approved chargers or ignoring manufacturer instructions can cause overheating, fires, or explosions. Always follow the recommended charging protocols for prevention.
Best Practices for Charging and Storage:
- Use only Зарядные устройства, одобренные производителем.
- Charge batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Never charge batteries overnight or unattended.
- Keep batteries away from flammable objects.
- Monitor for heat, bulging, or unusual sounds.
Choosing Certified Batteries
Choosing certified batteries is one of the most important measures to prevent lithium battery explosion. Certified batteries have passed strict safety tests and reduce the risk of defective or counterfeit products. Always check for safety certifications before buying. Avoid buying from unknown sellers, as counterfeit batteries are common and can be dangerous.
| Сертификация | Область применения | Role in Safety |
|---|---|---|
| UL 1642 | Individual lithium cells | Verifies fire resistance and electrical safety |
| UL 2054 | Battery packs for devices | Ensures consumer electronics meet safety standards |
| UN38.3 | Global transport | Confirms safe shipping and handling |
| CE | EU safety rules | Meets European safety and environmental standards |
🛑 Note: Counterfeit batteries often look real but use poor materials. These defective batteries can overheat, catch fire, or explode. Buy only from trusted sources and check for safety alerts and recalls.
Disposal and Recycling
Proper disposal is key for prevention of fires and explosions. Never throw lithium batteries in regular trash or recycling bins. Извлеките батареи из устройств перед утилизацией. Cover the terminals with tape to prevent short circuits. Take batteries to authorized collection points or recycling centers. Many stores and local programs accept used batteries. Store damaged or defective batteries in insulated bags until you can recycle them.
- Use certified recycling providers for hazardous materials.
- Participate in battery return programs.
- Follow all manufacturer and local disposal guidelines.
- Watch for recalls and dispose of recalled batteries safely.
Improper disposal can cause fires at waste facilities. In 2024, fires from defective batteries in trash increased by 15%. Always follow prevention steps to keep your home and community safe.
Lithium Battery Safety for E-Bikes, EVs, and New Devices

E-Bike and Scooter Risks
You face unique risks when using e-bikes and scooters powered by lithium-ion batteries. These batteries contain a flammable liquid electrolyte. High temperatures can cause the battery to overheat and start a fire. Charging indoors increases the danger, especially if you charge more than one battery at a time or leave batteries unattended. Physical damage from falls, collisions, or punctures can trigger thermal runaway, which leads to fire, smoke, and toxic gas release. Fires from these batteries spread quickly and are hard to put out.
- Unplug batteries when fully charged.
- Charge only one battery at a time, away from flammable items.
- Inspect batteries after any impact or overheating.
- Dispose of damaged batteries at proper recycling centers.
⚠️ Always avoid charging e-bike and scooter batteries indoors if possible. This simple step can lower your risk of fire and injury.
Electric Vehicle Safety
Lithium battery safety in electric vehicles (EVs) has improved as technology advances. EV batteries offer Высокая плотность энергии и быстрая зарядка, but they also bring new safety challenges. Thermal runaway can happen after a collision, short circuit, or water exposure. Even a “dead” battery can hold enough charge to cause a fire. Safety standards now require clear labeling of high-voltage cables and regular manual inspections. National guidelines recommend keeping damaged EVs at least 50 meters from anything that can burn.
| Практика безопасности | Почему это важно |
|---|---|
| Labeling high-voltage cables | Helps responders identify and avoid electric shock |
| Manual battery inspections | Detects hidden faults before they cause problems |
| Safe storage after accidents | Prevents fires from damaged batteries |
You should follow all manufacturer instructions and stay updated on new battery safety guidelines for EVs.
Smart Device Precautions
Smartphones, tablets, and laptops use lithium-ion batteries every day. To keep safe, always use devices and batteries with the UL Mark. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging and storage. Plug chargers directly into wall outlets and avoid extension cords. Charge devices on firm, non-combustible surfaces, away from exits and flammable materials. Monitor batteries for swelling, leaks, or strange smells. Stop using any device that shows these signs.
- Store batteries between 40-80°F.
- Avoid keeping batteries fully charged for long periods.
- Cover battery terminals before disposal.
- Recycle batteries at special drop-off sites, not in regular trash.
🛑 Never use or charge a battery that looks damaged. Safe habits protect you and your home from battery fires.
You face real risks from lithium battery explosion in daily life. Watch for warning signs like swelling, smoke, or odd smells. Quick action and regular safety checks help prevent explosion and injury.
- Built-in safety features and certified batteries lower explosion risks.
- Proper charging, safe disposal, and following manufacturer instructions protect you.
Stay alert and practice lithium battery explosion safety. Make regular checks part of your routine to keep your home and workplace safe from explosion.
ЧАСТО ЗАДАВАЕМЫЕ ВОПРОСЫ
What should you do if your device’s battery starts to swell?
If you see swelling, stop using the device right away. Move it to a safe area. Do not try to puncture or press the battery. Contact a recycling center or your device’s manufacturer for safe disposal.
Can you use water to put out a lithium battery fire?
You should not use water on a lithium battery fire. Water can make the fire worse. Use a Class D dry powder extinguisher or call emergency services for help.
How can you tell if a battery is certified and safe?
Look for safety marks like UL, CE, or UN38.3 on the battery or packaging. Buy batteries from trusted stores. Avoid products without clear safety labels.
Is it safe to charge your phone overnight?
Charging overnight can overheat the battery and increase fire risk. Unplug your phone once it is fully charged. Use only the charger that came with your device.
What is the safest way to store spare lithium batteries?
Store batteries in their original packaging or a battery case. Keep them in a cool, dry place. Make sure the terminals do not touch each other or metal objects.

