
Imagine you plug in your device and leave it charging overnight. The next morning, you find it hot and swollen. Overcharging can turn li-ion battery charging into a real danger. You must never exceed the maximum voltage limit, usually 4.2V per cell, to keep li-ion battery charging safe. Built-in overcharge protection helps maintain safety and extends the life of your battery.
Voltage Limits in Li-Ion Battery Charging

Why 4.2V Matters
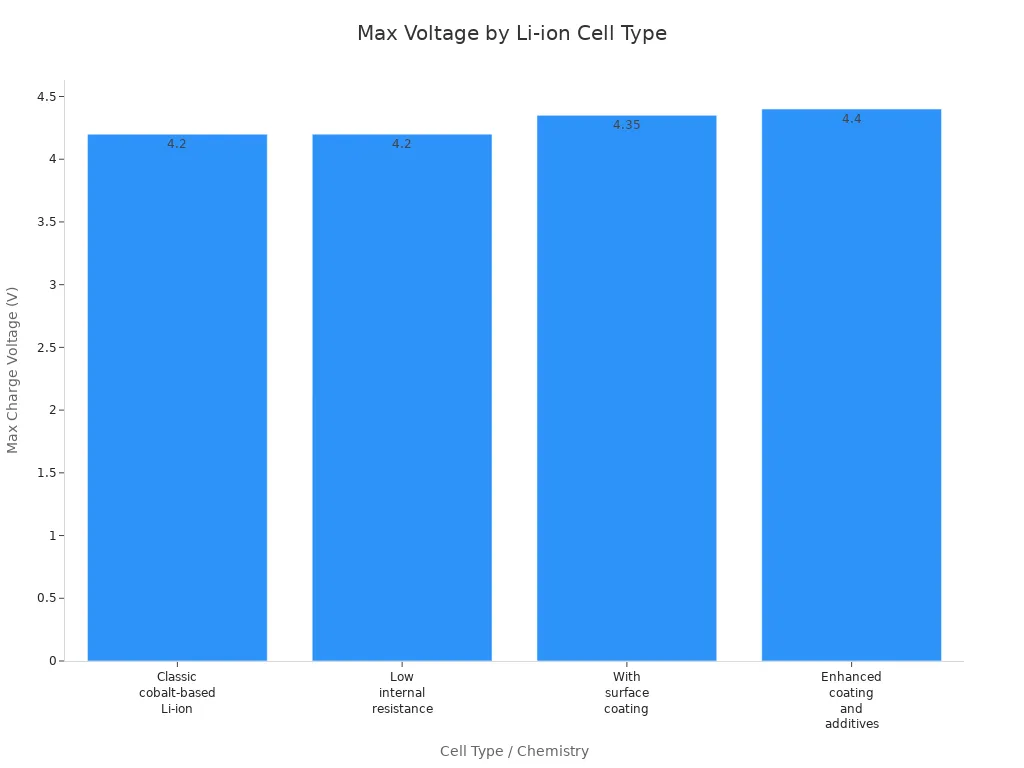
You might wonder why the number 4.2 volts is so important in li-ion battery charging. This value is not random. Scientists and engineers set this maximum voltage after many tests. They found that most lithium-ion cells work best and stay safe when you charge them up to 4.2 volts per cell. If you look at the table below, you can see how different cell types have different voltage limits, but 4.2 volts is the standard for most.
| Cell Type / Chemistry | Номинальное напряжение (В) | Typical End-of-Discharge Voltage (V) | Maximum Charge Voltage (V) | Примечания |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic cobalt-based Li-ion | 3.6 | 2.8-3.0 | 4.2 | Standard industry maximum voltage per cell |
| Low internal resistance variant | 3.7 | 2.8-3.0 | 4.2 | Marketing advantage, same max voltage |
| With surface coating and additives | 3.8 | 2.8-3.0 | 4.35 | Requires charger adjustment for higher voltage |
| Enhanced coating and additives | 3.85 | 2.8-3.0 | 4.4 | Charger must be set correctly for capacity gain |
The industry chose 4.2 volts because it balances safety, battery life, and performance. Charging above this voltage can make the battery unstable. The nominal voltage, usually 3.6 volts, sits between the full charge and the cutoff voltage. Some companies may list 3.7 volts or higher for marketing, but most devices stick to the 3.6-volt standard for safety.
Совет: Always check your device’s manual or battery label to know the correct voltage limit for safe li-ion battery charging.
Overcharge Dangers
Charging a lithium-ion cell above 4.2 volts can lead to serious problems. When you overcharge, the battery’s chemical balance breaks down. The pressure and temperature inside the cell rise quickly. This can cause the battery to swell, leak, or even explode. Scientists call this dangerous event тепловой удар.
Overcharge is not just about explosions. Even a small overcharge can cause the battery to lose capacity faster. You may notice your device does not last as long on a single charge. Over time, overcharge leads to degradation, which means the battery cannot hold as much energy. In some cases, overcharge causes lithium plating, where metallic lithium builds up inside the cell. This buildup can create short circuits and make the battery unsafe.
Here are some common dangers when you exceed the 4.2V per cell limit:
- Overheating and swelling (puffing)
- Loss of battery capacity and faster degradation
- Risk of fire or explosion due to thermal runaway
- Chemical leaks and gas emissions inside the battery
Overcharge also speeds up chemical reactions inside the battery. These reactions produce gases like carbon monoxide and methane. If these gases build up, the battery can burst. Overcharge protection circuits are essential. They stop the charging process before the voltage gets too high. Without these safety features, li-ion battery charging becomes risky.
Примечание: Using the wrong charger or ignoring voltage limits increases the risk of overcharge. Always use chargers designed for your device.
By respecting the 4.2V limit, you protect your battery and your safety. You also help your device last longer and work better.
Charging Science and Overcharge Protection

Lithium-Ion Charging Phases
You might wonder how li-ion battery charging works so safely and efficiently. The answer lies in a special process called constant current/constant voltage charging. This method helps you get the most out of your battery while keeping it safe from overcharge.
Here are the main phases of the charging process:
- Pre-charge Stage: If your battery voltage drops below about 3.0 volts, the charger starts with a gentle current. This step protects the battery from damage and helps it recover safely.
- Constant Current Stage: Once the voltage rises above 3.0 volts, the charger delivers a steady current. The voltage slowly climbs as the battery charges up to about 80% of its capacity. This phase is important for fast charging and strong charging performance.
- Constant Voltage Stage: When the battery voltage reaches around 4.2 volts, the charger switches to holding the voltage steady. The current begins to drop. Charging ends when the current falls to a low level, showing the battery is full.
Совет: The constant current/constant voltage method prevents overcharge by stopping the charging process at the right time. This approach also helps avoid lithium plating, which can damage the battery and reduce its lifespan.
Fast charging works best when you follow these phases. The charger controls the current and voltage to keep the battery safe. If you skip any phase or use the wrong charger, you risk overcharge and poor performance.
Internal Battery Overcharge Protection
You rely on internal battery overcharge protection every time you charge your device. This mechanism acts like a smart guard, watching for any sign of overcharge. Inside each lithium-ion battery, you find a set of protection circuits. These circuits use control ICs and MOSFET switches to monitor voltage and current. If the voltage goes above the safe limit—usually 4.2 volts—the circuit disconnects the battery from the charger right away.
Here are some common overcharge protection strategies used in modern batteries:
- Control ICs check the voltage and current during charging. They stop charging if they detect overcharge or unsafe conditions.
- MOSFET switches act fast to disconnect the battery when needed.
- PTC devices increase resistance if the battery gets too hot, adding another layer of protection.
- Temperature sensors, like NTC resistors, sense overheating and trigger protection.
- In multi-cell packs, special ICs watch each cell to prevent overcharge in any single cell.
- Secondary protection mechanisms handle sudden surges or short circuits, making sure the battery stays safe.
Примечание: These overcharge protection strategies work together to give you peace of mind. They help extend the overcharge protection lifespan of your battery and keep your device running smoothly.
Internal battery overcharge protection is very effective. The circuits react quickly to any voltage spike. They disconnect the battery before damage can happen. This active monitoring helps prevent problems like lithium plating, swelling, or even fire. You get better charging performance and longer battery life.
Next-generation internal battery safeguards continue to improve. They use smarter chips and faster switches. These upgrades help support fast charging while keeping safety as the top priority. When you use a charger designed for your device, you take full advantage of these advanced protection features.
Вызов: Always choose chargers and devices with strong overcharge protection strategies. This simple step protects your battery, boosts performance, and keeps you safe.
Правила безопасной зарядки
Choosing the Right Charger
You should always pick a charger that matches your device’s battery type. Chargers with built-in protection circuitry stop charging when the battery reaches its peak voltage, usually 4.2V per cell. This feature prevents overcharging and keeps your battery safe. Some chargers also protect against over-discharging, which helps avoid battery degradation. Using a charger with a Система управления аккумулятором (BMS) ensures the charger monitors voltage and temperature, adjusting charging for safety and efficiency. For extra safety, use surge protectors to guard against power surges. Chargers with overcharge protection greatly reduce the risk of overheating, swelling, or even fire compared to chargers without these features.
Совет: Always use the charger recommended by your device’s manufacturer to maintain energy efficiency and performance.
Device Settings and Indicators
You can use device settings and indicators to monitor charging. Many devices have LED lights or screen icons that show battery status. These indicators help you know when to stop charging. Some apps, like Battery Life for iOS or AccuBattery for Android, give you more details about battery health and temperature. However, remember that simple voltage-based indicators are not always exact. More advanced systems use coulomb counting for better accuracy. If you notice your device shutting down unexpectedly or the battery swelling, stop charging and check for damage. Inaccurate indicators can mislead you, causing unsafe charging habits and risking battery failure.
Environment and Usage
Charging in the right environment helps your battery last longer. The best temperature for charging is around 25°C (77°F). Charging in very cold or hot places can cause problems. At low temperatures, lithium plating may form, leading to short circuits and capacity loss. High temperatures speed up chemical reactions, which can cause thermal runaway and reduce battery life. Fast charging in extreme temperatures increases these risks. Try to avoid charging your device in direct sunlight or freezing conditions. Following the 20-80 rule—charging your battery between 20% and 80%—can also slow down degradation and improve efficiency. Charging to less than 100% helps your battery stay healthy for more cycles.
Вызов: Safe charging habits protect your device, boost battery lifespan, and keep you safe.
Common Charging Mistakes
Ignoring Voltage Limits
You might think your device will always protect itself, but ignoring voltage limits can cause serious problems. Many users let their batteries discharge completely or leave them plugged in for too long. Both habits can damage lithium-ion batteries. When you overcharge a battery or let its voltage drop below 2 volts per cell, you risk overheating, swelling, and even fire. Overcharging leads to lithium plating inside the cell, which can cause short circuits and battery failure. Letting the battery drain too much breaks down the materials inside, making the battery lose capacity quickly.
Совет: Recharge your battery before it is fully drained and unplug it once it is full. This simple habit helps prevent damage and keeps your battery safe.
Using Incompatible Chargers
Choosing the wrong charger is a common mistake. Chargers that do not match your battery’s voltage or current needs can cause overheating, swelling, or even explosions. Using a charger with too much current speeds up chemical reactions inside the battery, which can lead to thermal runaway. This is especially dangerous for devices like electric vehicles, where battery safety is critical. Chargers without proper temperature monitoring can also cause the battery to overheat. Always use the charger recommended by the manufacturer to avoid these risks.
- Incompatible chargers can:
- Deliver too much or too little current
- Cause battery wear and reduce lifespan
- Lead to fires or explosions in extreme cases
Using the right charger protects your devices and vehicles from serious safety hazards.
Overlooking Protection Features
Many people forget to check if their charger or device has the right protection features. Overcharge protection, temperature sensors, and precise voltage control are all important. Without these, your battery can overheat or fail. Some users rely only on built-in battery protection, but extra circuits in chargers add another layer of safety. For example, a thermistor can detect overheating and stop charging before damage occurs. Ignoring these features increases the risk of battery incidents, especially during fast charging or in hot environments.
Вызов: Always look for chargers with overcharge and temperature protection. These features help keep your battery safe and extend its life.
You protect your device and yourself when you respect voltage thresholds and rely on internal overcharge protection. Charging between 20% and 80% helps your battery last longer and prevents dangerous overheating. Overcharge protection inside your battery reduces the risk of fires and failures.
Review your charging habits and equipment today.
- Use certified chargers
- Avoid charging to 100%
- Keep batteries cool
Adopting these habits keeps your devices safe and extends battery life.
ЧАСТО ЗАДАВАЕМЫЕ ВОПРОСЫ
How do you know if your charger has overcharge protection?
Check your charger’s manual or label. Look for terms like “overcharge protection” or “BMS.” Most modern chargers for phones and laptops include this feature. If unsure, contact the manufacturer or use only certified chargers.
Можно ли оставлять устройство подключенным к сети на ночь?
You can leave most devices plugged in overnight if they have proper overcharge protection. The built-in circuits stop charging when the battery is full. For best battery health, unplug once charged or use a smart plug.
Совет: Unplugging after charging helps your battery last longer.
What happens if you charge a lithium-ion battery in extreme heat?
Charging in high temperatures can damage your battery. Heat speeds up chemical reactions inside the cell. This can cause swelling, leaks, or even fire. Always charge your device in a cool, dry place.
Is it safe to use third-party chargers?
Not all third-party chargers are safe. Some may lack voltage control or overcharge protection. Always choose certified chargers from trusted brands. Unsafe chargers can damage your battery or cause safety risks.
- Look for UL or CE certification
- Avoid very cheap, unbranded chargers
Why should you avoid charging to 100% every time?
Charging to 100% often stresses the battery. This can shorten its lifespan. Try to keep your battery between 20% and 80% for better long-term health.
Примечание: Partial charging helps your battery last for more cycles.

