
You need to safely discharge li-ion batteries before storage or disposal to prevent hazards. Always follow proper maintenance steps to keep lithium batteries stable and reduce risks. For storage, you do not need to fully discharge the battery. However, disposal guidelines require you to discharge lithium batteries until they drop below two volts under a low current. This process lowers the chance of fire during transport. You can protect yourself and the environment by following these simple maintenance rules for all lithium battery types.
Why Discharge Matters
Risks of Improper Discharge
When you do not handle lithium batteries correctly, you face serious risks. Many accidents happen because people store or dispose of batteries the wrong way. Here are some dangers you should know:
- Discharging lithium batteries below 3V can turn lithium ions into molten lithium metal. This can cause short circuits, fires, or explosions.
- Deep discharge can make copper inside the battery dissolve. This increases the chance of battery failure and raises internal resistance.
- Short-circuited or deeply discharged batteries may leak, burst, or even explode.
- Storing batteries at 0V or very low voltage makes them more dangerous.
- Improper discharge and storage can lead to emballement thermique. This means the battery gets very hot and may catch fire.
- If you damage a lithium battery, it can release toxic gases like hydrofluoric acid. These gases are harmful to your health.
- Fires from lithium batteries are hard to put out and need special tools.
- Overcharging or short circuits can cause the battery to overheat, leak, or explode.
- Mechanical abuse, such as dropping or crushing batteries, can cause them to catch fire.
- Environmental factors like high humidity or pressure changes can make batteries unstable.
⚠️ Remarque : Many real-life incidents, such as fires in warehouses and recycling plants, show how dangerous improper lithium battery handling can be. Famous cases include the Samsung Galaxy Note 7 and Boeing 787 Dreamliner battery fires.
Benefits for Maintenance and Storage
Proper discharge and storage help you keep lithium batteries safe and working longer. You can avoid many problems by following simple steps:
- Keep batteries charged between 40% and 60% for storage. This level is safest for lithium batteries.
- Avoid letting the battery drop to 0% or stay fully charged for long periods.
- Utilisation partial charges instead of waiting for the battery to run out completely.
- Recharge batteries soon after they shut down from low power. This prevents permanent damage.
- Shallow discharges, where you use only part of the battery’s power, help the battery last longer.
- Monitoring battery voltage and discharge patterns lets you spot problems early.
- Good maintenance reduces the cost of replacing batteries and keeps your devices running well.
- Storing batteries at the right charge level and in a cool, dry place lowers the risk of fire or leaks.
- Protect batteries from physical damage and keep them away from heat sources.
- Using certified lithium batteries and following safety rules keeps you and your environment safe.
Safety Precautions
Personal Protection
You must always protect yourself when handling lithium batteries. Safety starts with the right gear. Wear safety eyeglasses to shield your eyes from sparks or leaks. Specialty heat-resistant gloves keep your hands safe from burns. Remove all jewelry before you work with batteries. Metal rings or bracelets can cause short circuits if they touch battery terminals. Electrical hazard-rated footwear and gloves add another layer of safety, especially when you handle large lithium batteries. If you notice a damaged or leaking battery, put on safety glasses and gloves right away. Sometimes, you may need respiratory protection if fumes appear. In case of a battery fire, only trained people should use self-contained breathing apparatus and heat/fire protective gear. These safety procedures help you avoid injury and keep your workspace secure.
- Safety eyeglasses
- Heat-resistant gloves
- No jewelry
- Electrical hazard-rated footwear
- Respiratory protection (if needed)
- Self-contained breathing apparatus for fires
⚠️ Conseil : Always follow safety procedures and use the right personal protective equipment before you start any work with lithium batteries.
Safe Work Area
A safe work area helps you prevent overheating and accidents with lithium batteries. You should set up your workspace with special features that protect you and your surroundings. The table below shows important characteristics of a safe area for handling and discharging batteries:
| Caractéristique | Description & Purpose |
|---|---|
| Safety Cabinet Construction | Double-wall steel with insulating air gap to contain explosions and heat while keeping outer surface safe to touch. |
| Pressure Relief Vent System | Vented door panels to dampen explosive force and integrated filters to trap smoke and toxins. |
| Flame Arresters | Double-layer wire-mesh to absorb heat and prevent flames from escaping the cabinet. |
| Door Hinge Flame Guards | Prevent flames from escaping through door hinges to avoid secondary fires. |
| Ventilation System | Crossflow fan ventilation to keep batteries cool during charging and prevent heat buildup. |
| Temperature-activated Dampers | Spring-loaded dampers close at 135°F (57°C) to reduce release of smoke and gases by up to 99%. |
| Heat-activated Door Seals | Intumescent seals expand with heat to block smoke, fumes, and flames from escaping. |
| Storage Environment | Cool, dry, well-ventilated area to prevent overheating and accumulation of hazardous gases. |
| Battery Positioning | Store upright, secured against physical damage, separated to avoid short circuits, and protected from sunlight/humidity. |
| Charging Practices | Use certified chargers, charge away from combustibles, monitor for overheating, and limit charge level to 80% if possible. |
| Fire Protection & Preparedness | Provide fire extinguishers, smoke detectors, emergency plans, and employee training for battery fire scenarios. |
You should always keep lithium batteries in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. This helps prevent overheating and lowers the risk of thermal runaway. Store batteries upright and away from sunlight or moisture. Use certified chargers and never charge near flammable materials.
Battery Inspection
Before you discharge or store lithium batteries, inspect them for signs of damage. Look for excessive heat. If a battery feels too hot to touch, it may be unsafe. Check for bulging, swelling, or leaks. These signs show internal gas release or possible thermal runaway. Do not use batteries with damaged wrappers or insulators. Physical damage like punctures, cuts, or crushing makes batteries dangerous. Watch for smoke, strong odors, or rapid heating at the battery cap. These are early warnings of internal faults. If you see any of these signs, do not handle or discharge the battery. Misusing lithium batteries can cause explosion, fire, or serious injury. Always follow safety precautions and best practices to protect yourself and others.
- Chaleur excessive
- Bulging or swelling
- Smoke or strong odor
- Damaged wrappers or insulators
- Physical damage (punctures, cuts, crushing)
- Leaks or rapid heating
🛑 Remarque : Early detection of these problems helps you avoid thermal runaway and keeps your environment safe.
Proper Battery Maintenance
Battery Pack Maintenance Steps
You can keep your battery safe and working well by following a few simple battery pack maintenance steps. Good maintenance helps you avoid problems and keeps your battery life long. Here is a list of steps for proper battery maintenance:
- Charge your battery to about 60-80% before storing it for a long time. This helps reduce wear and keeps the battery healthy.
- Disconnect the battery from any device or system. This stops unnecessary drain during storage.
- Store the battery in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated place. Try to keep the temperature between 35°F and 90°F.
- Keep the battery away from direct sunlight and sudden temperature changes. This prevents damage and extends battery life.
- Use only high-quality chargers that the manufacturer approves. Avoid overcharging or deep discharging to protect the battery.
- Inspect the battery often for swelling, leaks, or other damage. Regular checks are part of optimal battery care.
- Recharge the battery every three months if you store it for a long time. This stops the battery from losing too much charge.
- Place the battery on racks or platforms that allow air to flow. Do not put batteries on metal or flammable surfaces.
- Never charge the battery on soft or combustible surfaces. Use a safe, non-combustible area for charging.
- Handle any damaged or swollen battery with care. Dispose of it safely to prevent hazards.
- For short-term storage, keep the battery at 40-60% charge and store it in a cool, dry place.
- For long-term storage, keep the battery at 40-60% charge, check it every three months, and use fireproof containers.
🛠️ Regular battery pack maintenance helps you avoid risks and supports extending battery life and performance.
Consistent Discharge Rate
You can protect your battery and make it last longer by using a consistent discharge rate. This is a key part of proper battery maintenance and care. Here are some tips for managing discharge:
- Try not to let your battery drop below 20% charge. This helps prevent damage and supports battery life.
- Keep the battery charge between 20% and 80% for most uses. This range reduces stress and helps with optimal battery care.
- Use a Battery Management System (BMS) to watch the battery’s voltage and temperature. The BMS can stop the battery from over-discharging.
- Choose smart chargers that adjust the voltage and stop charging when the battery is full.
- Check the battery terminals and keep them clean. Good maintenance helps the battery work better.
- Control the temperature around the battery. Avoid letting it get too hot or too cold.
- Avoid letting the battery stay empty for a long time. This can shorten its life.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for care and maintenance. This helps with extending battery life.
💡 Consistent discharge and regular care help you get the most out of your battery and keep it safe.
Li-ion Batteries Storage
Ideal Charge Level
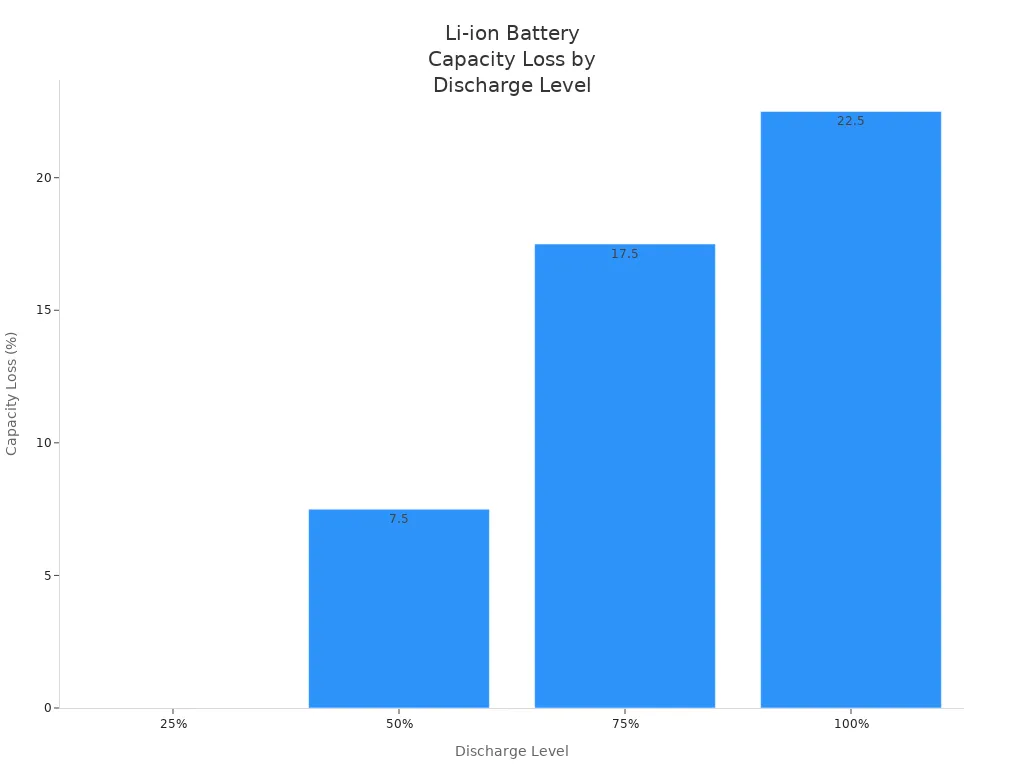
When you store lithium batteries, you need to pay close attention to the charge level. Battery manufacturers and safety organizations recommend keeping li-ion batteries at about 40% state of charge for storage. This level helps you avoid both overcharging and deep discharge, which can damage the battery. If you store lithium batteries fully charged, you increase the risk of capacity loss and shorten their lifespan. If you store them fully discharged, you risk voltage dropping too low, which can cause permanent damage.
You should aim for a voltage near 3.7 to 3.8 volts per cell. This range keeps the battery stable and safe. Most experts agree that storing at 40-60% charge is best for long-term storage. This practice helps you prevent battery breakdown and keeps your devices ready for use. Good battery charging habits, like charging lithium batteries to the right level before storage, protect your investment.
🟢 Conseil : Always check the battery’s voltage before you store lithium batteries. Use a voltmeter or a smart charger to confirm the charge level.
The table below shows how different charge levels affect battery health during storage:
| Storage Charge Level | Effect on Battery Health |
|---|---|
| 0% (Fully Discharged) | High risk of damage, shortens lifespan |
| 40% (Recommended) | Best for long-term storage, preserves capacity |
| 80-100% (Fully Charged) | Increases capacity loss, speeds up aging |
Temperature and Environment
The place where you store lithium batteries matters as much as the charge level. You should always choose a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area for lithium battery storage. The ideal temperature range for long-term storage is between 41°F and 68°F (5°C to 20°C). If you store lithium batteries in hot places, you speed up chemical reactions that wear out the battery. If you store them in freezing temperatures, you risk physical damage and voltage drops.
Humidity also affects lithium battery storage. High humidity can cause corrosion and damage the battery’s internal parts. You should use a dry environment and avoid places with moisture. In areas with high humidity, you can use dehumidifiers or moisture absorbers to protect your batteries.
- Store lithium batteries at 40-60% charge for long-term storage.
- Keep storage temperature between 50°F and 86°F for best results.
- Avoid direct sunlight, extreme heat, or freezing conditions.
- Use non-conductive or fireproof containers for extra safety.
- Make sure the storage area has good airflow.
🌡️ Remarque : Temperature swings and high humidity can ruin lithium batteries. Stable, cool, and dry conditions help you get the most out of your battery.
Periodic Checks
Even when you store lithium batteries correctly, you need to check them from time to time. Li-ion batteries slowly lose charge, even when not in use. If you leave them unchecked, the voltage can drop too low and cause damage. You should inspect and recharge your batteries every three to six months during long-term storage.
Set a reminder to check the charge level. If the battery drops below 40%, recharge it to the recommended range. Use a smart charger or a voltmeter to measure the voltage. Look for signs of swelling, leaks, or corrosion. If you find any problems, remove the battery from storage and handle it safely.
- Check the charge level every three to six months.
- Recharge to 40-60% if the voltage drops.
- Inspect for physical damage or leaks.
- Use intelligent monitors for large battery packs.
- Follow manufacturer recommendations for lithium battery storage.
🔋 Reminder: Regular checks and proper storage help you avoid costly battery replacements and keep your devices safe.
Discharge Methods
Using Devices
You can safely discharge lithium batteries by using the devices they power. Turn on your device and let it run until the battery level drops to the recommended range. This method works well for most small batteries, such as those in phones or laptops. It is simple and does not need extra tools. However, some batteries may shut off before reaching the lowest safe voltage. Always check the battery’s voltage with a voltmeter to make sure you do not go below the safe limit. For larger batteries, you may need to use special equipment or methods.
Another electronic method involves using a salt solution. You connect wires with crocodile clips to the battery terminals and dip the other ends into a saltwater bath. This setup allows for a controlled short circuit and can fully discharge batteries in less than five minutes. Only immerse the battery tips, not the whole battery, to avoid leaks or damage. This method is fast and cost-effective, but you must replace the wires often due to corrosion.
Using Resistors or Tools
You can also use resistors or special tools to discharge batteries safely. High-power adjustable resistors work well for testing and controlled discharge. Connect the resistor to the battery and monitor the current with an ammeter. Start with half the maximum current listed by the battery maker. Use temperature sensors to watch for overheating. Carbon film resistors with a 10-ohm value are often best for stable discharge. This method helps prevent damage to the battery’s internal parts. For large battery packs, you can use a battery cycler to bring the voltage down before applying the resistor.
Monitoring Voltage
Always monitor the voltage during discharge. The safe range for lithium batteries is between 3.0V and 4.2V per cell. Dropping below 3.0V can cause permanent damage and reduce battery life. Use a Battery Management System (BMS) or a voltmeter to check the voltage. The BMS also balances cells in multi-cell packs and adjusts for temperature changes. Regular monitoring keeps your batteries safe and helps you avoid costly mistakes.
🟢 Conseil : Never let lithium batteries discharge below the minimum safe voltage. Careful monitoring protects both the battery and your devices.
For Disposal

Full Discharge Process
You must fully discharge lithium-ion batteries before you send them for disposal. This step removes stored energy and helps prevent fires or explosions during handling. Recycling centers and safety experts recommend this process to keep everyone safe.
Start by using up all the battery power in a device until it shuts off. If you cannot do this, you can use special methods to discharge the batteries. Some common ways include soaking battery packs in a saltwater solution, connecting them to a closed-circuit resistor, or using special equipment like cryogenic or thermal processing. These methods help you safely remove any leftover charge.
Voici un simple step-by-step guide for preparing batteries for disposal:
- Fully discharge the battery using a device or a controlled method.
- Cover the battery terminals with non-conductive tape. This prevents short circuits.
- Keep each battery separate from others and label them as lithium-ion.
- Wear gloves and safety glasses to protect yourself during handling.
- Place the batteries in a non-conductive container for transport.
- Contact your local recycling center or use a manufacturer’s recycling program for instructions.
- Never throw batteries in regular trash or recycling bins.
⚠️ Remarque : Always follow local rules for battery disposal. Some areas have special drop-off points or collection events for batteries.
Safe Handling and Containers
Safe handling is important when you prepare batteries for disposal. You need to use containers that protect against fire, leaks, and physical damage. Certified storage containers designed for lithium-ion batteries are the best choice. These containers prevent electrical shorts and allow for ventilation, which helps stop overheating.
Some containers, like DENIOS BatterySafe™ cases, have extra features. They protect against fire, shock, and vibration. Many of these containers meet strict safety rules, such as UN 38.3 certification. This means they have passed tests for safe transport and storage. The US Department of Transportation also requires you to protect battery terminals and use approved packaging to prevent fires.
When you pack batteries for disposal, always use non-reactive absorbent materials. Sand or vermiculite works well to soak up any leaks. You can also use absorbent pads, spill kits, or universal absorbents. These materials help contain spills and lower the risk of fire.
Here is a table showing what to use for safe battery handling:
| Safety Item | Objectif |
|---|---|
| Non-conductive tape | Prevents short circuits at terminals |
| Certified battery container | Protects from fire, shock, and leaks |
| Sand or vermiculite | Absorbs leaked electrolyte |
| Absorbent pads/spill kits | Contains and cleans up spills |
| Safety gloves and glasses | Protects you from leaks and sparks |
🛑 Conseil : Always keep batteries in approved containers and use absorbents if you see any leaks. This keeps you and others safe during transport and disposal.
What to Avoid
Erreurs courantes
You can protect your batteries and extend their life by steering clear of common mistakes. Many people think it is safe to let batteries run all the way down, but this actually shortens their life. You should avoid overcharging, as leaving devices plugged in for too long causes overheating and damages battery cells. Storing batteries fully charged for long periods also leads to capacity loss. Always aim for a storage charge around 50% to keep your batteries healthy.
Here are some mistakes you should watch out for:
- Letting batteries discharge completely, which speeds up cell wear and reduces life.
- Storing batteries in hot or cold places, as extreme temperatures cause permanent damage.
- Keeping swollen, punctured, or leaking batteries at home, which increases fire risk.
- Using plastic bags for storage, since they trap heat and raise safety concerns.
- Hoarding old batteries instead of recycling them promptly.
Overcharging above 4.2 volts can cause lithium to build up inside the battery, leading to short circuits and permanent loss of capacity. Discharging below 2 volts breaks down the battery’s internal parts and can release dangerous chemicals. You should always follow good practices to keep your batteries safe and working well.
Unsafe Practices
Unsafe practices put you and your surroundings at risk. Never throw lithium-ion batteries in the regular trash. This can cause fires during transport or at waste facilities. Crushing, puncturing, or tampering with batteries may release toxic chemicals and start fires. Always cover battery contacts with non-conductive tape before disposal to prevent short circuits.
You should avoid storing batteries near flammable materials or in places with extreme temperatures. Handling batteries without gloves exposes you to harmful chemicals. Improper packaging, such as using regular bags instead of fire-resistant containers, increases the risk of accidents. Large batteries need special disposal as industrial waste, so always follow manufacturer guidance and local rules.
⚠️ Good practices help you avoid accidents and keep your environment safe. Always choose the right methods for handling and disposing of batteries.
After Discharge
Storage Tips
Once you finish discharging your lithium-ion batteries, you need to store lithium batteries with care. Safe storage keeps you and your environment protected from fire or leaks. Here are some important tips:
- Always store lithium batteries in a cool, dry place. Avoid areas with high humidity or direct sunlight.
- Use a resistor, such as a 47 to 100-ohm resistor, to discharge the battery slowly before storage. This method helps you reduce the voltage safely.
- After the voltage drops to zero, leave the resistor connected for another day or two. This step prevents the voltage from rebounding.
- Never use a saltwater bath to discharge or store lithium batteries. Saltwater can cause corrosion and harm the environment.
- Cover the battery terminals with electrical tape before you store lithium batteries. This action prevents short circuits.
- Keep each battery separated and insulated. Use non-conductive containers for storage, especially if you plan to transport the batteries later.
🟢 Conseil : Always check with your local recycling center for their specific rules on how to store lithium batteries before disposal.
Disposal Steps
Proper disposal of lithium-ion batteries protects both people and the environment. You must follow certain steps to meet safety and legal requirements:
- Identify the battery as hazardous waste because it contains flammable and reactive materials.
- Manage the battery under universal waste rules, which help you handle and store lithium batteries safely before recycling.
- Place batteries in closed, sturdy containers that prevent leaks or spills during storage and transport.
- Never crush or break batteries to remove parts. If a battery is damaged, treat it as hazardous waste right away.
- Ship batteries only to approved recycling or disposal facilities. Do not try to recycle them yourself.
- Follow Department of Transportation rules for moving batteries. This step helps prevent fires or toxic leaks.
- Check for any state or international rules that may apply to battery storage and disposal.
⚠️ Remarque : Proper disposal stops heavy metals and toxic chemicals from polluting soil and water. Always use the safest methods when you store lithium batteries or prepare them for recycling.
Liste de contrôle rapide
Here is a simple checklist to help you safely handle, store, and dispose of Li-ion batteries:
- Charge each battery to a level between 40% and 60% before storage. This range helps prevent overcharging or deep discharging, which can damage the battery and shorten its life.
- Inspect your batteries every three to six months. Look for swelling, leaks, corrosion, or any signs of damage. If you see any problems, remove the battery right away.
- Choose a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area for storage. Avoid places with extreme temperatures or direct sunlight. Never keep batteries in hot garages or cars, since heat can cause capacity loss or even fires.
- Keep batteries separated. Do not let them touch each other or become overcrowded. This step lowers the risk of short circuits and fire hazards.
- Retirer les piles des appareils avant de les mettre au rebut. Always keep them apart from other items and from each other.
- Cover battery terminals or wires with non-conductive tape. This action prevents short circuits during storage or transport.
- Use UN-approved containers or barrels for disposal. Layer dry sand between batteries, especially if you handle lithium-ion types.
- Store damaged, swollen, or leaking batteries in fireproof containers. Wrap them in plastic and add extra sand for extra safety.
- Never throw lithium-ion batteries in regular trash. Take them to a recycling center or follow local disposal rules.
- Do not crush, puncture, or mishandle batteries. These actions can cause fires or release harmful chemicals.
- Place discarded batteries outside or in fire-resistant containers until you can recycle them.
📝 Conseil : Following this checklist helps you protect yourself, your home, and the environment. Safe storage and disposal keep everyone safe.
You play a key role in keeping lithium-ion batteries safe. When you follow maintenance routines and industry guidelines, you help prevent fires and protect your devices. Safe discharge and proper storage lower risks and extend battery life. Always check local regulations and use approved recycling programs. By following these guidelines, you protect your health and the environment. Responsible maintenance and disposal keep everyone safer.
FAQ
How do you know when a Li-ion battery is safe to store?
Check the battery for swelling, leaks, or damage. Make sure the charge level is between 40% and 60%. Store it in a cool, dry place. If you see any problems, do not store the battery.
Can you throw Li-ion batteries in the trash?
No, you should never throw Li-ion batteries in the trash. Take them to a recycling center or a special collection point. This keeps people and the environment safe from fires and toxic leaks.
What should you do if a Li-ion battery leaks?
Wear gloves and safety glasses. Place the battery in a non-conductive container with sand or absorbent material. Do not touch the leak. Take the battery to a hazardous waste facility for safe disposal.
How often should you check stored Li-ion batteries?
Check stored Li-ion batteries every three to six months. Look for swelling, leaks, or low charge. Recharge the battery if the voltage drops below 40%. Regular checks help prevent damage and keep storage safe.

