
A battery high voltage system stores and delivers large amounts of energy for modern needs. You see these systems in electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, and backup power for hospitals. High voltage batteries help homes and industries use energy more efficiently. Understanding technical specifications and safety helps you choose the right system for your needs. The global market for battery high voltage systems is growing fast, as shown below:
| Year | Market Size (USD Billion) | CAGR (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 33.08 | – | Estimated market size |
| 2034 | 274.21 | 23.55 | Projected market size |
Battery High Voltage System Overview

What Is a Battery High Voltage System?
When you hear about a battery high voltage system, you are learning about a type of battery that stores and delivers large amounts of energy at high voltages. These systems usually operate at voltages like 192V, 220V, 384V, or even higher. You find high voltage batteries in electric vehicles, renewable energy storage systems, and industrial machines. Unlike low voltage batteries, high voltage battery systems use advanced technology to deliver more power and support heavy appliances.
High voltage battery systems often use rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. These batteries have high energy density, which means they can store a lot of energy in a small space. They also include a battery management system (BMS) that monitors each cell, balances the charge, and keeps the system safe. You benefit from features like accurate current measurement, state of charge tracking, and safety mechanisms that protect both you and your equipment.
Here is a quick comparison of battery system types:
| Battery System Type | Plage de tension | Applications typiques | Design & Function Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Voltage Systems | < 60V | Small devices, accessories | Thicker cables, less efficient, basic safety |
| High Voltage Systems | 400V – 800V | Electric vehicles, industry | Smaller cables, fast charging, advanced BMS, high efficiency |
| Off-Grid Energy Storage | 1000V – 1200V | Solar, wind energy storage | Standalone, focus on safety and isolation |
Why High Voltage Matters
You gain many advantages when you use high voltage batteries in energy storage systems. High voltage battery systems deliver power more efficiently because they produce less heat and waste less energy. You can use thinner cables, which saves space and lowers installation costs. High voltage batteries also charge and discharge faster, making them perfect for electric vehicles and fast-charging stations.
With high voltage battery systems, you get better scalability. You can add more modules to increase capacity or power as your needs grow. These systems also last longer because they generate less heat, which means less wear on the battery cells. Modern battery technology, like solid-state designs and improved thermal management, makes high voltage batteries safer and more reliable for your home or business.
Tip: High voltage batteries are ideal for applications that need lots of power quickly, such as electric vehicles and large-scale energy storage systems.
High Voltage Battery Systems: Key Specs
Voltage Range and Energy Density
When you look at high voltage batteries, you notice that they operate at much higher voltages than traditional batteries. Most high voltage battery systems used in electric vehicles and stationary storage work between 400V and 800V, but some large systems can go above 1000V. This high voltage allows you to use thinner cables, which makes the system lighter and more efficient. You also get better charge and discharge rates, which means your devices can run longer and charge faster.
High voltage lithium-ion battery technology gives you high energy density. This means you can store more energy in a smaller and lighter package. For example, high voltage lithium-ion batteries often reach energy densities of 150 Wh/kg to 250 Wh/kg or more. In comparison, traditional lead-acid batteries only offer about 30-50 Wh/kg. The higher voltage also reduces the current needed for the same power output, which lowers resistive losses and improves efficiency.
Here is a table that compares high voltage batteries with low voltage batteries:
| Aspect | High Voltage Battery | Low Voltage Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Output Power | Higher energy output power due to higher voltage | Lower energy output power |
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency with reduced resistive losses | Lower efficiency |
| Charging/Discharging Rates | Faster charging and discharging rates | Slower charging and discharging rates |
| Lifespan/Maintenance | Longer lifespan and lower maintenance | Shorter lifespan and higher maintenance |
| Initial Investment/Installation | Higher initial costs due to advanced components | Lower initial costs |
| Safety Concerns | Requires advanced Battery Management Systems for safety | Simpler safety protocols |
Note: High energy density lithium-ion batteries help you save space and weight, making them ideal for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
If you compare two battery systems with the same ampere-hour capacity, a high voltage battery delivers the same power with much less current. For example, a 204.8V system only needs about 24.41A to supply 5000W, while a 51.2V system needs 97.66A. This lower current reduces heat and energy loss, which helps your system last longer and work more efficiently.
Cycle Life and Performance
You want your high voltage batteries to last as long as possible. The cycle life tells you how many times you can fully charge and discharge the battery before its capacity drops below 80%. Most high voltage lithium-ion battery systems offer a cycle life of 300 à 500 cycles under standard conditions. If you use lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cells, you can expect 1800 to 2500 cycles at 80% depth of discharge, especially if you keep the temperature between 20°C and 50°C.
Les battery chemistry and how you manage temperature play a big role in battery performance and lifespan. For example, LFP batteries give you the longest cycle life and excellent safety, but they have lower energy density. Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC) batteries balance energy density and lifespan but degrade faster if you charge them quickly or use them in extreme temperatures. Solid-state batteries promise even longer life and higher energy density, but they are still new and not widely available.
Voici un chart that compares different battery chemistries:
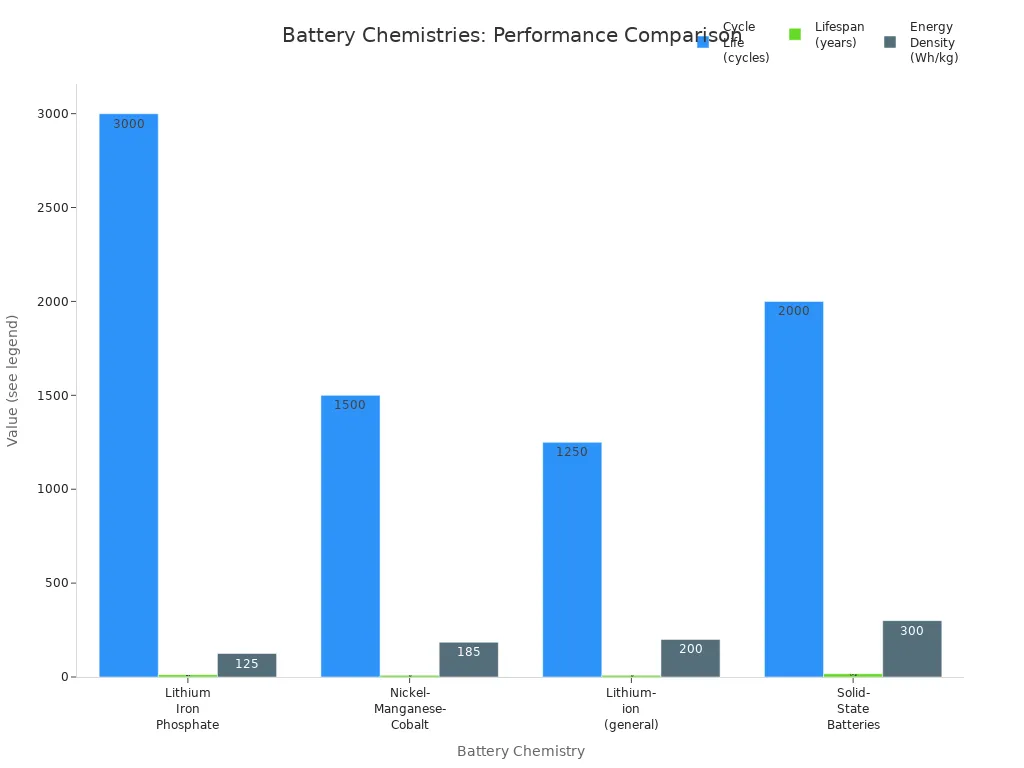
You can see that high voltage lithium-ion battery systems maintain performance best when you control temperature and avoid deep discharges. Good thermal management and a smart battery management system help you get the most out of your battery technology.
Caractéristiques de sécurité
Safety is one of the most important parts of high voltage batteries. These systems use several layers of protection to keep you safe from electrical and thermal hazards. High voltage lithium-ion battery packs include features like:
- High Voltage Interlock Loop (HVIL): This system checks all high-voltage connections. If a connection is loose or broken, it shuts down the battery to prevent electric shock.
- Fusing and Circuit Protection: Fuses and circuit breakers stop the flow of electricity if there is too much current, which prevents overheating and fires.
- Isolation Monitoring: This feature checks the insulation between high and low voltage parts. It helps prevent short circuits and electric shocks.
- IP-Rated Enclosures: High voltage batteries often use enclosures rated IP67 or higher. These keep out dust, water, and other contaminants.
- Système de gestion de la batterie (BMS) : The BMS monitors voltage, temperature, and charge. It controls cooling and power output to prevent overheating.
- Ventilation and Pressure Relief: Special vents release gases and balance pressure if the battery overheats, which prevents explosions.
- Manual Service Disconnects: These switches let you safely disconnect the battery during maintenance or emergencies.
Tip: Always check that your high voltage battery system includes advanced safety features like insulation, thermal management, and a reliable BMS.
Thermal management is also key for safety. High voltage lithium-ion batteries generate a lot of heat, especially during fast charging and discharging. Battery thermal management systems (BTMS) keep the battery at the right temperature, usually between 15°C and 35°C. These systems use air cooling, liquid cooling, or phase change materials to move heat away from the cells. Good insulation and advanced cooling help prevent emballement thermique, which is when the battery gets so hot that it catches fire or explodes.
Proper insulation and thermal management not only keep you safe but also extend the life of your high voltage batteries. New technologies, like liquid cooling with nanofluids and hybrid cooling systems, make these batteries even safer and more reliable for your needs.
Main Components of High Voltage Batteries
Cells and Modules
You find that battery cells are the building blocks of high voltage batteries. Each cell stores electrochemical energy and has its own voltage and capacity. When you connect battery cells in series, you increase the voltage. When you connect them in parallel, you increase the capacity. Manufacturers group these cells into battery modules. Battery modules help manage charge and discharge, monitor conditions, and provide cooling. This modular design lets you scale up energy storage and makes maintenance easier.
Battery modules also include safety features. They balance the voltage across cells and monitor performance. If one cell gets too hot or out of balance, the module can protect the rest of the system. This setup improves the reliability and lifespan of high voltage lithium-ion battery systems. You benefit from better control and protection at every level, from individual cells to full battery packs.
Système de gestion de la batterie (BMS)
A système de gestion de la batterie is the brain of high voltage batteries. It monitors each cell’s voltage, current, and temperature. The BMS protects your high voltage lithium-ion battery from overcharging, over-discharging, and overheating. It balances the charge between cells, making sure no cell gets stressed or damaged. The BMS also estimates the state of charge and health, so you always know how much energy you have left.
Battery monitoring systems play a key role in safety. They detect faults, control charging and discharging, and communicate with other systems. If a problem occurs, the BMS can disconnect the battery to prevent damage. This smart control helps extend the life of high voltage battery cells and keeps your system running smoothly.
Gestion thermique
High voltage batteries generate heat during use, especially when charging or discharging quickly. You need a good thermal management system to keep the temperature in a safe range. Some systems use passive cooling, which relies on natural airflow and heat dissipation. Others use active cooling, like fans or liquid coolant, to move heat away from the battery modules.
Advanced high voltage lithium-ion battery systems may use phase-change materials or immersion cooling for even better temperature control. Keeping the temperature steady helps prevent thermal runaway, which can cause fires or explosions. Good thermal management also improves the performance and lifespan of your high voltage battery packs.
Note: When you combine well-designed battery cells, smart battery monitoring systems, and effective thermal management, you get high voltage batteries that are safe, reliable, and efficient.
Applications of High Voltage Batteries
Véhicules électriques
You see high voltage batteries powering electric vehicles (EVs) on roads today. These batteries help cars, buses, and trucks travel farther and charge faster. When you use a higher voltage, like 800V instead of 400V, you get several benefits:
- Faster charging times, so you spend less time waiting.
- Lighter vehicles because thinner cables reduce weight and cost.
- More efficient power delivery, which means less energy wasted as heat.
- Better performance, as motors can run at higher speeds without losing power.
- Improved safety and reliability with advanced battery management systems.
Many automakers, such as Porsche and GM, use high voltage batteries in their newest EVs. Some vehicles, like the GM Hummer EV, can switch between 400V and 800V to optimize charging and driving. These systems also support features like software updates and emergency power, making your vehicle smarter and safer.
| Fonctionnalité | 400V System | 800V System |
|---|---|---|
| Temps de charge | Longer | About half as fast |
| Driving Range | Up to 250 miles | Up to 400 miles |
| Efficiency | Good | Even better |
Renewable Energy Storage
You rely on energy storage systems to make solar and wind power more useful. High voltage batteries store extra energy when the sun shines or the wind blows. Later, they release this energy when you need it most, like at night or during cloudy days. These batteries help balance the power grid and keep your lights on, even if the weather changes.
- They smooth out power from solar and wind, making energy supply steady.
- They provide backup power during outages, especially in remote areas.
- They help utilities avoid expensive upgrades by storing and releasing energy as needed.
- They support microgrids, which are small, local energy networks.
With high voltage energy storage systems, you can use more renewable energy and reduce your carbon footprint.
Industrial Uses
Factories, hospitals, and data centers use high voltage batteries to keep running during power outages. You benefit from these batteries in several ways:
- They provide backup power for critical equipment.
- They store cheap, clean energy for use during peak demand.
- They help smooth out power from renewable sources, making operations more reliable.
- They save space and weight, which is important in busy industrial settings.
You also find these batteries in uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, military vehicles, and even satellites. High voltage batteries deliver strong, steady power and last a long time, making them a smart choice for many industries.
Choosing the Right High Voltage Lithium Ion Battery
Adapter les spécifications à l'application
When you start choosing the right high voltage lithium ion battery, you need to match the battery’s technical specifications to your application. Each device or system has unique requirements. If you select a battery that does not fit, you risk damaging your equipment or reducing performance.
Voici un step-by-step guide to help you match specs to your needs:
- Check your device manual for the recommended battery type, voltage, and capacity.
- Match the battery voltage output exactly to your device’s voltage requirements. Even a small mismatch can cause malfunction or damage.
- Determine the required battery capacity based on your device’s power consumption and how long you want it to run.
- Consider the size and weight of the battery. Make sure it fits your device and does not make it too heavy or bulky.
- Choose a battery with a protection circuit board (PCB). This protects against overcharge, over-discharge, short circuits, and overheating.
- Look for batteries with a known cycle life and high-quality construction. This ensures safety and long-term use.
Safety tip: Batteries without proper protection can deform, leak, or even explode. Always choose batteries with built-in safety features.
You can also use this table to compare typical requirements for different applications:
| Application | Typical Voltage | Typical Peak Current | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Drills | ~18 V | ~20 A | Needs high peak power for heavy use |
| Drones | ~14.8 V | ~30 A | Needs high C-rate for fast throttle |
| LED Lighting | ~12 V | 2–5 A | Low current, prioritize long runtime |
Matching the right specs helps your high voltage lithium-ion battery deliver the power, efficiency, and safety your application needs.
Evaluating Quality and Safety
You want your high voltage lithium-ion battery to be safe and reliable. Before you buy, check for important safety certifications and quality marks. These show that the battery has passed strict tests and meets industry standards.
Look for these certifications:
- UN 38.3 – Tests for safe transport, including vibration, shock, heat, and short circuit resistance.
- IEC 62133 – Sets safety rules for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries in portable devices.
- UL 1642 and UL 2054 – Cover safety for battery cells and packs.
- Marquage CE – Shows the battery meets European safety, health, and environmental rules.
- RoHS – Ensures the battery does not contain hazardous substances.
You should also check for marks from trusted testing labs like UL, Intertek, or IEC. For large energy storage systems, look for extra certifications such as UL 1973, UL 9540, and NFPA 855. These address fire safety, installation, and thermal risks.
Note: Certified batteries protect you, your equipment, and the environment. Never skip this step when choosing the right high voltage lithium ion battery.
Supplier and Cost Considerations
When you compare suppliers and costs, you need to look beyond just the price tag. The right supplier gives you quality, safety, and long-term value. Here are some important factors to consider:
- Supplier reputation and safety record. Choose companies known for reliable products and strong customer support.
- Warranty coverage. A good warranty, such as 8 years or 100,000 miles, gives you peace of mind and helps keep resale value high.
- After-sales service. Reliable suppliers offer help with installation, troubleshooting, and repairs.
- Battery chemistry and design. Different chemistries like NCA, NMC, or LFP affect cost, performance, and lifespan.
- Raw material sourcing. Prices for nickel, cobalt, and lithium can change, affecting battery cost and availability.
- Production scale and infrastructure. Large suppliers often offer better prices and more consistent quality.
- Compliance with environmental and safety rules. Responsible suppliers follow strict guidelines and support sustainable practices.
| Factor Category | Principales considérations |
|---|---|
| Cathode Chemistry | NCA, NMC, LFP; affects capacity, voltage, and lifespan |
| Battery Pack Design | Number of cells, configuration, energy storage, power needs, weight, and size |
| Production Scale | Larger production often means lower cost and better quality control |
| Raw Material Sourcing | Availability and price of metals like nickel, cobalt, lithium |
| Supplier Reliability | Reputation, warranty, after-sales support, and compliance with standards |
Tip: Reliable suppliers build trust through quality, transparency, and strong warranties. This protects your investment in battery technology and ensures your high voltage lithium-ion battery performs well for years.
Maintenance and Safety for High Voltage Batteries
Routine Care
You can extend the life of your high voltage battery system by following a few simple steps. Regular care helps prevent problems and keeps your battery working well.
- Avoid overcharging or letting the battery run too low. Always follow the charging instructions from the manufacturer.
- Handle batteries gently. Dropping or hitting them can cause damage.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place. Keep them partially charged if you will not use them for a while.
- Inspect batteries often. Look for corrosion, leaks, or dirt on the terminals. Clean them to keep a good connection.
- Recharge batteries soon after use. Do not let them stay empty for long.
- Use only chargers that match your battery type.
- Wear gloves and eye protection when working with batteries. Clean up any spills right away.
Tip: Always check your battery management system (BMS) for updates and follow the owner’s manual for best results.
Safe Operation
You must follow safety rules when using high voltage batteries. These rules protect you from electric shock, burns, and other dangers.
- Utilisation safety equipment like insulated gloves, safety glasses, and special tools.
- Make sure only trained people work on high voltage systems.
- Keep the battery area dry and clean. Do not let water or metal objects touch the battery.
- Turn off and disconnect the battery before doing any repairs.
- Watch for warning lights or alarms. If you see one, stop using the battery and check for problems.
- Follow all safety signs and instructions from the manufacturer.
- Know what to do in an emergency. Make sure first responders know how to handle high voltage batteries.
Note: Always keep your battery system within the safe temperature range, usually between 20°C and 25°C, to prevent overheating.
Troubleshooting
You may face issues with your high voltage battery system. Common problems include faulty cables, charging errors, or overheating.
- Check cables and connectors for wear, moisture, or loose parts.
- Use your BMS to monitor voltage, temperature, and charge levels.
- Watch for leaks or strange smells, which can mean a problem inside the battery.
- If the battery gets too hot, check the cooling fans and sensors.
- Use only approved diagnostic tools to test the system.
- If you see warning lights or the battery does not charge, get help from a certified technician.
If you are unsure about a problem, always ask a professional. High voltage batteries can be dangerous if handled the wrong way.
You now understand that high voltage battery systems need careful handling and the right technical specs for safe, reliable use. Always match the battery to your application for better performance and safety. Key safety steps include using protective gear, checking voltage, and following manufacturer rules. When buying, choose trusted brands and check for safety features like BMS and HVIL. For maintenance, store batteries at the right charge, inspect them often, and keep detailed records to track health and performance.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of a high voltage battery system?
You get more power and efficiency from a high voltage battery system. It lets you use thinner cables, which saves space and reduces energy loss. You also charge and discharge your devices faster.
How do you keep a high voltage battery safe?
You should always use a battery with a built-in Battery Management System (BMS). Wear safety gear, follow the manufacturer’s instructions, and never open or repair the battery yourself. If you see warning lights, stop using the battery and call a professional.
Can you use a high voltage battery outdoors?
Yes, you can use many high voltage batteries outdoors. Look for batteries with IP67 or higher ratings. These batteries resist dust and water. Always check the product label for outdoor use approval.
How long does a high voltage lithium-ion battery last?
Most high voltage lithium-ion batteries last between 5 and 10 years. The exact lifespan depends on how often you use and charge the battery. Good care and regular checks help your battery last longer.
What should you do if your battery overheats?
If your battery feels hot or smells strange, turn it off right away. Move it to a safe place. Do not touch or open the battery. Call a trained technician for help.

