
The main lifepo4 battery series types include prismatic, cylindrical, pouch, and button cells. Each offers unique advantages for specific applications, such as electric vehicles, energy storage, and portable devices. Understanding lifepo4 battery series helps users maximize safety, performance, and lifespan. For example, lithium iron phosphate batteries show superior thermal stability and cycle life, making them ideal for high-risk environments. The key benefits of lifepo4 lithium batteries include reliable power, enhanced safety, and long-term value. Knowledge of these series types allows users to choose the right lithium lifepo4 battery for their needs.
Series Type Description Applications typiques Prismatic Cells Space-optimized, high capacity Electric vehicles, storage Cylindrical Cells Durable, robust power delivery Power tools, electronics Pouch Cells Lightweight, customizable Laptops, EVs, portable gear Button Cells Small, high energy density Watches, medical devices
LiFePO4 Battery Series Overview
What Is a LiFePO4 Battery Series?
A lifepo4 battery series refers to a group of lithium iron phosphate cells connected end-to-end. This configuration increases the total voltage while keeping the current capacity the same as a single cell. In a series connection, the positive terminal of one cell links to the negative terminal of the next. For example, connecting four 3.2V lifepo4 batteries in series creates a 12.8V battery pack. This method is common in applications that require higher voltage, such as electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
In contrast, a parallel connection links all positive terminals together and all negative terminals together. This setup keeps the voltage the same as a single cell but increases the total amp-hour capacity and current output. Both series and parallel configurations play a vital role in the functionalities of lifepo4 batteries. Using batteries of the same type, voltage, and capacity in each configuration prevents imbalance and extends battery life.
Conseil : Always use matched lifepo4 batteries in any configuration to avoid premature failure or damage.
| Aspect | Série Connexion | Connexion en parallèle |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Method | Positive terminal of one battery connected to negative terminal of the next in sequence | All positive terminals connected together and all negative terminals connected together |
| Tension | Total voltage is the sum of all batteries’ voltages (increases voltage) | Voltage remains the same as a single battery |
| Current | Current remains the same as a single battery | Total current capacity increases (increases current and capacity) |
| Objectif | Used to achieve higher voltage for devices requiring it | Used to increase capacity and current output for longer usage or higher current demand |
| Example | Four 3.2V LiFePO4 cells in series produce 12.8V (3.2V * 4) | Five 51.2V 200Ah batteries in parallel produce 51.2V 1000Ah (capacity sums up) |
| Avantages | Increases voltage without changing current; simple wiring; no need for voltage converters | Increases current and capacity; voltage remains constant; can continue operation if one battery fails |
| Practical Note | Suitable for devices needing higher voltage; current limited to single battery rating | Suitable for devices needing longer runtime or higher current; voltage must match battery specifications |
Why Series and Parallel Matter
The way lifepo4 batteries connect—either in series, parallel, or both—directly affects their voltage, capacity, and application. Series connections add the voltages of individual lithium iron phosphate cells, making them essential for high-voltage devices like electric vehicles, drones, and power tools. Parallel connections keep the voltage steady but boost the amp-hour capacity, which extends runtime and reduces stress on each battery.
Many energy storage systems use a combination of series and parallel connections. This approach allows designers to tailor battery packs for both higher voltage and increased capacity. For example, a 4S2P configuration means four cells in series and two in parallel, balancing voltage and capacity for specific needs.
- Series connections reduce current for the same power output, which allows for smaller wiring and better efficiency. This feature is important in weight-sensitive applications like drones.
- Parallel connections share the current load among cells, lowering heat and improving the lifespan of lifepo4 batteries.
- Battery management systems (BMS) are crucial in these setups. They balance the cells and protect against overcharge or over-discharge, ensuring safety and long life.
Understanding the different series of lifepo4 batteries helps users select the right configuration for their application, whether for energy storage, electric vehicles, or portable devices. Lifepo4 technology offers flexibility, safety, and reliability, making it a top choice in modern battery design.
Main Types of LiFePO4 Batteries

Cylindrical LiFePO4 Cells
Cylindrical LiFePO4 cells have a round shape and a metal casing. Manufacturers often use sizes like 18650 and 21700. These batteries deliver high current bursts, making them ideal for electric scooters, wheelchairs, and power tools. They also help stabilize power in solar systems during short-term fluctuations.
Key features of cylindrical LiFePO4 batteries:
- High energy density and compact form.
- Strong metal casing for mechanical stability.
- Efficient heat dissipation, which reduces overheating.
- Easier and cheaper to manufacture due to mature technology.
| Fonctionnalité | Description |
|---|---|
| Durée de vie | 300–500 cycles, shorter than prismatic cells |
| Poids | Heavier due to steel casing |
| Space Utilization | Less efficient; gaps between cells |
| Applications | Laptops, e-bikes, power tools, portable devices |
Avantages :
Cylindrical LiFePO4 batteries offer reliable performance, strong protection, and flexible arrangements for small-capacity packs. They are safer because damage to one cell rarely affects the whole pack.
Limites :
These batteries are heavier and less space-efficient. Assembly can be complex due to many spot welds. Large packs require many cells, which increases failure risk.
Prismatic LiFePO4 Batteries
Prismatic LiFePO4 batteries use a flat, rectangular design with aluminum or steel casing. This shape allows for better space use and higher energy storage. They provide excellent safety, long cycle life, and stable performance across temperatures.
Typical applications include:
- Electric vehicles
- Renewable energy storage systems
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS)
- Industrial and grid storage
Avantages :
Prismatic LiFePO4 batteries have a long lifespan, often lasting over 2,000 cycles. Their space-efficient design supports larger capacity and better performance in electric vehicles. They also offer superior thermal stability and consistent voltage.
Limites :
These batteries cost more to manufacture. They are less suitable for small devices and have limited high discharge current. The initial price can be higher for consumers.
Pouch LiFePO4 Cells
Pouch LiFePO4 cells use a flexible aluminum-laminated pouch instead of a rigid case. This design makes them lightweight and adaptable to many shapes. They are common in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and portable power stations.
Main characteristics:
- High energy density for compact devices
- Flexible form factor for custom designs
- Excellent safety with reduced explosion risk
- Long cycle life, sometimes over 6,000 cycles
Avantages :
Pouch LiFePO4 batteries are up to 40% lighter than cylindrical types. Their flexible design fits irregular spaces. They are cost-effective and safe for many uses.
Limites :
These batteries lack rigid protection, making them more sensitive to damage. They may swell if overcharged and have lower structural strength than other types.
Choosing the right type from the different series of lifepo4 batteries depends on the application’s needs for weight, space, safety, and cost.
LiFePO4 Battery Series Configurations
12V, 24V, and 48V Series
LiFePO4 battery packs often come in 12V, 24V, and 48V series. Each voltage series fits different power needs and applications.
- 12V LiFePO4 battery packs work well for RVs, trolling motors, portable solar systems, and small off-grid cabins.
- 24V batteries suit larger solar energy systems, electric bikes, and small to medium boats.
- 48V batteries handle high-power demands in off-grid solar, electric vehicles, and industrial equipment.
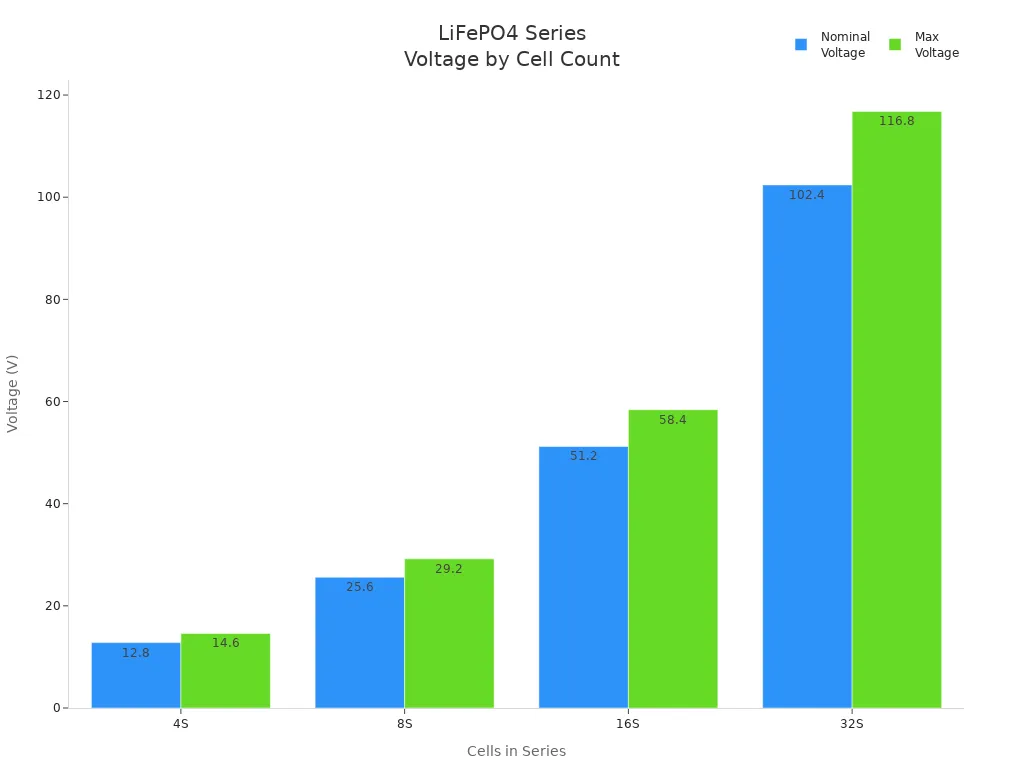
These voltage series match nominal voltages of about 12.8V, 25.6V, and 51.2V. Choosing the right series helps optimize efficiency and lifespan for each application.
| Voltage Series | Tension nominale (V) | Typical Charging Voltage Range (V) | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12V | ~12.8 | 14.2 – 14.6 | RVs, trolling motors, portable solar, small cabins |
| 24V | ~25.6 | 28.4 – 29.2 | Larger solar, e-bikes, small to medium boats |
| 48V | ~51.2 | 56.8 – 58.4 | Off-grid solar, electric vehicles, industrial equipment |
A 12V LiFePO4 battery is ideal for home solar systems and smaller setups. The 24V series offers a balance between power and compactness for medium-sized installations. The 48V series reduces amperage, saving on wiring and equipment costs in high-power systems.
Series vs. Parallel Connections
Series and parallel connections change how batteries perform. Series connections increase voltage while keeping capacity the same. This setup is necessary for systems that need higher voltage, such as 24V or 48V power systems. However, if one cell fails in a series, the whole battery pack can lose voltage and stop working.
Parallel connections keep voltage the same but increase capacity. This means more energy storage and longer run times. Parallel setups also improve redundancy. If one battery fails, the system can still work. Many designers combine series and parallel connections to customize voltage and capacity for each application. Proper battery management systems (BMS) are essential to keep all batteries balanced and safe.
| Connection Type | Effect on Voltage | Effect on Capacity | Avantages | Inconvénients | Considérations de sécurité |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Series | Increases | Same as single | High voltage, simple wiring, better efficiency | Single-point failure risk, needs balancing | One cell failure affects all; balancing needed |
| Parallel | Same as single | Increases | More storage, better redundancy, balanced current | Complex wiring, possible uneven charge/discharge | Safer discharge, less critical failure, needs matching |
Voltage and Capacity Considerations
Configuring LiFePO4 battery packs requires careful attention to voltage and capacity. Each series configuration matches a specific nominal voltage. For example, a 4S pack gives about 12.8V, while a 16S pack gives about 51.2V. These voltages fit standard equipment and help maintain efficiency. The voltage of a battery pack changes with its state of charge, so monitoring voltage helps estimate remaining capacity.
Combining series and parallel connections allows users to build packs for both high discharge series and deep cycle series needs. Voltage balance among cells is critical. A battery management system protects against overcharge and deep discharge. As the number of batteries in series increases, thermal management becomes more important. Regular monitoring of voltage, temperature, and state of charge ensures long life and safe operation.
Tip: Always match batteries by type, capacity, and age to maximize efficiency and safety in any configuration.
Applications of LiFePO4 Batteries

LiFePO4 batteries serve a wide range of applications due to their safety, long cycle life, and stable performance. These batteries power everything from home energy storage systems to electric vehicles and medical devices. The following sections highlight the most common uses and the best battery configurations for each area.
Energy Storage Systems
Energy storage systems rely on lifepo4 batteries for reliable backup and grid support. These batteries offer excellent thermal stability and a long lifespan, making them ideal for residential and commercial setups. Most energy storage systems use a combination of series and parallel connections to achieve the required voltage and capacity. A battery management system (BMS) ensures safe operation by balancing cell voltages and protecting against overcharge or deep discharge. Homeowners and businesses choose lifepo4 batteries for solar energy storage, off-grid cabins, and backup power because of their efficiency and safety.
| Configuration Type | Effect on Voltage | Effect on Capacity | Suitable Applications | Avantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Series | Increases voltage | Same as single | Large solar arrays, RVs, boats | Higher voltage output, efficient power transfer | Needs balanced BMS |
| Parallel | Same as single | Increases | Solar energy storage, longer run time | Increased capacity, longer run time | Needs careful balancing |
| Combined | Increases both | Increases both | Off-grid solar, industrial use | Flexibility, meets complex needs | Complex design |
Note: The Asia-Pacific region leads the market for energy storage systems using lifepo4 batteries, driven by renewable energy projects and strong demand for reliable backup power.
Electric Vehicles and Mobility
Electric vehicles depend on lifepo4 batteries for safe, efficient, and long-lasting power. These batteries provide stable voltage, high cycle life, and strong thermal stability. Manufacturers use lifepo4 battery packs in electric cars, buses, bikes, and scooters. The most common configurations are high-voltage series packs, which deliver consistent power and range. Lifepo4 batteries also support fast charging and low maintenance, making them a top choice for sustainable mobility.
- Safety and chemical stability protect users and vehicles.
- High cycle life supports years of daily use.
- Consistent power output ensures reliable vehicle performance.
Marine and RV Power
Marine and RV power systems require batteries that can handle deep cycling, harsh environments, and long trips. Lifepo4 batteries excel in these conditions due to their robust design and deep cycle capability. Popular models include 12V and 24V series, which power trolling motors, appliances, and lighting. Integrated BMS units add safety and extend battery life. Lightweight and compact lifepo4 batteries fit well in boats and RVs with limited space.
Tip: Choose lifepo4 batteries with the right voltage and capacity for your marine or RV setup to maximize efficiency and minimize maintenance.
Solar and Off-Grid Uses
Solar and off-grid applications benefit from lifepo4 batteries because of their modular design and high energy density. Rack-mounted battery systems allow easy expansion and fit well in remote homes, cabins, and microgrids. These batteries support rapid charge and discharge, making them suitable for both daily use and backup power. A BMS monitors voltage, current, and temperature, ensuring safe operation even in extreme environments.
- Remote homes and cabins achieve energy independence.
- Industrial monitoring stations and telecom towers rely on lifepo4 batteries for continuous power.
- Community microgrids use scalable battery racks for reliable electricity.
Tools and Medical Devices
Lifepo4 batteries power a variety of tools and medical devices that require stable and safe energy. These batteries meet strict safety and performance standards, such as ANSI/AAMI ES 60601-1 and IEC 62133. Certified lifepo4 battery packs provide reliable power for portable medical equipment, dental tools, and electric wheelchairs. Their long lifespan and low self-discharge make them ideal for critical applications where failure is not an option.
- Medical device batteries must comply with international safety standards.
- Certified lifepo4 batteries ensure safe operation and reliable performance.
- Professional manufacturers supply tested and approved battery packs for sensitive uses.
Lithium batteries lifepo4 used for tools and medical devices offer unmatched safety, reliability, and long-term value.
How to Choose the Right Lithium LiFePO4 Battery
Selecting the best lifepo4 battery for any application requires careful planning and attention to detail. The following step-by-step guide helps users match battery specifications to their needs, ensuring safety, efficiency, and longevity.
Assessing Voltage and Capacity Needs
Understanding voltage and capacity requirements forms the foundation of choosing the right battery. Each application demands a specific voltage and energy storage level. Matching these parameters prevents inefficiency and extends the battery’s long lifespan.
- Identify the power requirement of the device or system. Determine if the application needs low, moderate, or high power.
- Calculate the total energy demand in watt-hours (Wh) or amp-hours (Ah).
- Select a lifepo4 battery with a voltage that matches the system’s input. For example, solar inverters and electric vehicles often require 12V, 24V, or 48V packs.
- Choose a capacity that supports typical usage patterns and peak loads.
- Ensure the battery’s charging and discharging rates align with the system’s needs.
Conseil : Always select deep cycle lifepo4 batteries that match the application’s voltage and capacity. Using the wrong battery can cause poor performance or early failure.
- Capacity must match the device’s power consumption and expected runtime.
- Voltage compatibility with system components, such as inverters, is essential for seamless operation.
- Charging and discharging rates affect both performance and longevity.
Properly charge a lifepo4 battery to maintain efficiency and avoid overcharging or undercharging. Regular monitoring of voltage differences between cells, keeping them within 50mV, helps extend battery life.
Considering Size, Weight, and Form Factor
Physical dimensions and weight play a crucial role in battery selection. Lifepo4 batteries come in various shapes, including cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch cells. Each form factor suits different installation spaces and mobility requirements.
- Measure the available space in the device or system before purchasing.
- Lightweight batteries are ideal for portable or mobile applications, such as AGVs or portable energy storage units.
- For stationary systems, prioritize capacity and durability over weight.
- Always check product specifications for size and weight to ensure a proper fit.
| Facteur de forme | Typical Use Cases | Size Considerations | Weight Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cylindrique | Power tools, e-bikes | Less space-efficient, robust casing | Plus lourd |
| Prismatique | EVs, solar storage | Space-optimized, easy stacking | Modéré |
| Pouch | Laptops, portable devices | Flexible, fits irregular spaces | Lightest |
Lifepo4 technology offers more compact and lighter batteries compared to traditional lead-acid types. This advantage simplifies installation and improves portability.
Evaluating Discharge Rate and Cycle Life
Discharge rate and cycle life determine how well a battery performs over time. The cycle life refers to the number of charge and discharge cycles before the battery’s capacity drops to about 80%. A higher discharge rate supports rapid energy delivery but may reduce longevity.
| Facteur | Influence on Cycle Life and Discharge Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Depth of Discharge | Higher DoD reduces cycle life; ≤50% DoD recommended for long life | Shallower discharges extend battery lifespan |
| Température | Extreme temperatures shorten cycle life | Optimal: 0°C to 45°C |
| Charge/Discharge Rate | Higher rates can reduce cycle life | Balance performance and longevity |
| Storage Conditions | Proper storage preserves battery health | 40%-60% charge, room temperature |
| Application Needs | Match discharge rate and cycle life to usage | Critical for selection |
- For low-power applications, select low C-rate (1C–2C) batteries for stable, long discharges.
- For moderate power, choose medium C-rate (3C–5C) batteries for a balance of power and durability.
- For high-performance needs, opt for high C-rate (6C–10C+) batteries that support rapid energy discharge.
Maintaining lifepo4 battery for longevity involves balancing discharge rates and avoiding deep discharges. Properly charge a lifepo4 battery to maximize cycle life and performance.
Safety, BMS, and Environmental Factors
Safety remains a top priority when selecting any lifepo4 battery. A reliable Battery Management System (BMS) protects against overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, short circuits, and extreme temperatures. The BMS continuously monitors voltage, current, and temperature to ensure safe operation during charging and discharging.
- Look for batteries with robust protection circuitry and enclosures that withstand shocks, vibrations, humidity, and temperature extremes.
- The BMS should manage thermal conditions, activating heating in cold environments or cooling in hot conditions to prevent thermal runaway.
- Communication interfaces like CANBUS, RS485, or UART enable real-time monitoring and diagnostics for preventive maintenance.
- Environmental factors include the eco-friendliness of lifepo4 batteries, which contain no heavy metals and offer recyclability and a long lifespan.
Note: Always fully charge all batteries before connecting them in series to ensure consistency. Use a battery balancer if voltage differences are large. Regular maintenance and monitoring help maintain safety and extend longevity.
Lithium battery lifepo4 charging and maintenance tips include keeping batteries within recommended temperature ranges, avoiding overcharge or deep discharge, and storing them at 40%-60% charge for long-term health. Maintaining lifepo4 battery for longevity also means using a high-quality BMS and following proper installation practices.
By following these steps and considering all key factors, users can confidently choose the right lithium lifepo4 battery for any application. Lifepo4 technology delivers unmatched safety, efficiency, and long lifespan when paired with proper maintenance and care.
Comparing LiFePO4 Battery Series
Strengths and Limitations
LiFePO4 batteries offer several advantages for modern energy needs. Cylindrical batteries provide robust construction and good thermal stability. Prismatic batteries maximize space and support large-scale storage. Pouch batteries deliver lightweight and flexible options for custom designs. Each type has unique strengths and some limitations.
- Cylindrical batteries: Strong casing, high energy density, and easy manufacturing. However, they can be heavier and less space-efficient.
- Prismatic batteries: Compact design and efficient packaging. They suit electric vehicles and large storage but may cost more.
- Pouch batteries: Lightweight and customizable. They fit small devices but need careful handling to avoid damage.
Note: The key benefits of lifepo4 lithium batteries include reliable power, enhanced safety, and a long lifespan, making them suitable for many applications.
Performance and Cost
Performance and cost vary across lifepo4 battery series and capacity segments. The table below summarizes these differences:
| Battery Series / Capacity Segment | Caractéristiques de performance | Cost Characteristics | Applications typiques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical LiFePO4 Batteries | Robust, high energy density, standardized sizes, good thermal stability | Cost-effective, widely produced | Power tools, medical devices, electric bicycles |
| Prismatic LiFePO4 Batteries | Compact design, better packaging efficiency, enhanced thermal management | Moderate cost, suitable for large-scale production | Electric vehicles, large-scale energy storage systems |
| Pouch LiFePO4 Batteries | Lightweight, flexible, customizable, high energy density, good safety | Cost reducing due to tech advancements | Consumer electronics (smartphones, tablets, wearables) |
| Capacity < 1000mAh | Lightweight, compact, suitable for miniaturized devices | Generally lower cost | Wearables, remote controls, small medical devices |
| Capacity 1000-5000mAh | Balanced energy density and size | Moderate cost, improving with technology | Smartphones, tablets, portable electronics |
| Capacity > 5000mAh | High power and energy density, long cycle life, high safety | Higher cost but justified by performance | Electric vehicles, energy storage systems, industrial equipment |
The lifepo4 battery market continues to grow, driven by demand for renewable energy and electric vehicles. Manufacturers improve efficiency and reduce costs through technology and large-scale production. These advancements help lifepo4 batteries deliver strong performance at competitive prices.
Safety and Longevity
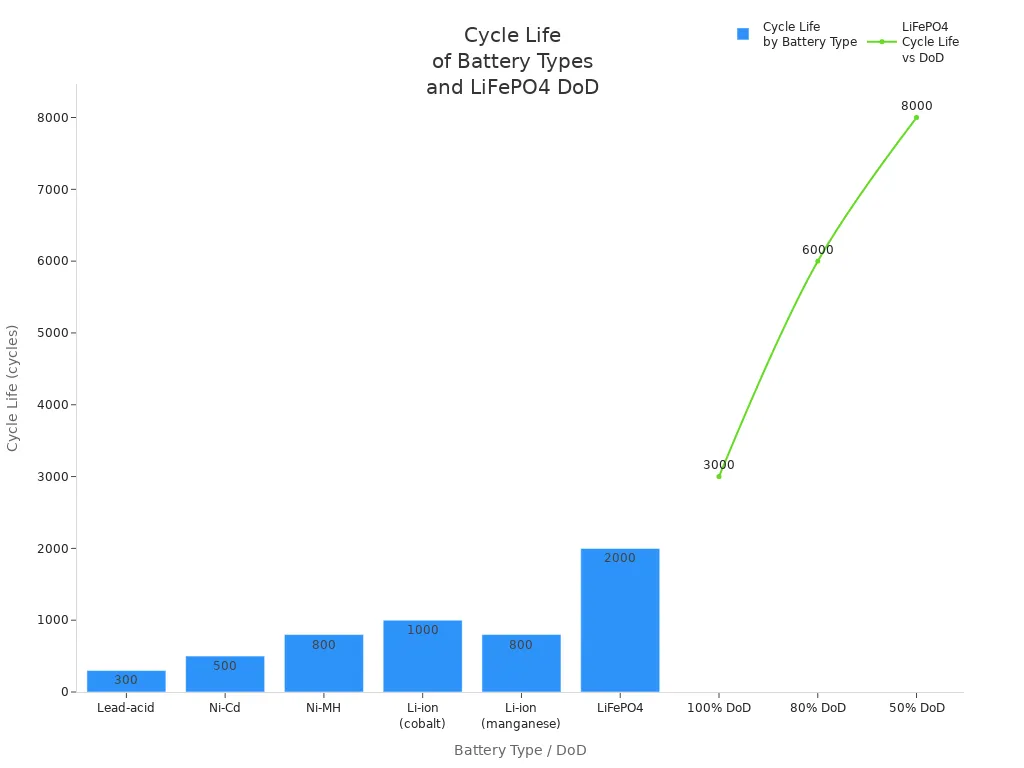
Safety and longevity set lifepo4 batteries apart from other lithium-ion types. The table below highlights key differences:
| Type de batterie | Cycle Life (Typical) | Safety Characteristics | Longevity Notes |
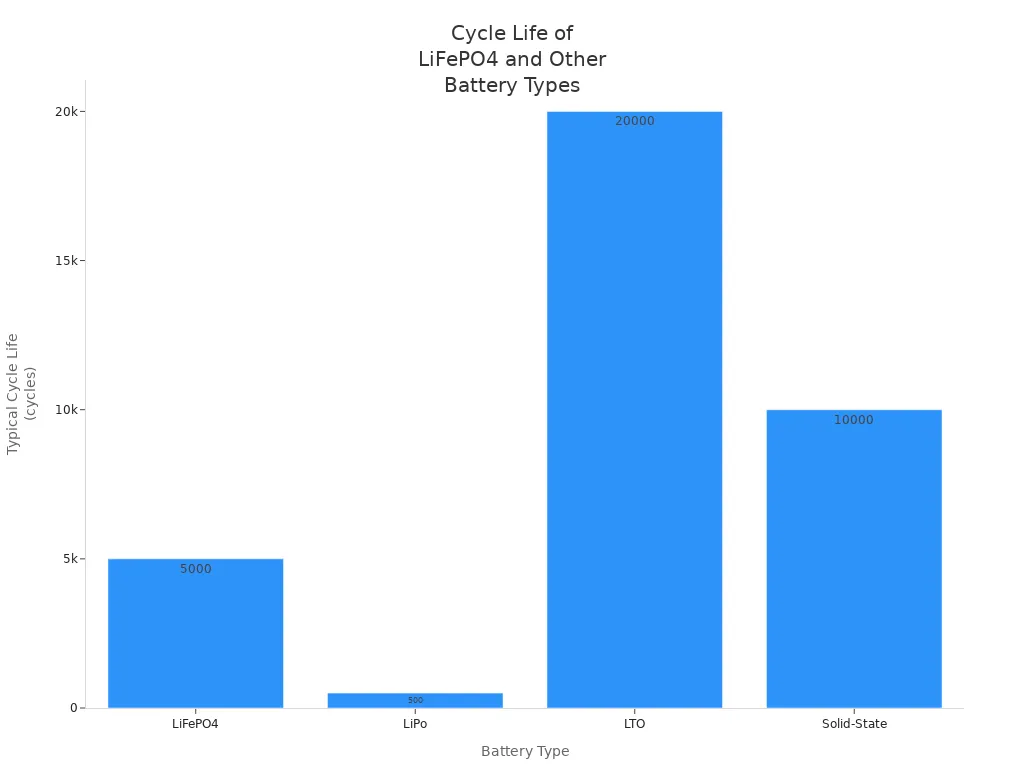
|---|---|---|---|
| LiFePO4 (phosphate de fer lithié) | 2,000 to 5,000 cycles (some models >6,000) | High thermal stability, low risk of thermal runaway, non-combustible components | Long lifespan, stable voltage output, wide operating temperature (0°C to 45°C) |
| Lithium Polymère (LiPo) | 300 à 500 cycles | Lightweight but prone to swelling and overheating | Shorter lifespan, less durable in high-demand applications |
| Lithium-Titanate (LTO) | 10,000 to 20,000 cycles | Excellent performance in extreme temperatures, very durable | Extraordinary cycle life but lower energy density |
| Solid-State Lithium (Emerging) | 5,000 to 10,000 cycles (potential) | Enhanced safety due to solid electrolyte, higher energy density | Promising longevity but still under development and costly |
LiFePO4 batteries maintain stable voltage and resist overheating. Their long lifespan supports thousands of cycles, making them ideal for solar storage and electric vehicles. Proper maintenance, such as using compatible chargers and avoiding extreme temperatures, extends battery longevity and ensures safety. These advantages make lifepo4 batteries a reliable choice for users who value efficiency and low maintenance.
LiFePO4 batteries stand out for their long cycle life, safety, and versatility across many applications. Users can select the right battery by following these steps:
- Assess power and voltage needs.
- Check cycle life and safety features.
- Match battery size to the device.
- Review brand reputation and support.
For best results, consult experts and use a battery management system for reliable performance. Careful selection ensures lasting value and safety in every application.
| Expert Tip | Bénéfice |
|---|---|
| Consult professionals | Receive tailored solutions and avoid costly mistakes |
FAQ
What makes LiFePO4 batteries safer than other lithium batteries?
LiFePO4 batteries use a stable chemical structure. This structure resists overheating and fire. The battery management system (BMS) adds extra protection. Users can trust these batteries in demanding environments.
How long do LiFePO4 batteries usually last?
Most LiFePO4 batteries last between 2,000 and 5,000 cycles. Some high-quality models reach over 6,000 cycles. Proper care and regular maintenance help extend battery life.
Can users replace lead-acid batteries with LiFePO4 batteries?
Yes, users can replace lead-acid batteries with LiFePO4 batteries in many systems. They must check voltage and size compatibility. LiFePO4 batteries offer longer life and better performance.
Do LiFePO4 batteries need a special charger?
LiFePO4 batteries work best with chargers designed for their chemistry. These chargers control voltage and current. Using the correct charger ensures safety and extends battery life.

