Définition en une phrase
A high discharge rate in lithium batteries refers to the ability of a cell to safely deliver current at or above 10C (ten times its rated capacity per hour) continuously and even higher in short bursts, making it suitable for applications that demand rapid or substantial power delivery.¹
In-Depth Explanation
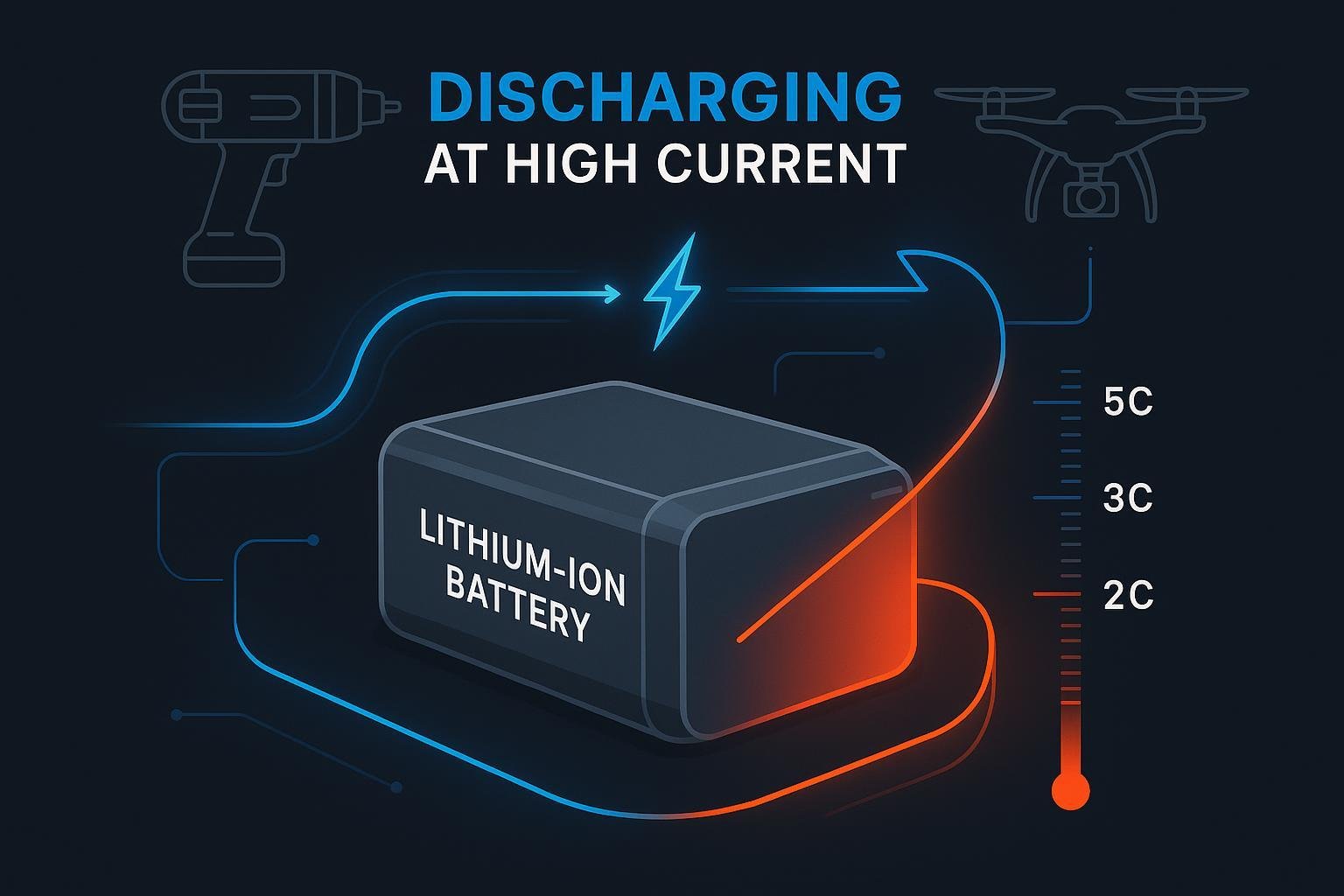
Discharge rate quantifies how quickly a battery can release its stored energy. This is typically expressed as a C-rate, defined as the ratio of discharge current (amps) to the battery’s nominal capacity (amp-hours). For example, a 2,000 mAh cell discharged at 1C provides 2,000 mA (or 2A) over one hour. At 10C, the same battery would deliver 20A and be fully discharged in six minutes.
- Continuous discharge rate indicates the maximum current a battery can sustain over extended periods without overheating or damaging internal components.
- Peak (or burst) discharge rate specifies the higher current a battery can supply for a short duration (usually a few seconds), beyond which performance and safety are compromised.
High discharge rate batteries are differentiated by their ability to support these elevated currents, typically through advanced cell chemistry, low internal resistance, enhanced electrode design, and superior thermal management systems.²
Key Components of High Discharge Rate
- Taux C: Central in quantifying discharge; a higher C-rate means faster available discharge. A “high” C-rate is generally ≥10C (continuous), with peak rates reaching 40C, 100C, or even more, depending on chemistry and manufacturer. See Ampxell’s high-rate definitions.
- Electrode Materials and Design: High-rate cells rely on premium materials (like advanced lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate), thinner electrodes for lower resistance, and optimized layouts to ensure even current distribution.
- Gestion thermique: Operating at high discharge rates produces significant heat. Designs often include advanced heat sinks, liquid or phase-change cooling, and intelligent battery management systems (BMS) to maintain safety and performance.
- Testing Standards: Reputable manufacturers reference standards (IEC 62133, IEC 61960, UL1642, etc.) in their datasheets, though some marketing claims may use nonstandard tests—making it essential for engineers and procurement specialists to verify test protocols.
Applications dans le monde réel
- Cordless Power Tools: Require continuous high discharge rates (10–30C) for sustained torque and performance.
- Hobby Drones and RC Vehicles: Need extreme burst discharges (20C to >40C) for rapid climbs or acceleration.
- Véhicules électriques (VE): During acceleration or in “boost” mode, batteries often operate at 5C–10C.
- Emergency Medical Devices and UPS: Depend on reliable, short-term peak discharge rates for critical operations.
Calculation Example:
A 2,500 mAh (2.5 Ah) battery with a 20C continuous rating:
- Maximum sustainable current = 2.5 Ah × 20C = 50A
- At this rate, the cell would be depleted in 3 minutes.
Related Concepts and Glossary
- Taux C: Current (A) / Capacity (Ah); drives how discharge rate is quantified.
- Continuous Discharge Rate: Max current for long-term operation (e.g., five minutes or more).
- Peak (Burst) Discharge Rate: Max current for seconds to a minute.
- High Drain Device: Not a battery spec, but refers to devices requiring high power draw (e.g., power tools, drones).
- Capacité de la batterie: Total energy stored, not discharge rate.
- Emballement thermique: Dangerous condition where excess heat from high-rate discharge causes further overheating.
- BMS (Battery Management System): Electronics that monitor and control charging/discharging for safety.
Practical Tips and Industry Guidance
- Always verify discharge rates in product datasheets against international standards.
- Assess specific application needs: prioritize continuous over peak discharge for prolonged use-cases and ensure robust cooling for safety and lifespan.
- Be aware of exaggerated marketing claims—reference manufacturer ratings only when supported by recognized testing (IEC/UL, etc.).
Références :
- Ampxell: High Rate Discharge Battery Explained
- Ossila: What is Battery C-rate?
- BatteryUniversity: C-Rate for Batteries
For more on adjacent concepts, see: Taux C, Continuous Discharge, High Drain Battery

