
Lead-acid batteries power many industrial systems. Lead acid battery certification proves that these batteries meet strict safety and quality rules. When a company uses lead-acid batteries with proper certification, it lowers risks and keeps workers safe. Lead-acid battery certification also makes sure that a business follows the law. Certified lead-acid batteries work well and last longer. Many industries trust lead-acid batteries with certification to run machines and backup systems. Companies that choose lead acid battery certification avoid costly problems. Lead-acid batteries with certification give peace of mind to managers and teams.
Certification Requirements
Industrial Lead-Acid Batteries
Industrial lead-acid batteries serve as the backbone for many critical systems. These batteries feature thicker plates and higher energy capacity than consumer models. The battery manufacturing industry designs them for long-term, reliable power. They support applications such as cell tower backup, emergency lighting, and energy storage for renewable systems.
| Тип батареи | Описание | Типовые применения |
|---|---|---|
| VRLA | Sealed, maintenance-free, valve-regulated | UPS, telecom backup, emergency lighting |
| AGM | Electrolyte in fiberglass mats, sealed, maintenance-free | Automotive, marine, solar storage, electric scooters |
| GEL Sealed Lead-Acid | Gel electrolyte, sealed, spill-proof | Safe operation in any orientation |
| OPzV Tubular | Gel electrolyte, tubular plates, deep cycling | Renewable storage, off-grid, telecom backup |
| OPzS | Liquid electrolyte, tubular plates, deep discharge resistance | Railways, energy storage, critical infrastructure |
| High-Rate | Rapid energy bursts, high discharge rates | Forklifts, material handling, telecom systems |
| Start-Stop/Engine Start | AGM or improved flooded tech, start-stop vehicles | Modern automobiles |
The battery manufacturing industry must follow strict battery manufacturing standards and bis standards to ensure these batteries meet all requirements. Each type of lead-acid battery must pass specific tests for safety, performance, and durability. The bis certification process checks that every product matches the intended use and meets all regulatory requirements.
Mandatory Certifications
Industrial lead-acid batteries must comply with a range of certification requirements before entering the market. The battery manufacturing industry faces different requirements in the United States, European Union, and Asia.
- In the United States, UL certification stands as a key requirement. Underwriters Laboratories (UL) sets rigorous standards for electrical, mechanical, and thermal safety. The battery manufacturing industry often seeks UL certification for high-capacity lead-acid batteries, even when not mandatory. The bis certification process in the US also includes compliance with IEC/EN 60896 series standards for stationary lead-acid batteries.
- In the European Union, CE marking is mandatory for all batteries sold in the European Economic Area. The CE mark shows that the product meets health, safety, and environmental protection requirements. The battery manufacturing industry must follow the EU Batteries Regulation, which covers safety, sustainability, labeling, and documentation. The bis certification process in Europe includes using harmonized standards such as EN IEC 62485-1 and EN 60896-22. These standards ensure that lead-acid batteries do not endanger health, safety, or the environment.
- In Asia, the battery manufacturing industry often follows international standards like ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. IEC 62133 and IEC 62619 set safety requirements for secondary cells and batteries. The bis certification process in Asia may also require RoHS and REACH compliance, which restrict hazardous substances. China Compulsory Certification (CCC) may apply to some products.
Note: The bis certification process requires detailed documentation, including technical files, test reports, and instructions for safe use. The battery manufacturing industry must also provide a Declaration of Conformity and, in some regions, a digital battery passport with a QR code for traceability.
The organizations responsible for setting these requirements include Underwriters Laboratories (UL), Conformité Européene (CE), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The United Nations sets transportation testing standards, while RoHS and REACH regulate hazardous substances. The bis certification process ensures that all lead-acid batteries meet the highest safety and quality standards.
The battery manufacturing industry must also consider shipping requirements. While lead-acid batteries do not require UN38.3 certification, they are classified as dangerous goods under class 9 shipping rules. The bis certification process ensures compliance with these shipping requirements.
The bis certification process and bis standards play a central role in the battery manufacturing industry. These requirements protect users, the environment, and property. The battery manufacturing industry must stay updated on changes to bis standards and battery manufacturing standards to maintain compliance.
Why Certification Matters
Safety & Risk
Сертификация plays a vital role in protecting workers and facilities that use lead-acid batteries. Certified lead-acid batteries must pass strict safety requirements, including electrical, mechanical, thermal, and chemical tests. These tests confirm that the batteries operate within safe voltage and current limits, withstand physical stress, and resist overheating. They also ensure that hazardous materials stay contained.
- Electrical tests prevent electrical hazards.
- Mechanical tests check for strong structure.
- Thermal tests stop overheating and fires.
- Chemical tests keep dangerous substances inside.
| Сертификация | Safety Focus Areas | Safety Risk Reduction Impact |
|---|---|---|
| UL | Fire resistance, chemical leakage prevention, electrical performance | Reduces fire and chemical hazards |
| CE | Health, safety, environmental protection | Lowers risks to users and environment |
| IEC/EN 62133 | Safe transport, handling, use | Prevents accidents |
| ROHS | Restricts hazardous materials | Protects users and environment |
| FCC | Electromagnetic interference | Ensures operational safety |
| IATF 16949 | Mechanical integrity, quality | Reduces failure risks |
Meeting these safety requirements helps prevent fires, explosions, and chemical leaks. Certified lead-acid batteries give managers confidence that their systems meet battery safety standards.
Legal & Regulatory
Regulatory compliance is not optional for companies using lead-acid batteries. Certification proves that lead-acid batteries meet all legal requirements. Without proper certification, businesses risk serious consequences:
- Financial fines can reach thousands of dollars for each violation.
- Legal actions may lead to lawsuits or even imprisonment.
- Reputational damage can harm a company’s brand and trust.
- Cleanup costs for environmental harm can be very high.
- Operational disruptions may force a business to stop work until compliance returns.
Lead-acid batteries are hazardous waste. Laws from the EPA, DOT, and OSHA set strict requirements for handling, transport, and disposal. Regulatory compliance protects companies from penalties and keeps operations running smoothly.
Operational Impact
Certification supports reliable operations for all industrial users of lead-acid batteries. Certified lead-acid batteries meet strict requirements for quality and performance. ISO certifications help companies build trust in their manufacturing processes and reduce defects. UL certification for battery management systems ensures safe monitoring and control, which lowers the risk of overcharging or short circuits.
- Certified lead-acid batteries last longer and perform better.
- Regulatory compliance helps companies avoid recalls and costly repairs.
- Meeting safety requirements gives companies a competitive edge and supports market access.
Certified lead-acid batteries help companies meet battery safety standards, keep workers safe, and maintain efficient operations.
Key Standards & Regulations
UL & ANSI Standards
UL certification stands as a cornerstone for lead-acid batteries in industrial settings. UL 1989 covers valve-regulated and vented batteries with aqueous electrolytes. This standard applies to stationary, portable, and mobile uses, such as emergency power and UPS systems. UL 1973 addresses batteries for stationary and motive auxiliary power, requiring installation compliance with electrical codes like NFPA 70 and the Canadian Electrical Code C22.1. Both UL 1989 and UL 1973 focus on safety testing, battery management, and system components. These standards help reduce electrical, fire, and explosion risks. While UL certification is often voluntary, authorities may require it under us battery manufacturing regulations or canadian battery manufacturing regulations. ANSI standards, such as ANSI/CAN/UL 1973, align closely with UL requirements for lead-acid batteries.
- UL 1989: Stationary, portable, and mobile lead-acid batteries
- UL 1973: Stationary and motive auxiliary power applications
- Emphasis: Safety, installation, and compliance with electrical codes
IEC & EN Standards
IEC standards provide global guidance for lead-acid battery safety and performance. The IEC 60095 series sets requirements for starter batteries in vehicles and industrial use. IEC 62485-5 focuses on safety for stationary secondary batteries. IEC/TR 61431 offers monitoring guidelines for traction batteries. EN standards, such as EN 62620 and EN 62619, address safety and performance for industrial batteries in Europe. These standards form the backbone of european battery regulations and bis requirements.
| IEC Standard | Scope/Application | Addressed Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| IEC 60095 | Starter batteries for vehicles and industry | Safety, operational guidelines |
| IEC 62485-5 | Stationary secondary batteries | Installation and operation safety |
| IEC/TR 61431 | Traction battery monitoring | Safety, performance monitoring |
IEC and EN standards focus on safety and operational testing, not direct environmental compliance.
ISO & IATF Standards
ISO and IATF standards ensure quality management for lead-acid battery manufacturers. ISO 9001 certification covers basic quality systems for all manufacturers. IATF 16949 applies to automotive lead-acid batteries, requiring strict process control, risk management, and continuous improvement. These standards support industry standards and key certification standards for automotive and industrial applications.
| Certification Type | Описание | Applicability/Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality management system | All manufacturers |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive-specific quality management | Automotive lead-acid battery manufacturers |
Manufacturers benefit from improved consistency, customer confidence, and efficient production.
Environmental Compliance
Environmental compliance is critical for lead-acid batteries. The RoHS Directive restricts hazardous substances in batteries. CE marking certifies that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental standards. Compliance with the EU Battery Directive and RoHS is mandatory for exports to the EU. Non-compliance can result in penalties and sales bans. EN 62620 and EN 62619 support environmental and safety requirements under european battery regulations.
- RoHS: Restricts hazardous materials in lead-acid batteries
- CE: Certifies safety, health, and environmental protection
- EN standards: Ensure compliance and safety for industrial batteries
International Shipping
International shipping of lead-acid batteries requires strict certification and compliance. Lead-acid batteries fall under UN2794 (wet, filled with acid) and UN2800 (wet, non-spillable), both classified as Hazard Class 8. Sealed lead-acid batteries using Gel or AGM technology are often non-spillable, affecting packaging and certification. Exporting spent lead-acid batteries for recycling must follow U.S. export rules, destination country laws, and international agreements like the Basel Convention and OECD Decision. Packaging must prevent leaks and short circuits, using UN-rated containers and proper labeling. The IMDG Code and IATA Packing Instructions set global shipping standards.
Proper packaging, labeling, and documentation ensure safe and legal transport of lead-acid batteries worldwide.
Certification bodies such as CSA Group and TÜV Rheinland play a vital role in verifying compliance with these bis and battery certification standards.
Certification Process
The battery certification process for industrial lead-acid batteries follows a clear path. Each step ensures that lead-acid batteries meet safety, quality, and regulatory requirements. Companies must understand and follow this process to achieve and maintain certification.
Identifying Standards
Manufacturers begin the battery certification process by identifying which standards apply to their lead-acid batteries. These standards depend on the battery type, intended use, and market destination. For example, UL and ANSI standards often apply in North America, while IEC and EN standards are common in Europe. The bis certification process requires companies to check if their products must meet Indian standards like IS 15549. Companies also consider environmental and shipping standards, such as RoHS, CE, and UN shipping codes. Identifying the correct standards at the start helps avoid delays and ensures full compliance.
Tip: Companies should consult with certification bodies or regulatory experts to confirm all required standards before starting the battery certification process.
Documentation
Proper documentation forms the backbone of the battery certification process. Manufacturers must gather and submit a range of documents to prove compliance with standards and regulations. The bis certification process, for example, requires the following documents:
- Factory registration or incorporation certificate
- GST certificate
- IEC (Importer-Exporter Code), if applicable
- Layout diagram of the manufacturing process
- Technical drawings and product datasheets
- Authorization letter if using a BIS certification consultant
- Test reports from BIS-recognized laboratories
- Details of the quality control system
- Previous certificates if renewing certification
- ISO certificate, if available
These documents show that the manufacturer follows the correct procedures and meets all requirements for lead-acid batteries. Accurate and complete documentation speeds up the battery certification process and supports successful audits.
Battery Certification Process
The battery certification process for lead-acid batteries involves several key steps. Each step builds on the previous one to ensure that the batteries meet all standards and regulatory requirements.
- Identify all applicable standards and regulations for the target market.
- Prepare and organize all required documentation, including technical files and test reports.
- Submit an application to the relevant certification body, such as BIS, UL, or CE.
- Undergo product testing in accredited laboratories to verify compliance with safety and performance standards.
- Complete factory audits and inspections to confirm quality control systems and manufacturing practices.
- Address any non-conformities or issues found during testing or inspection.
- Receive certification if all requirements are met.
- Maintain certification through regular audits, renewals, and updates as standards change.
The bis certification process often includes both product testing and factory audits. Certification bodies may require additional steps for specific applications, such as shipping or environmental compliance.
Testing & Inspection
Testing and inspection play a critical role in the battery certification process. Manufacturers must prove that their lead-acid batteries meet all safety, performance, and environmental standards. The process includes several types of tests:
- Charge and discharge tests check battery longevity and reliability.
- Short circuit tests ensure safety under fault conditions.
- Environmental tests assess performance under extreme temperature and humidity.
Regular inspections and audits help maintain certification. For example, monthly inspections may include electrical measurements, visual checks, and safety equipment verification. Quarterly and annual inspections involve more detailed testing, such as measuring cell voltages, specific gravity, and connection resistance. Capacity testing determines the actual performance of the battery under controlled discharge. Safety tests, such as short circuit tests, prevent fire or explosion risks. Environmental stress tests confirm that batteries can operate safely in harsh conditions. Compliance with standards like IEEE 450-2010, UL, and CE is essential. Certification bodies conduct audits and require renewal of certification to ensure ongoing compliance.
| Inspection Frequency | Test/Inspection Type | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly | Electrical Measurements | Measure and record DC float voltage, current, charger output, pilot cell voltage, temperature |
| Monthly | Visual Inspections | Check electrolyte levels, corrosion, cracks, leakage, terminal and connector condition |
| Monthly | Проверки безопасности | Verify ventilation, HVAC, lighting, safety equipment, battery-monitoring systems |
| Quarterly | Electrical Measurements | Measure all cell voltages, specific gravity, internal ohmic values, temperature |
| Annual | Electrical & Visual | Detailed inspection of all cells, measure resistance, inspect rack/cabinet integrity |
| Capacity Testing | Performance Test | Controlled discharge to determine ampere-hour or wattage capacity |
| Safety Tests | Short Circuit Test | Verify safety under short circuit conditions |
| Environmental Tests | Stress Testing | Assess performance under extreme temperature and humidity |
| Compliance | Standards & Audits | Ensure adherence to standards, conduct audits, renew certifications |
Certification Issuance
After successful completion of all steps in the battery certification process, the certification body issues the official certificate. This document confirms that the lead-acid batteries meet all required standards and regulations. The certificate allows manufacturers to market and sell their products legally. It also provides proof of compliance during inspections or audits by authorities. Companies must keep the certificate up to date by renewing it as required and updating documentation when standards change.
Note: Certification bodies such as BIS, UL, and CE play a vital role in verifying compliance. Their approval demonstrates that the manufacturer has met all requirements for lead acid battery certification.
Rigorous testing and professional certification bodies ensure that only safe, reliable, and compliant lead-acid batteries reach the market. The battery certification process protects users, supports regulatory compliance testing, and builds trust in industrial applications.
Ongoing Compliance
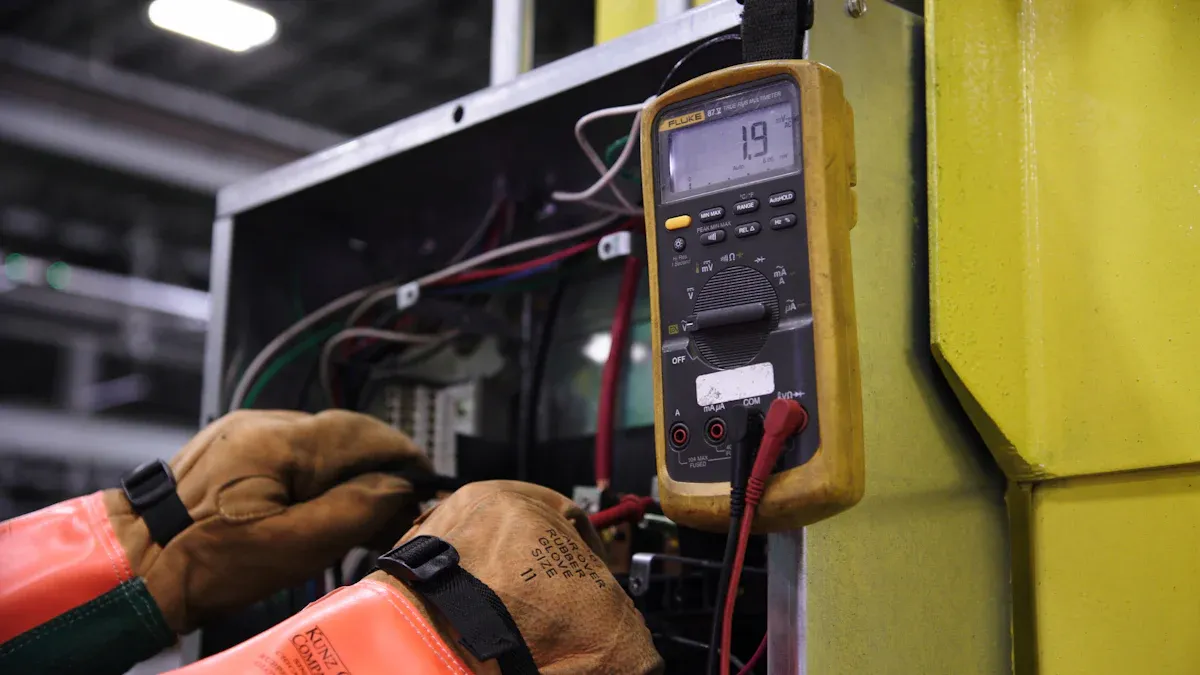

Regular Audits
Industrial facilities must schedule regular audits to maintain compliance with certification standards for lead-acid batteries. Audits help companies check if their lead-acid batteries meet all safety, environmental, and operational requirements. Auditors review battery storage, handling, and disposal practices. They also inspect documentation and test records to confirm ongoing compliance. These audits identify gaps in battery certification compliance and help prevent costly violations. Companies that perform regular audits can quickly address issues and keep their certification valid.
Regular audits support a proactive approach to battery compliance certification and reduce the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Renewals & Updates
Certification for lead-acid batteries does not last forever. Most certifications, including those for recycling plants, remain valid for two years. Companies must submit renewal applications at least six months before the expiration date. The renewal process requires several documents, such as GST registration, ID proof, address proof, PAN card, and a consent certificate from the State Pollution Control Board. Companies also need authorization under Hazardous Waste Rules, registration with the District Industries Centre, proof of installed capacity, and a no-objection certificate from local authorities. The application goes to the Joint Secretary of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change or an authorized officer. Officials review the application, verify documents, and inspect the facility to ensure ongoing compliance. If everything meets the standards, the authority renews the certification for another two years. If they find problems, they may refuse renewal.
| Шаг | Action Required |
|---|---|
| 1 | Prepare renewal documents and submit Form VI |
| 2 | Submit application six months before expiry |
| 3 | Undergo document review and facility inspection |
| 4 | Receive decision within 90 days |
| 5 | Certification renewed or refused based on compliance |
Training & PPE
Staff who handle lead-acid batteries must receive proper training and use personal protective equipment (PPE) to maintain compliance. Training covers battery operation, safe handling, spill management, and hazard awareness. Workers learn about risks such as chemical burns, corrosion, lead poisoning, and electric shock. Companies must remind staff to remove metal jewelry and watches to prevent sparks and electrical hazards. PPE includes gloves, protective eyewear, hard hats, face shields, aprons, and rubber gloves that resist acid and electrical shock. Workers should use back braces and proper lifting techniques to avoid injury. Facilities must keep acid spill neutralizing agents, eye wash stations, and fire protection equipment nearby. Staff should wash hands before and after handling lead-acid batteries. Emergency procedures require flushing skin or eyes with water after acid contact and seeking medical help. First aid and CPR training are also recommended for all staff.
- Train staff in battery handling, lifting, and emergency response.
- Require PPE such as gloves, face shields, and aprons.
- Remove all metal objects before working with lead-acid batteries.
- Keep safety equipment and neutralizing agents accessible.
Ongoing training and proper PPE help companies achieve battery certification compliance and protect workers from harm.
Challenges & Best Practices
Navigating Regulations
Industrial organizations face several challenges when seeking certification for lead-acid batteries. The increasing complexity of lead-acid battery technologies requires constant updates to testing methods and standards. Companies must adapt quickly, which raises operational costs. Global inconsistencies in regulatory standards create confusion and delays, especially when exporting lead-acid batteries to different countries. Supply chain disruptions and design changes, such as updates to microcontroller ICs, can force manufacturers to repeat certification steps. Transport regulations for lead-acid batteries, classified as dangerous goods, add further testing requirements. These challenges often result in higher costs, delayed product launches, and increased expenses for manufacturers.
To overcome these obstacles, organizations should follow лучшие практики:
- Stay informed about changing standards and regulations by engaging with industry associations.
- Work with certification bodies early in the product development process to identify compliance issues.
- Maintain detailed technical files and risk assessments to meet CE marking and other requirements.
- Invest in robust quality assurance and testing systems for lead-acid batteries.
- Build strong relationships with regulatory agencies to stay ahead of changes.
- Follow recognized industry best practices, such as IEEE standards for maintenance and training.
Proactive engagement with regulatory bodies and early planning help companies avoid costly delays and ensure smooth certification for lead-acid batteries.
Recordkeeping
Proper recordkeeping is essential for ongoing compliance with certification standards for lead-acid batteries. Companies must keep detailed records to demonstrate that their lead-acid batteries meet all requirements.
| Recordkeeping Requirement | Описание |
|---|---|
| Monitoring Parameters | Track pressure drops, liquid flow rates, filter inspections, and leak detection system outputs. |
| Record Retention Period | Store all records onsite for at least 5 years. |
| Standard Operating Procedures | Document daily or periodic quality checks for manufacturing equipment. |
| Certification and Raw Data | Keep certification reports, raw data, and operator certifications. |
| Corrective Actions | Record all corrective action plans, failure events, and actions taken. |
| Bag Leak Detection System | Maintain SOPs for system adjustments and alarm responses. |
| Continuous Monitoring Quality | Keep written procedures and all versions of performance evaluation plans for 5 years. |
| Failure Records | Log all failures, including dates, causes, and corrective actions. |
Accurate records support audits and help companies maintain certification for lead-acid batteries.
Working with Certifiers
Selecting the right certification body is critical for lead-acid battery manufacturers. Companies should understand the specific safety and performance standards that apply to their lead-acid batteries. The target market determines which certification is necessary, such as CE marking for Europe or UL certification for North America. Manufacturers should evaluate the reputation and recognition of the certification body, focusing on well-known organizations like IEC, UL, and RoHS. The certification body must verify compliance with all relevant standards and review technical documentation, including test reports and design schematics. Aligning the certification process with the intended application ensures that lead-acid batteries meet all safety and legal requirements.
Tip: Early collaboration with certifiers helps identify potential issues and streamlines the certification process for lead-acid batteries.
Lead-acid batteries power many industrial systems. Companies rely on lead-acid batteries for backup and daily operations. Certification proves that lead-acid batteries meet strict safety rules. Lead-acid batteries with certification protect workers and property. Facility managers trust lead-acid batteries for reliable energy. Lead-acid batteries must pass tests for certification. Lead-acid batteries with certification help avoid legal trouble. Lead-acid batteries support safe workplaces. Compliance with certification keeps lead-acid batteries working well. Facility managers should review lead-acid battery certification, consult experts, and follow best practices.
ЧАСТО ЗАДАВАЕМЫЕ ВОПРОСЫ
What is lead acid battery certification, and why does it matter?
Lead acid battery certification proves that lead-acid batteries meet safety requirements and industry standards. Certification helps companies achieve regulatory compliance and avoid legal issues. Certified batteries support safe workplaces and reliable operations. Certification also builds trust with customers and regulators.
Which standards apply to industrial lead-acid batteries?
Industrial lead-acid batteries must meet key certification standards such as UL certification, IEC standard, and bis certification. These standards cover battery safety standards, battery manufacturing standards, and environmental requirements. Companies must follow european battery regulations, us battery manufacturing regulations, and canadian battery manufacturing regulations.
How does the battery certification process work?
The battery certification process starts with identifying battery certification requirements. Manufacturers prepare documents and submit batteries for regulatory compliance testing. Certification bodies review the results and issue certification if the batteries meet all requirements. Ongoing audits and renewals keep certification valid.
What are the main challenges in maintaining battery certification compliance?
Companies face changing standards, complex regulations, and supply chain disruptions. The battery manufacturing industry must keep up with bis standards, IEC, and other requirements. Regular audits, strong recordkeeping, and working with certifiers help maintain battery certification compliance.
Why is training important for battery compliance certification?
Training ensures workers understand safety requirements and proper handling of lead-acid batteries. Staff learn about battery safety standards, PPE, and emergency procedures. Good training supports compliance with bis certification process and reduces workplace accidents.

