Définition en une phrase
Internal resistance is the opposition within a battery or power source that impedes the flow of electric current, causing a voltage drop and energy loss when current flows.
Explication détaillée
In battery technology, internal resistance (IR) refers to the sum of all resistive elements inside a cell that hinder the movement of electrons and ions during charging and discharging. This resistance is modeled as a resistor in series with the ideal voltage source in circuit diagrams (Wikipedia (en anglais)). When current flows, IR causes a voltage drop and generates heat, reducing the battery’s efficiency and available power. The value of internal resistance is not fixed; it varies with temperature, state of charge, battery age, and manufacturing quality.
Key Components of Internal Resistance
- Ohmic Resistance: Originates from the resistivity of the battery’s materials (electrodes, electrolyte, connectors).
- Charge Transfer Resistance: Occurs at the interface between the electrode and electrolyte, related to the speed of electrochemical reactions.
- Polarization Resistance: Results from ion diffusion limitations within the cell, especially at high current loads.
These components together determine the total internal resistance, which is typically measured in milliohms (mΩ) for lithium-ion cells.
Measurement Methods and Industry Standards
- DC Load Method: Measures the voltage drop under a known load; applies Ohm’s law (R = ΔV/ΔI). Simple but blends multiple resistance effects (Université de la batterie).
- AC Impedance (ACIR): Uses a 1kHz AC signal to measure resistance, commonly used in production lines for speed and accuracy (Hioki).
- Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): Advanced lab method that separates different resistance components across frequencies.
- Industry Standards: IEC 61960 and ISO 12405 specify procedures for DCIR and ACIR measurement, ensuring consistency across manufacturers (BatteryDesign.net).
Applications dans le monde réel
- Battery Production and Quality Control: Manufacturers like Yungbang rigorously test internal resistance at multiple stages—post-assembly, pre-shipment, and during aging—to ensure only cells with low, consistent IR are used in custom battery packs. This minimizes pack imbalance, overheating, and extends battery life.
- Performance and Safety: Low internal resistance enables higher power output, longer runtime, and reduced heat generation. High IR can signal cell aging or defects, prompting replacement or rejection during quality checks.
- Custom Solutions: For industrial clients requiring high-drain or long-life batteries, controlling IR is critical. Yungbang’s custom production lines use ACIR testing to sort and match cells, ensuring optimal performance for each application.
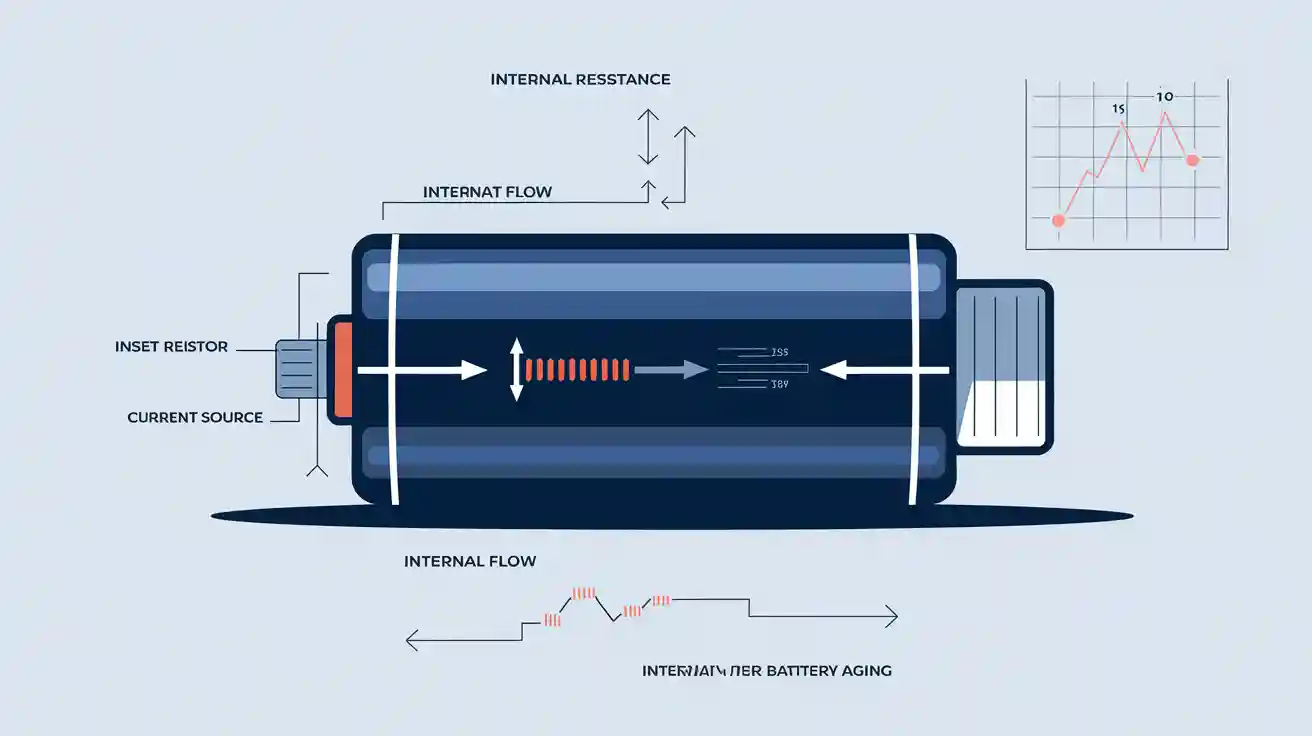
Visualizing Internal Resistance
- Equivalent Circuit Model:
- IR vs. Aging Curve:

Concepts connexes
- Open Circuit Voltage (OCV): The voltage of a battery when no current is flowing.
- Capacité: The total charge a battery can deliver at a specified rate.
- État de charge (SoC): The current charge level relative to the battery’s capacity.
- Impedance: Includes both resistance and reactance; internal resistance is the real (resistive) part.
- DCIR/ACIR: Direct Current Internal Resistance and Alternating Current Internal Resistance, two standard measurement approaches.
For more on custom lithium-ion battery solutions and how internal resistance impacts your application, visit Yungbang.


