
The critical difference between these batteries is simple. A 3.7v lithium battery is rechargeable, while a 3V cell is a single-use primary battery. These lithium ion batteries often look alike. They have different chemistries and are not interchangeable.
Have you ever wondered if a rechargeable 3.7v battery can power a key fob? This idea presents a significant safety risk.
3V vs. 3.7V: Core Distinctions

Understanding the core differences between these batteries prevents device damage. The main distinctions involve voltage behavior, chemistry, and intended use. A 3.7v lithium battery has a different purpose than a 3V cell.
Voltage and Discharge Curves
The voltage rating on a battery tells a complex story. A 3.7v lithium battery has a nominal voltage of 3.7V. This nominal voltage is an average. A fully charged 3.7v battery actually starts at 4.2V. Its voltage gradually drops to around 3.0V as it discharges. This variable output is suitable for modern electronics designed to handle it.
In contrast, a 3V primary lithium cell provides a very stable output. It maintains a voltage close to 3.0V for most of its life. This flat discharge curve means the device receives a consistent power level until the battery is nearly empty. The nominal voltage of 3V is a reliable figure. A 3.6v lithium battery and a 3.7v lithium-ion battery share a similar variable discharge curve, unlike the steady 3 volt cell. The nominal voltage is key.
Rechargeable vs. Primary Chemistries
The most significant difference is reusability. The 3.7V lithium ion batteries are secondary cells, meaning they are rechargeable. Their chemistry allows for a reversible process.
- During charging, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode.
- This process stores electrical energy.
- During discharging, the ions return to the cathode.
- This movement releases the stored energy for use.
Примечание: A 3.6v lithium battery also uses this rechargeable chemistry. Its nominal voltage is slightly different, but it functions the same as a 3.7V cell.
Primary 3V lithium cells, like Li-MnO2 batteries, are designed for single use. Their chemical reaction is not reversible. Attempting to recharge them can cause dangerous internal reactions, making them unsafe. Their design prioritizes a long, stable life over reusability. The nominal voltage of a 3.7v battery is a key indicator of its rechargeable nature, while the nominal voltage of a 3V cell indicates it is primary.
Energy Density and Shelf Life
A rechargeable lithium-ion battery packs more power into a smaller space. This higher energy density makes it ideal for high-drain devices that need a lot of energy quickly. However, these lithium ion batteries lose their charge over time, even when not in use.
Primary 3V lithium cells have a lower energy density. Their strength is an incredibly long shelf life.
- They can be stored for 5 to 10 years.
- They lose less than 1% of their charge per year.
- This low self-discharge rate makes them perfect for standby devices.
The nominal voltage of a 3.7v battery is associated with high power, while the nominal voltage of a 3V cell is linked to longevity. The nominal voltage helps identify the battery’s intended application.
3.6V Lithium Battery vs. 3.7V: What’s the Difference?
When looking at rechargeable cells, people often see both a 3.6v lithium battery and a 3.7v lithium battery. This can cause confusion, but the distinction is less important than it seems. The debate over a 3.6v vs 3.7v lithium battery is mostly a technicality.
Are They Interchangeable?
Yes, for almost all consumer purposes, a 3.6v lithium battery and a 3.7v lithium battery are interchangeable. Both types of lithium ion batteries operate on a similar voltage range. They start at 4.2V when fully charged and are considered empty around 3.0V. Сайт 0.1V difference in their nominal voltage is only about 2.7% of the total, which is a negligible amount. Modern electronics have voltage regulators that easily manage this small variation. The key takeaway is that the performance difference between a 3.6v vs 3.7v lithium battery is not a concern for end-users.
Minor Chemistry Differences
The slight difference in nominal voltage comes from minor variations in the battery’s chemistry. Manufacturers use different materials for the cathode, which affects the cell’s rated nominal voltage.
| Материал катода | Typical Nominal Voltage |
|---|---|
| Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO₂) | 3.7V |
| Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn₂O₄) | 3.6V |
A 3.6v lithium battery often uses a manganese-based cathode, while a 3.7v lithium battery typically uses a cobalt-based one. Despite this, both a 3.6v lithium-ion battery and a 3.7v lithium-ion battery must pass strict safety tests, such as IEC 62133, to be sold. This ensures a 3.6v lithium battery is just as safe as a 3.7v battery. The nominal voltage is simply a label reflecting its internal chemistry.
The Real Concern: 3V vs. 3.6V/3.7V
Users should not worry about choosing between a 3.6v lithium battery and a 3.7v lithium battery. The real danger lies in confusing either of these with a 3V primary cell. A rechargeable 3.6v lithium battery has a full charge of 4.2V. Placing this high-voltage lithium-ion battery into a device designed for a steady 3V can cause permanent damage.
Внимание: ⚠️ Never use a higher voltage battery than your device manufacturer specifies. Using a 3.6v lithium battery in a 3V device can cause overheating, circuit failure, or even fire. The nominal voltage on the original battery is the only one you should use.
Applications of 3.7V Batteries vs. 3V
The voltage and chemistry of a battery directly determine its best use. A 3.7v lithium battery excels in power-hungry electronics. A 3V primary cell provides reliability for low-energy devices. Understanding these distinct applications of 3.7v batteries versus 3V cells is essential for device performance and safety.
High-Drain Devices
High-drain devices demand a large amount of power in a short time. Their complex functions require the high energy density and variable voltage output of rechargeable lithium-ion cells.
-
Vapes and E-Cigarettes: These devices need significant power to heat a coil. The ideal voltage for vaping often falls between 3.3V and 4.2V, making a 3.7v battery a perfect match. Higher voltage produces more vapor. Many popular vape batteries are 18650 or 21700 models, which are types of 3.7V cells.
Battery Model Емкость (мАч) CDR (Amps) Molicel 18650-P26A 2600 25 Sony 18650VTC5A 2500 25 Samsung 18650-25R 2500 20 Samsung 21700 40T 4000 25 Molicel 21700 4000 30 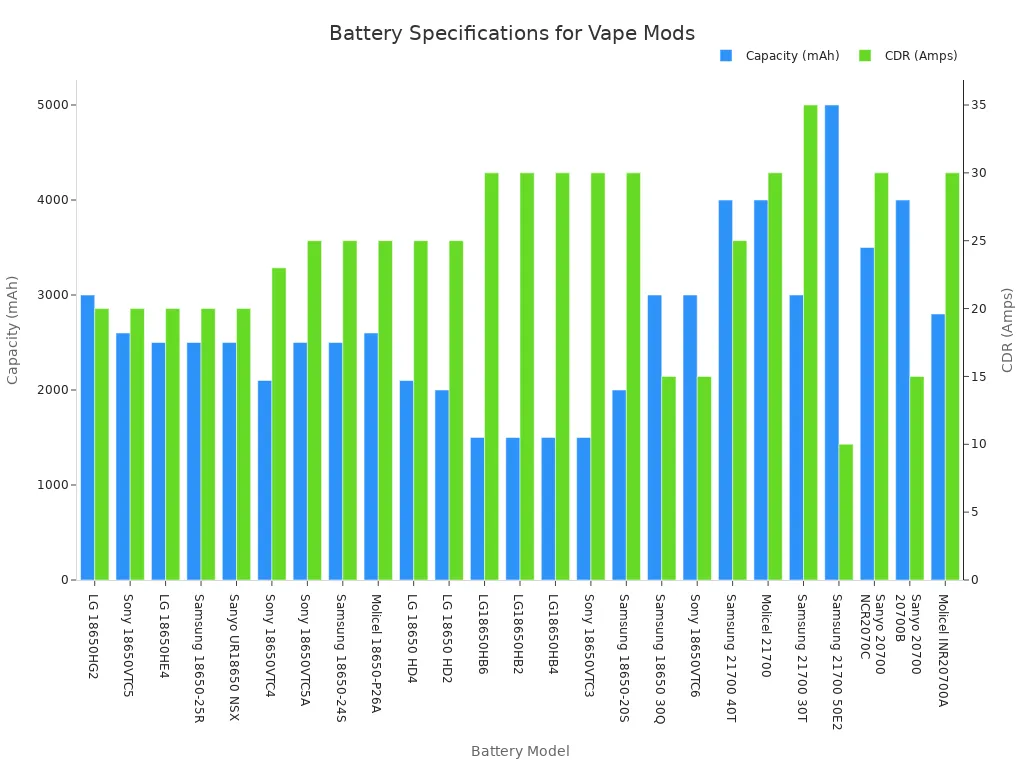
-
Laptops and Power Banks: Modern portable electronics rely on battery packs made from multiple cells. Laptop battery packs often use a
4s2pconfiguration. This setup connects four 3.6v lithium battery cells in series to create a higher voltage and two parallel strings to increase capacity. High-capacity power banks also use these cells to deliver enough power to charge a laptop, requiring features like:- Power Delivery (PD) for fast charging up to 100W.
- A minimum capacity of 20,000mAh.
- USB-C or other ports that match the laptop’s needs.
Other examples include high-power flashlights, drones, and electric tools. Each device needs the robust power that a 3.7v lithium battery provides.
Low-Drain and Standby Devices
Low-drain devices consume very little power over a long period. They need a stable, reliable power source with a long shelf life. This makes 3V primary lithium cells the ideal choice.
- Watches and Key Fobs: These small electronics need to run for years without a battery change. They commonly use 3V lithium coin cells. The CR2032 (20mm diameter, 3.2mm height) и CR2025 (20mm diameter, 2.5mm height) are two of the most common types found in watches, car key fobs, and small TV remotes.
- Smoke Detectors and Medical Devices: Safety and reliability are critical for these items. While many modern smoke alarms are hardwired, they often rely on backup batteries. Devices that are fully battery-powered, especially older models or certain medical monitors, use primary cells for their dependability. The long shelf life ensures they are ready when needed. Some alarms now feature sealed 10-year batteries, which eliminates low-battery chirps and provides protection during power outages, embodying the “set it and forget it” principle of primary cells.
The Dangers of Over-Voltage
The most critical rule in battery replacement is to match the voltage. Using a higher voltage battery than specified can lead to catastrophic failure. This is especially true when substituting a 3.7V cell for a 3V cell.
A fully charged 3.7v battery provides 4.2V of power. A device designed for a steady 3V cannot handle this 40% increase in voltage. The electronic components inside have strict tolerances.
Critical Safety Warning: ⚠️ An electronic component rated for 3V often has a maximum input tolerance of only VDD + 0.3V, or 3.3V. A 4.2V battery will immediately exceed this limit, sending far too much electrical pressure through the circuit.
This over-voltage condition can cause several problems:
- Instant Burnout: Sensitive microchips and processors can be permanently destroyed in an instant.
- Перегрев: The excess voltage forces components to dissipate energy as heat, which can melt plastic, damage circuit boards, and create a fire hazard.
- Battery Failure: Forcing a high-voltage battery into a low-voltage device can also cause the battery itself to fail. This misuse can lead to internal structural damage, increasing the risk of a dangerous chemical leak or thermal event.
Proper battery selection is a fundamental aspect of electronic safety. Always confirm the device’s required voltage before inserting a new battery. A 3.6v lithium battery presents the same danger as a 3.7V cell in this scenario. Prioritizing safety ensures your devices function correctly and without risk.
How to Choose the Correct Battery
Selecting the correct battery is essential for device performance and user safety. A few simple checks can prevent costly damage and potential hazards. Users should always verify a battery’s specifications before installation.
Read Your Device’s Manual
The safest first step is to read the device’s manual. Manufacturers provide specific power requirements to ensure proper operation. The manual will state the required battery type, size, and nominal voltage. Ignoring these guidelines can lead to serious problems. For example, many manuals include direct warnings about this.
“Voltage: The voltage rating of the battery should be clearly stated to avoid mismatching or overloading devices.”
Charger manuals for a lithium-ion battery often contain even more specific instructions for safety:
- You must select 3-Cell for charging. * Selecting a cell count other than the one printed on the battery (always confirm label is correct), can cause fire.
- Set voltage and current correctly (failure to do so can cause fire).
Identifying Your 3.7V Battery Label
A battery’s label contains vital information. A genuine 3.7v battery will clearly display its nominal voltage, often alongside its capacity (e.g., ‘2500mAh’) and chemistry (‘Li-ion’). However, users must watch for fakes. Some counterfeit cells have unrealistic capacity claims, such as a ‘9900 mAh’ rating on an 18650 battery, which is physically impossible. These misrepresentations are a clear sign of a low-quality and potentially dangerous product. Choosing between different 3.7v battery sizes also requires checking the label for a match.
Warning: ‘3V’ Rechargeable Sizing
A common point of confusion involves rechargeable batteries made in the same size as primary cells. For instance, the 16340 (RCR123A) and 14500 (AA-sized) are two common 3.7v battery sizes. A rechargeable RCR123A battery has a higher voltage than a primary 3V CR123A battery. Using this higher-voltage cell in a device designed for 3V can damage its electronics. The device must be explicitly compatible with the higher voltage of an RCR123A for safe use. This is a critical safety consideration, as the voltage difference can lead to malfunction or permanent failure. Always verify device compatibility with these common 3.7v battery sizes.
The most important rule is simple: users must only use the voltage their device manufacturer specifies. A 3.7V battery, which reaches 4.2V when full, will damage electronics designed for a steady 3V. This is a critical point for user safety. When in doubt, sticking to the original type of lithium ion batteries is the best practice.
This simple step ensures devices work correctly and prioritizes personal safety.
ЧАСТО ЗАДАВАЕМЫЕ ВОПРОСЫ
Can a user charge a 3V lithium battery?
No. A 3V lithium battery is a primary cell designed for single use. Attempting to charge it is extremely dangerous. This action can cause the battery to leak, overheat, or even explode. Only batteries labeled “rechargeable,” like 3.7V Li-ion cells, are safe to charge.
What happens if a 3.7V battery is used in a 3V device?
Using a 3.7V battery in a 3V device will cause damage. The higher voltage (4.2V when full) overloads the electronics.
This over-voltage can instantly burn out circuits, melt components, and create a fire hazard. A user must always match the battery voltage to the device’s requirement.
Are 3.6V and 3.7V batteries the same for a user?
Yes, for most purposes, a user can treat 3.6V and 3.7V rechargeable batteries as interchangeable. They share a similar operating voltage range (4.2V full to ~3.0V empty). Electronics can easily handle the minor difference. The key is not to confuse either with a 3V primary cell.
How does a user find the correct battery?
A user should check the device’s manual or look at the original battery. The label provides the required voltage (V) and size code (e.g., CR2032, 18650). Matching these specifications exactly ensures safety and proper device function. When in doubt, use the original battery type. ✅

