
A portable battery often goes by the name ‘power bank.’ Consumers also search for terms like ‘portable battery pack.’ Knowing the right name for each battery is important. The market’s size highlights its significance:
- The global portable power bank market was valued at USD 13.48 billion in 2022.
- Projections estimate it will reach USD 31.06 billion by 2030.
Personal battery pack names

People use many names for personal charging devices. These names often describe the same product from different angles. Understanding these terms helps consumers find the right device for their needs.
The power bank
The term ‘power bank’ is the most popular name for a personal, portable battery. A power bank is a self-contained unit with a rechargeable battery and control circuitry. Its main purpose is to charge personal electronics like phones and tablets through a USB port. The internal components of a power bank are quite sophisticated.
Inside a Power Bank ⚙️ A typical power bank contains several key electronic parts:
- Charging IC: This circuit manages how the internal battery charges from a power source.
- Battery Protection IC: This vital component protects the lithium ion cells from over-voltage, under-voltage, and over-current. It prevents safety hazards.
- Voltage Boosting IC: This circuit converts the battery’s variable voltage into a stable 5V output for charging other devices.
- Integrated Power Management IC: Many modern power banks use a single chip that combines all these functions for greater efficiency.
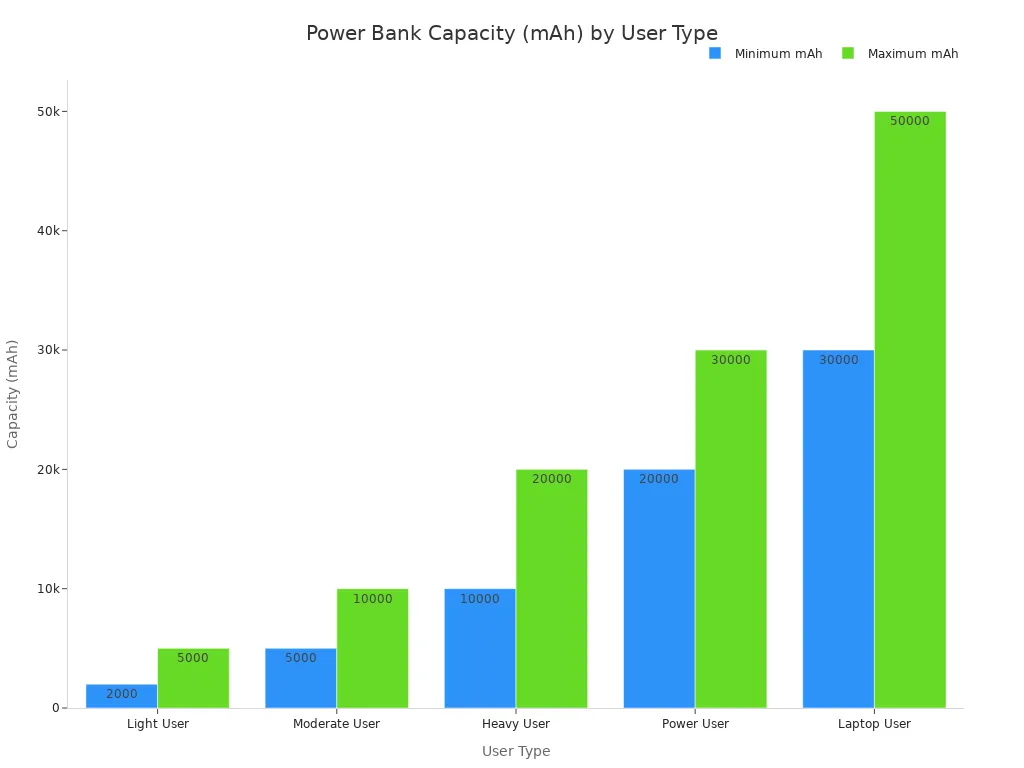
Power banks come in various capacities, measured in milliamp-hours (mAh). The right capacity depends on the user’s needs.
| User Type | mAh Range | Meilleur pour |
|---|---|---|
| Light User | 2,000-5,000 mAh | Topping off a smartphone once. |
| Moderate User | 5,000-10,000 mAh | Fully charging a smartphone 1-3 times. |
| Heavy User | 10,000-20,000 mAh | Charging multiple devices or a phone several times. |
| Power User | 20,000 mAh+ | Extended trips or powering laptops. |
Modern power banks also support fast charging. They often include advanced protocols to deliver power more quickly.
- USB-C Power Delivery (PD) is a common standard for fast charging.
- Many devices also support Qualcomm Quick Charge (QC) and other protocols.
The portable charger
The name ‘portable charger’ focuses on the device’s function: charging on the go. Marketers often prefer this term. It sounds familiar to consumers and highlights convenience. While ‘power bank’ and ‘portable charger’ often refer to the same battery pack, ‘portable charger’ can sometimes be used more broadly.
Les key difference between a portable charger and a wall charger is the power source. A portable charger uses its internal battery. A wall charger draws power directly from an electrical outlet. This distinction defines their primary use cases.
| Fonctionnalité | Wall Charger | Portable Charger (Battery-Based) |
|---|---|---|
| Source d'énergie | Electrical Outlet | Internal Battery |
| Portability | Not Portable | Highly Portable |
| Installation | Fixed Installation | No Installation Required |
| Usage Scenario | Regular use at home or office | Travel, emergencies, backup power |
External battery and other terms
‘External battery’ is another common synonym, particularly in the United States. This name accurately describes the device as a battery that operates outside of a phone or laptop. It provides an external source of power.
There are also more technical names for these devices. Scientists and engineers might use terms like ‘secondary cell’ or ‘storage battery’.
A secondary cell is any battery that is rechargeable. Its chemical reaction is reversible. An electric current can restore the battery to its original state after use. This is the core technology inside every power bank. The term ‘storage battery’ is another name for a rechargeable battery because it accumulates and stores energy.
Most power banks use a lithium ion battery. This technology offers good energy density for its weight. Other rechargeable battery chemistries exist, such as nickel cadmium and nickel metal hydride, but they are less common in modern power banks. A power bank contains at least one battery cell, which is the fundamental unit that stores power.
High-capacity battery types
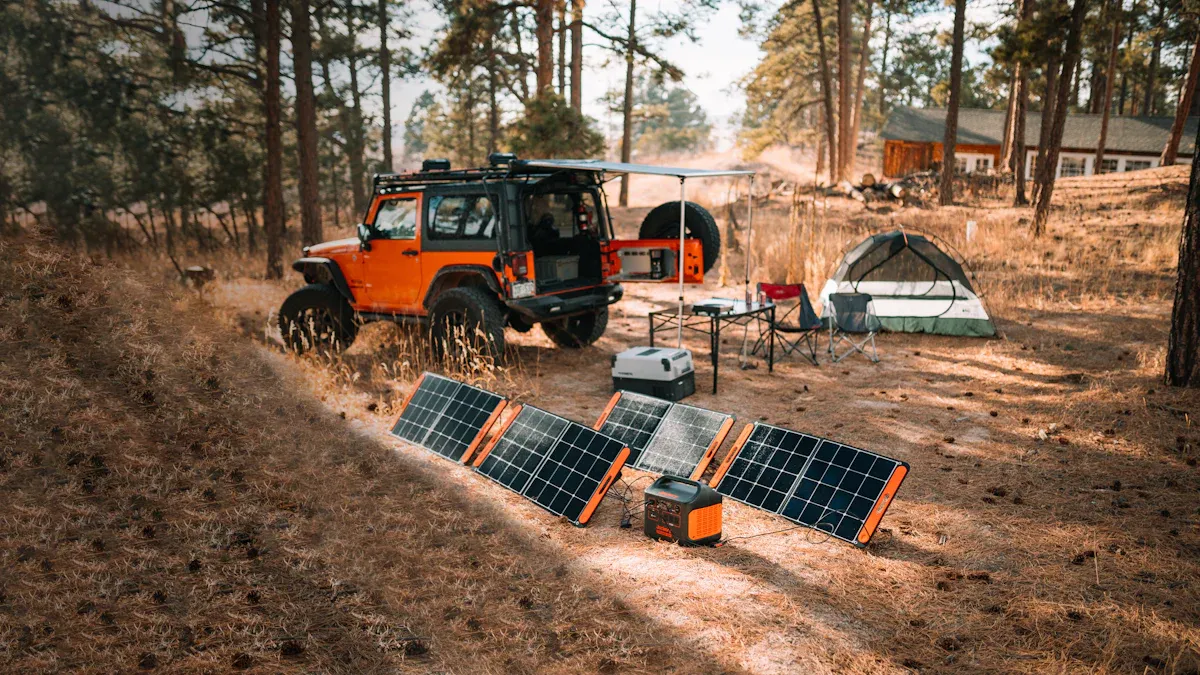

While smaller, portable chargers are great for personal devices, larger power needs require more robust solutions. These high-capacity units are often called power stations or generators, and they serve a different purpose than their pocket-sized counterparts.
Portable power station
A portable power station (PPS) is a significant step up from a standard power bank. It’s a larger, rechargeable battery-powered generator designed to power a wide range of devices, from smartphones to small appliances. Think of it as a mobile power outlet for situations where traditional power isn’t available.
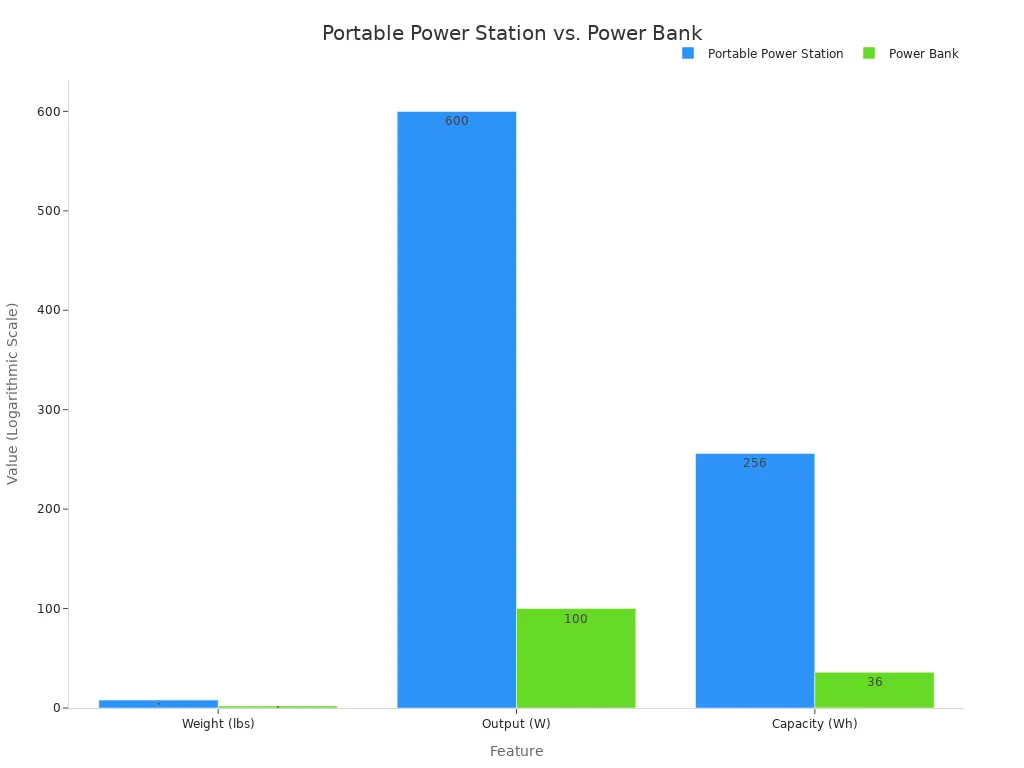
The primary difference between a power bank and a portable power station lies in their capacity, output power, and versatility.
| Fonctionnalité | Portable Power Station (PPS) | Power Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Weight/Size | Larger, heavier (e.g., 8 lbs, size of a boombox stereo) | Smaller, lighter (e.g., less than 2 lbs) |
| Output | High-wattage appliances (e.g., up to 600W for refrigerators, TVs, blenders) | Smaller devices (e.g., smartphones, laptops, tablets) |
| Capacité | Larger (e.g., up to 256Wh) | Smaller (e.g., 2,000-10,000mAh, or 36Wh) |
| Recharging | Multiple options, including solar charging | Primarily relies on grid electricity |
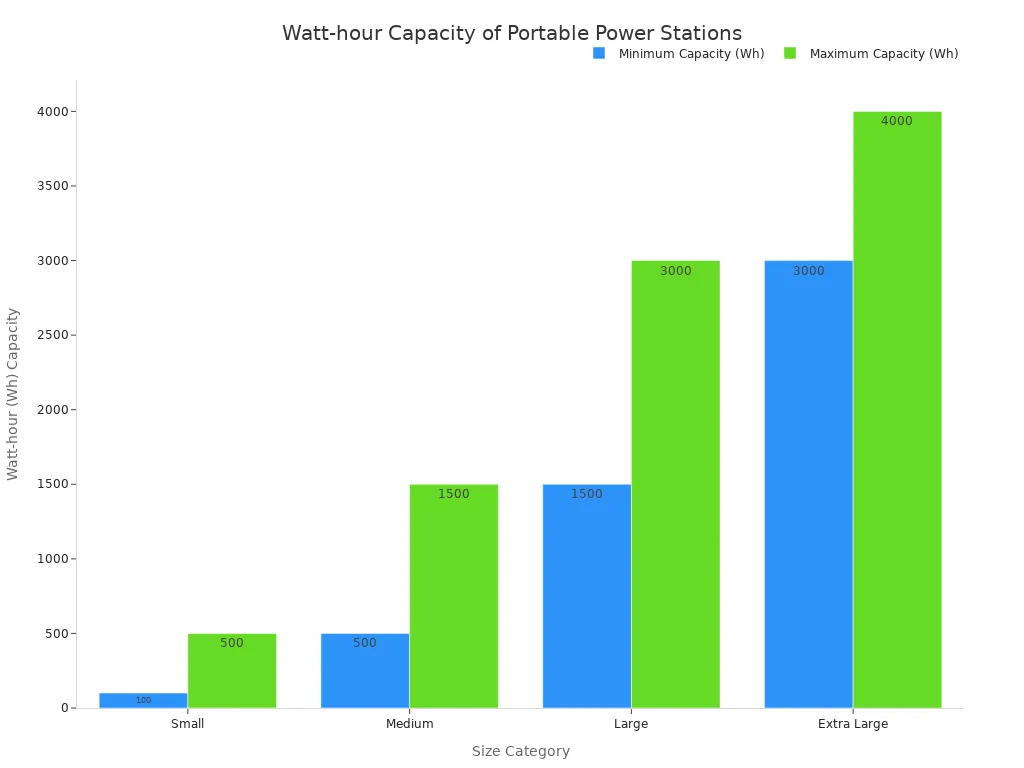
These stations come in various sizes, with their capacity measured in Watt-hours (Wh). This unit indicates how many watts a battery can supply for one hour.
| Size Category | Watt-hour (Wh) Capacity Range |
|---|---|
| Small | 100-500Wh |
| Moyen | 500-1500Wh |
| Large | 1500-3000Wh |
| Extra Large | 3000Wh+ |
A key feature of a portable power station is its variety of output ports. Most include standard AC wall outlets, DC car sockets, and multiple USB ports. This allows them to power a wide range of electronics and appliances.
| Port Type | Tension | Max Power (per port) | Utilisations courantes |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC Barrel | 12 V regulated | 120 W (10 A) | Fridges, routers, radios |
| Car Socket | 12 V regulated | 120 W (10 A) | Auto accessories |
| AC Pure Sine | 230/120 V | Varies by model (e.g., 600–2400 W) | Tools, power bricks, appliances |
These features make them incredibly useful in many situations:
- Camping and Outdoor Adventures: Powering lights, phones, cameras, laptops, fans, speakers, and portable refrigerators.
- RV and Van Life: Supplying electricity for cooking appliances, lighting, electronics, water pumps, and CPAP machines, especially when paired with solar panels for off-grid living.
- Emergency Home Backup: Keeping essential devices like Wi-Fi routers, medical equipment, smartphones, LED lights, and small appliances operational during power outages.
- Work on the Go: Providing power for tools, monitors, laptops, and recording equipment for professionals like photographers, filmmakers, and contractors in locations without traditional outlets.
Solar generator
A solar generator is essentially a portable power station bundled with solar panels. This combination creates a self-sustaining power system. The term “generator” can be a bit misleading, as it doesn’t create energy from fuel like a gas generator. Instead, it captures and stores solar energy.
The system works in a few simple steps:
- Capture: Solar panels, made of photovoltaic (PV) cells, absorb sunlight. This process excites electrons within the cells, generating a direct current (DC) of electricity.
- Store: The DC electricity flows to the battery pack, which is a rechargeable battery system. A charge controller manages this process, ensuring the battery charges safely and efficiently.
- Convert & Use: When you need power, an internal device called an inverter converts the stored DC power into alternating current (AC) power. This is the standard electricity used by most household appliances.
The main advantage of a solar generator is its ability to recharge using sunlight, making it ideal for off-grid living or extended power outages. The charging speed depends on the wattage of the solar panels and the amount of available sunlight. A cloudy day, for example, will significantly reduce the charging rate.
Battery module
A battery module is a fundamental building block of larger power systems, including some high-capacity portable power stations and electric vehicles. It is not a consumer product on its own but rather a component within a larger assembly.
A module consists of multiple individual battery cells, often lithium-ion, connected to increase the overall voltage and capacity. These cells are arranged in series, parallel, or a combination of both to achieve the desired power output.
Inside a Battery Module:
- Battery Cells: The basic units that store energy. Most modern systems use lithium-ion or lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cells. Older technologies like nickel cadmium or nickel metal hydride are less common now.
- Système de gestion de la batterie (BMS) : This is the brain of the battery. The BMS monitors the health, temperature, and charge of each cell. It protects the battery from overcharging, overheating, and deep discharging, which ensures both safety and a long lifespan.
- Housing: A protective case that holds the cells and electronics together.
These modules are designed to be scalable. You can connect multiple battery modules to create a larger battery pack with more energy storage. This modularity is crucial for applications like home energy storage systems, where you might want to expand your capacity over time, and for electric vehicles, where a large, powerful battery is essential for range and performance.
A power bank is a small battery for personal devices. A portable power station is a large battery for appliances. While any rechargeable battery is technically a ‘storage battery,’ common names describe function. This knowledge helps people confidently identify the right battery pack for their needs and choose the best battery.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a power bank and a portable power station?
A power bank is a small battery for personal devices like phones. A portable power station is a large battery. It powers bigger items like small appliances. The station’s battery offers much more energy.
Can I take any battery on an airplane?
Airlines have strict rules for lithium-ion batteries. Passengers must carry spare batteries in their carry-on bags. The batteries must be under a certain size limit for safety.
Why are some batteries called “solar generators”?
A solar generator is a portable power station that comes with solar panels. This type of battery system captures and stores the sun’s energy. It does not burn fuel like a traditional generator.

