Définition en une phrase
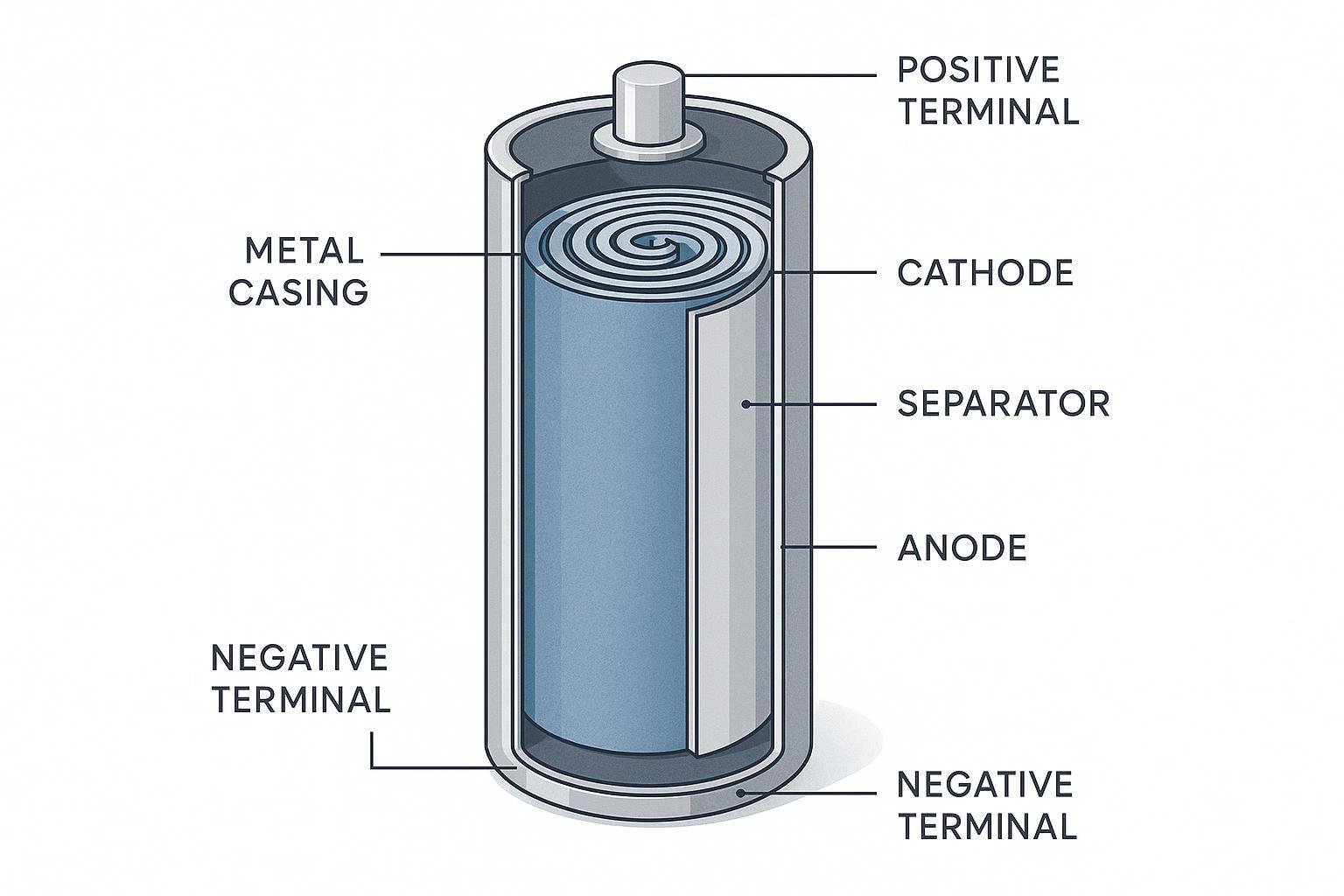
A cylindrical cell is a rechargeable battery with a circular cross-section, featuring internal electrodes and separator films tightly wound into a spiral (“jelly roll”) and securely housed in a rigid metal can.
In-Depth Explanation
Cylindrical cells, a staple in lithium-ion battery technology, are constructed by layering ultra-thin sheets of positive (cathode) and negative (anode) electrode material with a porous separator, then winding them together into a spiral—the “jelly roll”—before inserting this assembly into a metal tube. The cell’s outer casing, usually steel or aluminum, not only provides mechanical strength but also aids in heat dissipation and pressure containment. This design enables robust structural integrity and supports fully automated, high-volume manufacturing, making cylindrical cells a leading choice for both consumer and industrial applications. Learn more from BatteryDesign.net.
Key Compositions and Mainstream Sizes
- Chemistries: Cylindrical cells support a variety of lithium-ion chemistries, such as NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide), LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate), and NCA (Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide), each influencing performance, safety, price, and lifespan.
- Standard Sizes: The most widespread cylindrical cell sizes include:
- 18650: 18mm diameter, 65mm length (used in laptops, e-bikes, and early Tesla cars)
- 21700: 21mm diameter, 70mm length (now common in electric vehicles)
- 4680: 46mm diameter, 80mm length (Tesla’s next-gen EV platforms)
- 26650: 26mm diameter, 65mm length (industrial and high-discharge tools)
| Taille | Diameter × Length (mm) | Applications typiques |
|---|---|---|
| 18650 | 18 × 65 | Laptops, early EVs, e-bikes |
| 21700 | 21 × 70 | Modern EVs, power tools |
| 26650 | 26 × 65 | Power tools, energy storage |
| 4680 | 46 × 80 | Tesla EVs, grid storage, future |
Technical Advantages and Performance
- Mechanical stability: The cylindrical can resists deformation, swelling, and physical shock.
- Thermal management: The spiral (radial) layout provides efficient heat dissipation during charge/discharge.
- Manufacturability: Standardized formats enable automated, cost-effective mass production.
- La sécurité : Sturdy cans usually include safety vents and withstand high internal pressures.
- Scalability: Modular use in packs is straightforward, beneficial for electric vehicles and large storage arrays.
Comparison with Prismatic and Pouch Cells
| Caractéristique | Cylindrique | Prismatique | Pouch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Circular (tube) | Rectangular (block) | Flexible (envelope) |
| Packing Density | Modéré | Haut | Moderate to High |
| Mechanical Strength | Haut | Modéré | Faible |
| Heat Dissipation | Excellent (radial) | Variable | Variable (risk of swelling) |
| Automation | Very high | Modéré | Limited |
| Cycle Life* | 1000–4000 cycles | 800–2500 cycles | 800–2000 cycles |
| Typical Use Cases | EVs, tools, laptops | EVs, ESS, drones | Phones, wearables, drones |
*Cycle life depends on chemistry and conditions.
Cylindrical cells are generally favored in scenarios where reliability, safety, and modular assembly matter most, while prismatic and pouch cells excel in compact or custom-shaped battery designs.
Applications dans le monde réel
- Electric vehicles: Used in almost every Tesla model (18650, 21700, and new 4680 cells), Lucid Air, and Formula E packs.
- Consumer electronics: Found in laptops, cameras, flashlights, and high-performance e-bikes.
- Power tools: Cylindrical cells (usually 18650 or 21700) power drills, saws, and heavy-duty equipment.
- Energy storage systems: Used in grid storage and backup power due to modular design and long cycle life.
- Specialty uses: Medical defibrillators, aerospace, and high-reliability remote installations.
Related Terms and Concepts
- Prismatic Cell: A rectangular, rigid battery cell often used in automotive packs for higher packing density (learn more).
- Pouch Cell: A soft, flexible battery type with high gravimetric density, commonly seen in smartphones and wearables.
- BMS (Battery Management System): Electronics that monitor and protect each cell in multi-cell battery packs, ensuring safe charging, discharging, and thermal management—critical for cylindrical-based systems.
- Mainstream Cell Sizes: 18650, 21700, 4680, 26650—each with specific application niches as shown above.
- Lithium-Ion Chemistries: NMC, LFP, NCA—determine performance, cost, and safety profiles for various use cases.
Further Reading
- Pros and cons of lithium prismatic cells vs. cylindrical cells
- Prismatic vs. Pouch vs. Cylindrical lithium-ion battery cell (Grepow Blog)
- BatteryDesign.net’s cylindrical cell explainer
Cylindrical cells remain a cornerstone of both established and emerging battery-powered technologies, bringing together safety, scalability, and manufacturability in a unique and reliable form factor.

