
When you use a 18650 lithium-ion battery, you must follow the safe operating voltage range of 2.5V to 4.2V per cell. Major manufacturers set this voltage window to keep your battery safe and working well. If you let your battery voltage drop too low or climb too high, you risk damaging the battery or causing safety problems. Most 18650 batteries have a nominal voltage of about 3.6V or 3.7V. Staying within the safe operating voltages helps prevent issues like overheating, fire, or reduced battery life. Different lithium-ion chemistries and brands can have small changes in their recommended voltage limits, so always check your battery’s guidelines.
Safe Operating Voltage for 18650

Minimum and Maximum Thresholds
You need to know the safe operating voltage for your 18650 battery. Most 18650 lithium-ion batteries have a safe operating voltage range from 2.5V to 4.2V per cell. This range keeps your battery safe and helps it last longer. If you let the battery voltage drop below the minimum voltage or rise above the maximum voltage, you can damage the battery or cause safety problems. The minimum voltage threshold is usually 2.5V, and the maximum voltage is 4.2V for most lithium-ion chemistries.
Conseil : Always check your battery’s datasheet or label for the exact voltage range of a li-ion battery cell. Some brands may have slightly different limits.
Voici un tableau montrant les common 18650 battery voltage limits for different chemistries:
| Type de chimie | Tension nominale (V) | Maximum Charging Voltage (V) | Minimum Discharge Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide) | 3.6 – 3.7 | 4.2 | 2.5 |
| LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | ~3.2 | ~3.65 | 2.0 (recommended not below 2.5) |
You can see that the safe operating range depends on the chemistry. For NMC, the voltage range of a li-ion battery cell is 2.5V to 4.2V. For LFP, the range is about 2.5V to 3.65V. Always stay within the safe operating voltage to protect your battery.
Tension nominale
Les nominal voltage of a li-ion battery is the average voltage the battery holds during normal use. For most 18650 cells, the nominal voltage is 3.6V or 3.7V. This value helps you compare batteries and design devices that use them. The nominal voltage of a li-ion battery does not show the highest or lowest voltage. Instead, it shows the middle point where the battery spends most of its time during discharge.
- NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide): 3.6V
- LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate): 3.2V
- LiCoO2 (Lithium Cobalt Oxide): 3.7V
- LiMn2O4 (Lithium Manganese Oxide): 4.0V
When you look at the relationship between 18650 battery voltage and soc (state of charge), the nominal voltage is where the battery is about half full. The fully charged voltage is higher, usually 4.2V, and the battery voltage drops as you use the battery. The common 18650 battery voltage you see in devices is close to the nominal voltage during most of the battery’s life.
Chemistry Variations
Not all 18650 batteries use the same chemistry. The chemistry changes the voltage range of a li-ion battery cell and affects how you use the battery. NMC and LFP are two popular types. NMC cells have a higher maximum voltage, up to 4.2V, and a nominal voltage of 3.6V to 3.7V. LFP cells have a lower maximum voltage, about 3.65V, and a nominal voltage of 3.2V.
Voici un table to help you compare:
| Chimie | Tension nominale (V) | Operating Voltage Range (V) |
|---|---|---|
| NMC | 3.6 – 3.7 | 2.5 – 4.2 |
| LFP | 3.2 – 3.3 | 2.5 – 3.65 |
You should always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the safe operating voltage. Panasonic, LG, and Samsung suggest a nominal voltage of 3.6V or 3.7V, a full charge at 4.2V, and a minimum voltage between 2.5V and 3.0V. If you want your battery to last longer, try to keep the battery voltage between 3.0V and 4.0V. This helps extend the life of your 18650 lithium-ion battery.
The relationship between 18650 battery voltage and soc is important. When the battery voltage is near the maximum, the battery is almost fully charged. When the battery voltage is near the minimum, the battery is almost empty. By staying within the safe operating voltage, you keep your battery safe and working well.
Why Safe Operating Voltages Matter
When you use a 18650 battery, you must pay close attention to the battery voltage. Staying within the safe operating voltages keeps you and your devices safe. If the voltage exceeds 4.2V or drops below the minimum voltage, you risk damaging the battery and creating safety hazards.
Overcharging Risks
Charging your 18650 battery above the maximum voltage can cause serious problems. When the voltage exceeds 4.2V, the battery faces several dangers:
- The battery temperature rises because the electrolyte breaks down at the electrodes.
- Extra lithium ions leave the cathode, which can release oxygen and make the battery unstable.
- Lithium dendrites form on the anode, increasing the chance of short circuits and overheating.
- Overheating can lead to battery rupture or even fire.
- Overcharging damages the electrode materials and causes perte de capacité.
- The battery’s internal resistance increases, making it harder for lithium ions to move.
- The battery produces gases that reduce thermal stability and increase pressure inside the cell.
- Overcharging often happens when the système de gestion de la batterie fails or you use the wrong charger.
You should always use a charger designed for 18650 batteries and check that your battery management system works properly. These safety considerations help prevent overcharging and keep your battery voltage in the safe range.
Over-Discharging Risks
Letting your 18650 battery voltage drop below the minimum voltage can also cause harm. Over-discharging leads to:
- Irreversible capacity loss because the battery loses active lithium and the anode degrades.
- The battery’s internal resistance increases, making it less efficient.
- The copper current collector can dissolve and deposit on the anode, which fades capacity.
- The battery’s structure changes, and the electrolyte breaks down.
- Over-discharge can cause internal short circuits, which may trigger thermal runaway and even fire.
- The battery can lose up to 25% of its capacity if you discharge it too far.
- High-rate discharge increases heat and can damage the battery’s structure.
To avoid these risks, you should never let your battery voltage fall below the recommended minimum. Always follow safety considerations and use a battery management system to protect your battery.
Battery Performance and Safety
Keeping your 18650 battery voltage within the safe operating voltages helps your battery last longer and work better. Studies show that charging to the recommended maximum voltage of 4.2V gives you the best capacity retention and slows down battery aging. Charging above this voltage, such as when the voltage exceeds 4.2V, causes faster capacity loss and shortens the battery’s life.
| Charge Cut-Off Voltage (CCOV) | Capacity Retention at 180th Cycle | Cycle Life Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 4.2 V | 97.5% | Best retention, slower degradation |
| 4.3 V | 84.5% | Faster capacity loss |
| 4.4 V | 67.3% | Rapid degradation |
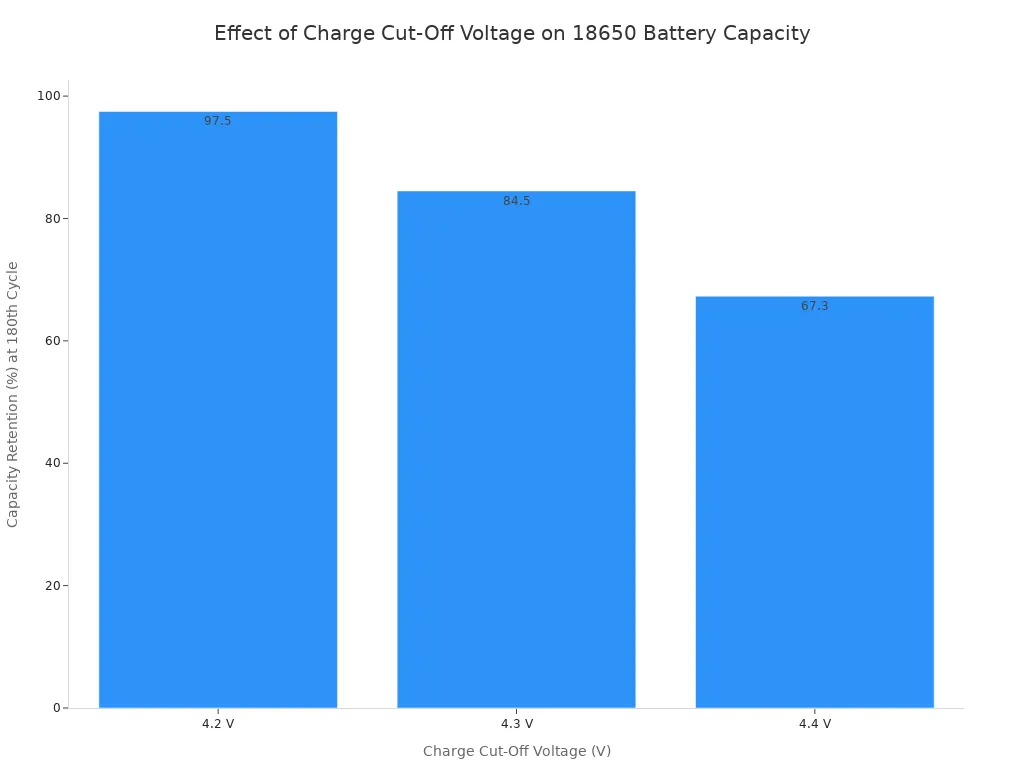
When you keep the battery voltage in the safe range, you avoid safety problems and get more cycles from your battery. Using a quality charger and a working battery management system helps you maintain the right voltage and protect your battery from overcharge or over-discharge. This way, you keep your devices safe and your battery working well for a long time.
Factors Affecting Safe Operating Voltage Range
Chimie des batteries
You will notice that the chemistry of your battery plays a big role in its safe operating voltage. Different lithium-ion chemistries have different voltage ranges. For example, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries have a nominal voltage of about 3.2V, while NMC and NCA batteries have a nominal voltage closer to 3.6V or 3.7V. Les safe voltage range for most 18650 batteries is between 2.5V and 4.2V. If you go above 4.2V, you risk electrolyte breakdown and thermal runaway. If you drop below 2.5V, you can cause permanent chemical damage. Battery Management Systems (BMS) help keep the voltage within these safe limits. Always check the technical datasheet for your battery to find the exact voltage range.
| Chimie | Tension nominale | Tension maximale | Discharge Plateau | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiFePO4 | ~3.2 V | ~3.6 V | 3.2–3.3 V | Solar, UPS |
| NMC/NCA | 3.6–3.7 V | 4.2 V | Modéré | Power tools, EVs |
| IMR | 3.6–3.7 V | 4.2 V | Flatter | High-drain devices |
Effets de la température
Temperature changes can affect the safe voltage range of your lithium-ion battery. Cold temperatures, like 0°C or below, increase the battery’s internal resistance. This makes the voltage drop faster under load and can lead to lithium plating, which is a safety risk. High temperatures, above 45°C, can make the voltage rise slightly but also speed up battery aging. Charging your battery in freezing conditions can cause dangerous reactions and lower the safety margin. You should use a BMS that monitors both voltage and temperature. This helps adjust the voltage cut-offs and keeps your battery safe in different environments.
- Cold weather can make the 18650 battery voltage change more quickly.
- High heat can shorten the battery’s life and reduce safety.
- Always use batteries rated for your climate and follow manufacturer guidelines.
Âge de la batterie
As your battery ages, its safe voltage range can get smaller. Each charge and discharge cycle puts stress on the battery. High energy chemistries like NMC can lose capacity faster if you always charge to 4.2V or discharge below 3.0V. More stable chemistries, like LiFePO4, handle aging better but still need care. Over time, the 18650 battery voltage change becomes more noticeable. To keep your battery healthy, avoid full charges and deep discharges. Try to keep the voltage between 3.2V and 3.8V as the battery gets older. This helps maintain safety and extends the battery’s life.
Remarque : Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for voltage and safety, especially as your battery ages or if you use it in extreme temperatures.
Monitoring the Voltage Range of a Li-Ion Battery Cell

Keeping your lithium-ion battery safe means you must watch the voltage closely. You have several ways to check and maintain the right voltage range of a li-ion battery cell. Each method helps you protect your battery and get the best performance.
Using a Multimeter
A digital multimeter gives you a simple way to check the battery voltage. To use it, set the multimeter to DC volts. Touch the red probe to the positive terminal and the black probe to the negative terminal. You will see the lithium-ion battery cell voltage on the display. This method works well for single cells or when you want a quick check. For more accurate and real-time results, continuous monitoring of terminal voltage and current is best. Advanced methods like the ECBE technique can estimate the state of charge and battery health in real time, but most users rely on a multimeter for basic checks.
Conseil : Always measure the battery voltage when the battery is at rest. This gives you a more accurate reading.
Systèmes de gestion des batteries (BMS)
A Système de gestion de la batterie, or BMS, keeps your lithium-ion battery safe by watching each cell’s voltage. The BMS uses sensors to check the lithium-ion battery cell voltage in real time. If any cell goes above or below the safe voltage, the BMS disconnects the charge or discharge circuit using special switches. The BMS also balances the voltage between cells. It can move extra charge from one cell to another or release it as heat. This keeps all cells at a similar voltage and prevents overcharging or over-discharging. The BMS acts as a safety guard, stopping problems before they start.
- Monitors each cell’s voltage and keeps it in the safe range
- Disconnects the battery if voltage goes too high or too low
- Balances charge between cells for longer battery life
Charger Selection
Choosing the right charger is important for safety and battery health. Smart chargers control the voltage and current during charging. They use two main stages: constant current (CC) and constant voltage (CV). The charger first sends a steady current until the battery voltage reaches about 4.2V. Then, it holds the voltage steady while the current drops. Charging stops when the current falls below a set level. Good chargers have features like protection contre les surcharges, short circuit protection, and temperature monitoring.
| Fonctionnalité | Description |
|---|---|
| Protection contre les surcharges | Stops charging if voltage goes above safe limit |
| Protection contre les courts-circuits | Prevents damage if a short happens |
| Temperature Monitoring | Arrêt de la charge si la batterie devient trop chaude |
| Adjustable Voltage/Current | Lets you set safe limits for your battery |
| LCD Display | Shows real-time battery voltage and charging status |
Remarque : Always use a charger made for lithium-ion batteries. This helps you keep the lithium-ion battery cell voltage in the safe range and protects your battery from damage.
Best Practices for 18650 Safe Operating Voltage
Maintenance Tips
You can keep your 18650 batteries safe and reliable by following a few simple steps. Always use protected 18650 batteries with built-in safety circuits. These circuits help prevent overcharging and over-discharging, which are the most common causes of battery failure. Choose chargers that match the battery voltage and are designed for 18650 cells. Avoid using poor-quality or incompatible chargers, as they can cause unsafe voltage conditions and damage your battery.
- Store your batteries at room temperature, between 20°C and 25°C.
- Keep batteries away from moisture and extreme heat or cold.
- Charge your batteries in a safe area and monitor the temperature during charging.
- Store batteries at about 50% charge, which is around 3.7V, for long-term storage.
- Use your batteries regularly to prevent deep discharge.
- Inspect batteries for swelling or damage before each use.
- Match batteries in multi-cell devices to keep voltage balanced.
Conseil : Never try to jump-start a deeply discharged 18650 cell. This can cause fire or explosion.
Maximizing Battery Lifespan
You can extend the life of your 18650 battery by managing the charge and discharge voltages carefully. The best charge voltage for a 18650 battery is slightly below the standard maximum. Charging up to 4.0V or 4.1V per cell, instead of 4.2V, greatly increases cycle life, even though it reduces capacity a little. For discharge, set the cutoff voltage higher than the lowest safe limit. Try to avoid dropping below 2.8V to 3.0V per cell. These small changes reduce stress on the battery and help maintain stable battery voltage over time.
Laboratory tests show that keeping your battery at a mid-state-of-charge, around 60%, and using shallow discharge cycles can extend the battery’s life up to 21 times compared to full cycles. Periodic full charges to 4.2V every 10 to 15 cycles help restore capacity. Avoid deep discharges and high charge rates, as these increase internal resistance and shorten lifespan.
Keeping your battery voltage within safe limits is the best way to prevent failure and get the most out of your 18650 batteries.
You protect your battery and improve safety by keeping the voltage between 2.5V and 4.2V. Regularly check your battery with a multimeter or use a battery management system for extra safety. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid damage and reduce fire risks. Using the right charger et storing your battery at about half charge helps extend its life. Make safety your top priority and handle every battery with care.
FAQ
What happens if you overcharge a 18650 battery?
Overcharging a 18650 battery can cause it to overheat. You may see swelling or even fire. Always use a charger with overcharge protection to keep your battery safe.
Can you use any charger for 18650 batteries?
You should only use chargers made for 18650 lithium-ion batteries. Other chargers may not control voltage correctly. This can damage your battery or cause safety problems.
How do you know when to stop discharging a 18650 battery?
Stop using your battery when the voltage drops to about 2.8V to 3.0V. Going lower can damage the battery. Many devices and battery management systems cut off power at this safe level.
Is it safe to store 18650 batteries fully charged?
You should not store 18650 batteries fully charged. Store them at about 50% charge, which is around 3.7V. This helps your battery last longer and stay safe.

