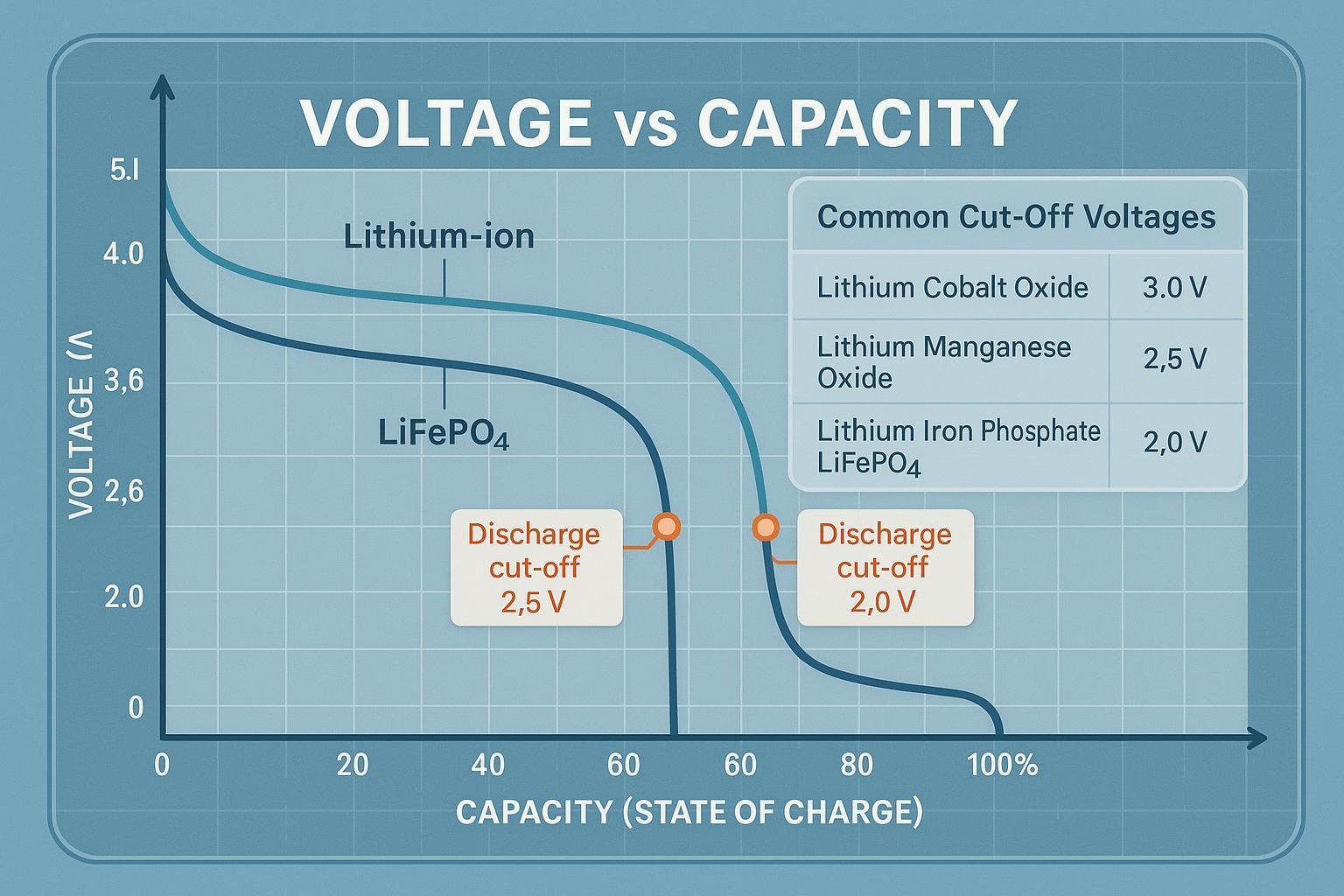
Discharge Cut-off Voltage: A Precise Definition
Discharge cut-off voltage is the lowest voltage point at which a battery cell or pack is permitted to discharge before the discharge process must be stopped to prevent capacity loss, cell damage, and compromised safety (source).
Explication détaillée
In lithium battery systems, the discharge cut-off voltage is an engineering safeguard set by cell manufacturers, enforced by a battery management system (BMS) or device electronics. This voltage is chemistry-specific: for common lithium-ion cells, the cut-off is typically set between 3.0V and 2.5V per cell (Université de la batterie), while lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) often uses 2.5–3.0V per cell. The main purpose is to balance usable capacity with long-term reliability and safety—lowering the cut-off slightly accesses more energy, but dramatically accelerates battery aging and the risk of irreversible damage.
Cut-off enforcement works as follows: A BMS or protection circuit continuously monitors each cell’s voltage. When the lowest cell reaches the defined cut-off, the BMS disconnects the load. Disregarding cut-off can lead to copper dissolution, lithium plating, and drastic capacity fade, disabling battery packs or even causing safety incidents.
Key Components and Influencing Factors
- Cell Chemistry: The safe discharge threshold depends on lithium chemistry (e.g., NMC vs. LFP).
- Manufacturers’ Data: Each datasheet specifies minimum voltage values and corresponding cycle life impacts.
- Operating Conditions: High current (C-rate) and low temperature may require higher cut-off settings.
- System Controls: BMS integration allows programmable cut-offs tailored to pack design, aging, and safety margins.
Comparative Table: Typical Discharge Cut-off Voltages by Chemistry
| Chimie | Typical Cut-off (V/cell) | Absolute Minimum (V/cell) |
|---|---|---|
| Li-ion (NMC/CO) | 3.0 (recommended) | 2.5–2.7 |
| LiFePO4 (LFP) | 2.8–3.0 | 2.5 |
| LCO | 3.0 | 2.7 |
| ANC | 3.0 | 2.7 |
Application Examples and System Relevance
- Électronique grand public : Phones and laptops set BMS cut-off near 3.0V/cell, maximizing safety and battery cycle life.
- Véhicules électriques (VE) : BMS rigorously enforces 3.0V or higher for NMC/LFP, as deep discharge risks costly pack damage.
- Stationary Storage: Solar/grid packs standardize at 2.8–3.0V/cell to balance usable energy and field reliability.
Concepts connexes
- Upper Cut-off Voltage: Highest charging voltage (e.g., 4.2V for Li-ion) before overcharge risks begin.
- Tension nominale : Average working voltage (e.g., 3.6V for Li-ion, 3.2V for LFP) used for system design.
- État de charge (SoC) : Percentage of available capacity relative to full charge.
- Depth of Discharge (DOD): Percentage of capacity removed from full.
- Système de gestion de la batterie (BMS) : Electronic system implementing voltage cut-off and protection.
- End-of-Discharge Voltage: Sometimes used interchangeably, but should be defined per cell or pack/application.
Conclusion
Correctly specifying and implementing discharge cut-off voltage is critical for the safety, lifetime, and efficient utilization of lithium battery packs. Industry best practice is always to adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendation and leverage advanced BMS for robust, programmable cut-off enforcement.

