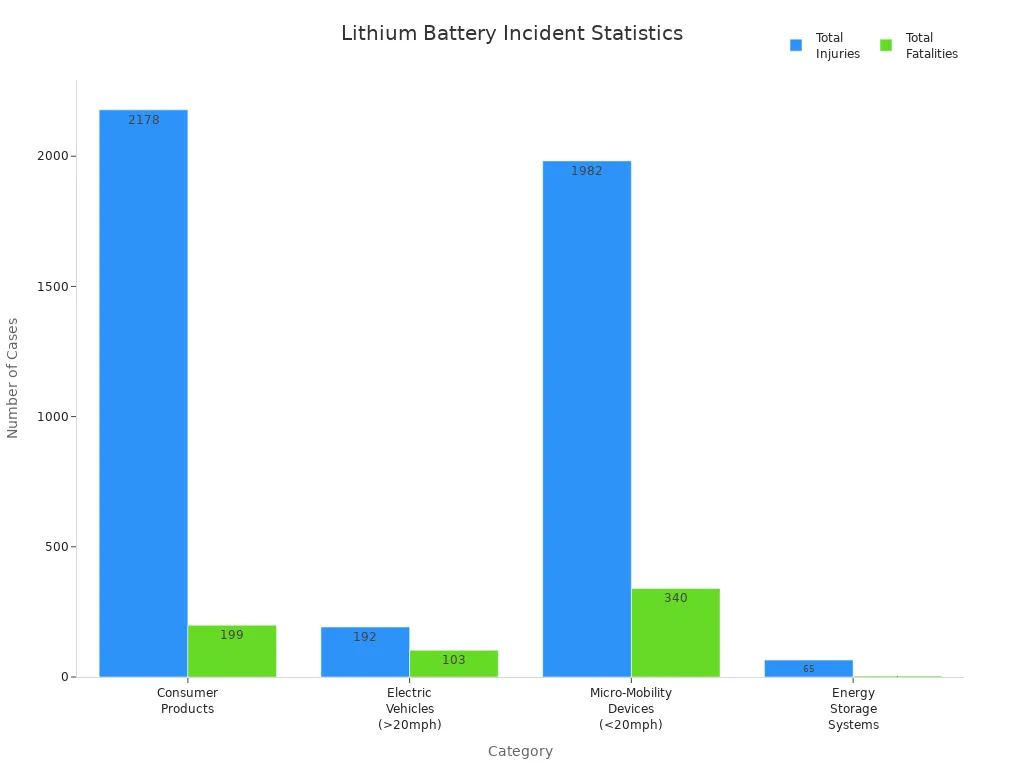
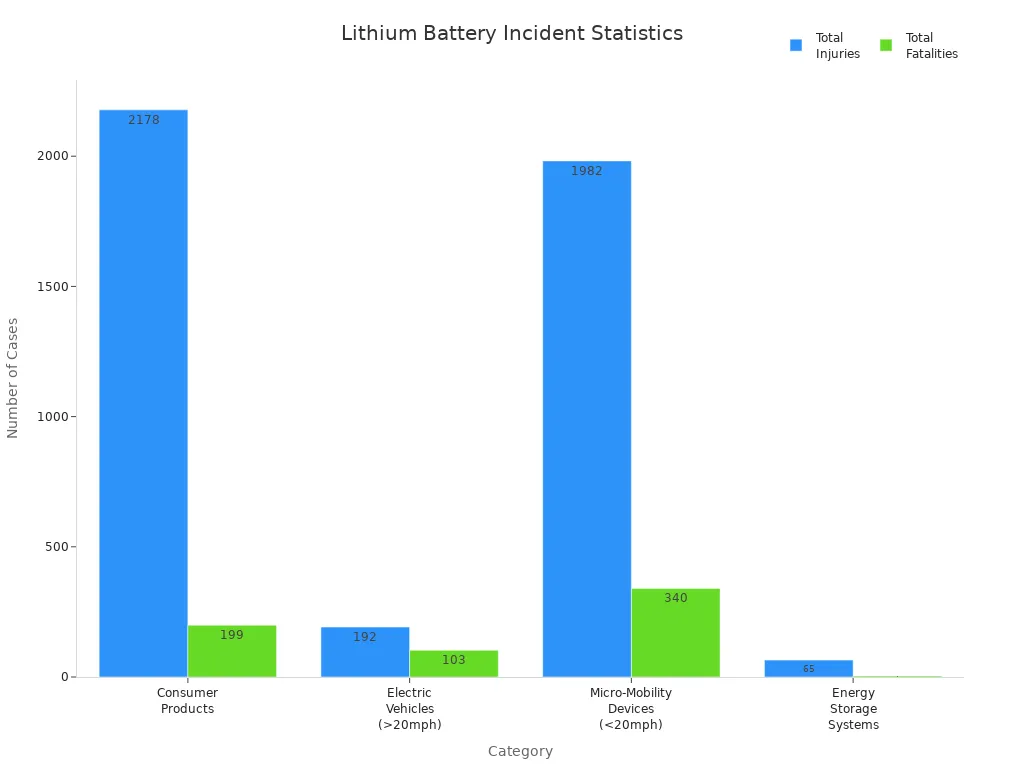
You want to keep your devices safe, but lithium polymer battery safety can feel confusing. Recent incidents show why you must pay close attention. In 2023, New York City alone saw 92 lithium-ion battery fires, which led to 64 injuries and 9 deaths. Fires linked to lithium-ion battery failures also rose sharply in the UK, especially with e-bikes.
Improper handling can cause fires, explosions, or chemical leaks. You can avoid these hazards by following best practices and recommended safe handling steps. Battery safety starts with your awareness and action.
Battery Safety Basics
Common Hazards
You face several hazards when handling lithium polymer batteries. Fires and explosions can happen if you damage the battery, overcharge it, or let it overheat. These batteries may bulge, leak, or even emit toxic vapors. Sometimes, a damaged battery can reignite days after the first incident. Saltwater exposure can also cause short-circuiting, which leads to fires.
Here are the main hazards you should watch for:
- Fire and explosion risks from physical damage, overcharging, or overheating
- Bulging, leaking, or emission of flammable or toxic vapors
- Reignition days after initial damage
- Short-circuiting from saltwater exposure
- Fire hazards from using non-certified chargers or batteries
- Overcharging or over-discharging, which increases fire risk
- Ignoring manufacturer guidelines for storage and charging
You should always use certified chargers and batteries that meet safety standards like UL 1642 or IEC 61960. Store your lithium-ion battery in a cool, dry place. Avoid dropping or puncturing the battery. Never leave a charging battery unattended, and use a fire-retardant bag for extra protection. Monitoring battery condition helps prevent runaway reactions and reduces fire hazard.
Warning Signs
You can spot warning signs of failure before a serious problem occurs. Hinchazón o abombamiento often means gas is building up inside the battery. If your device feels hot or the battery casing looks cracked or deformed, stop using it right away.
Look for these warning signs of failure:
- Visible smoke or a burning odor (immediate fire danger)
- Swollen battery pack
- Excessive heat from your device
- Cracked or deformed battery casing
- Unusual hissing or popping sounds
Other warning signs of failure include longer charging times, shorter battery life, or the device shutting down unexpectedly. If you notice any of these hazards, replace the battery immediately to protect yourself from fire or explosion. Staying alert to these signs is a key part of lithium polymer battery safety and lithium battery safety.
Safe Handling Guidelines
Handling Precautions
You can protect yourself and your devices by following important safety precautions when working with lithium-ion battery packs. Always wear protective equipment, such as safety glasses, to shield your eyes from possible leaks or sparks. Use fire-resistant containers or Lipo Guard bags when charging or storing batteries. These safety features help contain fires if something goes wrong.
Consejo: Always charge your lithium-ion battery in an approved location, away from flammable materials.
To prevent short circuits, keep battery terminals from touching each other or any metal objects. You can do this by taping the terminals with non-conductive tape or placing each battery in a separate plastic bag. This simple step stops the terminals from making contact, which greatly lowers the risk of fire during storage or transport. The EPA recommends isolating battery terminals to prevent thermal runaway and fire hazards.
Here are some safe handling steps you should follow:
- Handle batteries gently and avoid using force.
- Never stack batteries in a way that could cause them to tip or fall.
- Store batteries in their original packaging or in anti-static bags.
- Keep batteries in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, between 40 and 80 °F.
- Separate lithium-ion battery types from other batteries and keep them away from flammable items.
- Dispose of any swollen, dented, or damaged batteries properly.
If you notice any abnormal signs, such as heat, swelling, or a strange smell, disconnect the battery right away. These safety features help you catch problems early and prevent accidents.
Preventing Damage
Physical damage is one of the main causes of lithium-ion battery failure. You can avoid many risks by using careful battery handling techniques. Always handle batteries with care to prevent drops, punctures, or crushing. Even a small dent can harm the battery’s internal structure and lead to dangerous situations.
Follow these steps to prevent damage:
- Use protective cases when storing or transporting batteries. These cases shield batteries from impacts and accidental drops.
- Insert and remove batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This helps you avoid bending or stressing the battery.
- Never place heavy objects on top of batteries. Stacking batteries incorrectly can cause them to deform or break.
- Inspect batteries regularly for dents, leaks, or swelling. If you see any damage, stop using the battery and dispose of it safely.
- Store batteries in a stable position to prevent tipping or falling.
Nota: Always treat damaged or spent batteries as hazardous waste. Follow local rules for disposal and recycling.
By following these safe handling guidelines, you add extra safety features to your daily routine. Careful prevention and regular inspection help you avoid accidents and extend the life of your lithium-ion battery.
Purchasing and Inspection
Choosing Quality Batteries
You want to avoid dangerous products and costly recalls. When you buy a lithium-ion battery, always check for safety certifications. These certifications show that the battery meets strict safety and quality standards. Many recalls happen because batteries do not meet these requirements. You can use the table below to help you identify trusted certifications and reduce your risk of recalls:
| Certification/Standard | Region/Scope | Purpose/Importance |
|---|---|---|
| IEC 62133-2:2017 | International | Battery-specific safety standard for lithium-ion batteries export and use. |
| UN38.3 | International (UN) | Transport safety standard for lithium batteries ensuring safe shipment of dangerous goods. |
| RoHS | Unión Europea | Restriction of hazardous substances to ensure environmental compliance. |
| UL1642 & UL2054 | Estados Unidos | Safety standards for lithium batteries covering construction and safety testing. |
| Marcado CE | European Economic Area | Conformity with EU directives; requires compliance with IEC 62133, UN38.3. |
| ISO 9001 | International | Quality management system ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. |
| ISO 14001 | International | Environmental management system for sustainability in production. |
| CB Scheme | International (IECEE) | Harmonizes testing for global market entry using IEC standards. |
| PSE Mark | Japón | Safety certification under Japan’s Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law. |
| UKCA Mark | United Kingdom | Post-Brexit equivalent to CE marking for UK market access. |
| KC Certification | South Korea | Product safety, EMC compliance, and consumer protection. |
| BIS / ISI Mark | India | Mandatory for lithium-ion batteries; based on IS 16046 harmonized with IEC 62133. |
| GB 31241 | China | Safety requirements for lithium-ion batteries in portable electronics. |
Consejo: Always ask for the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) before you buy. This sheet gives you important chemical safety information.
Inspection Checklist
You can prevent accidents and avoid recalls by inspecting every lithium-ion battery before use. Follow this checklist to keep your devices and home safe:
- Check that the battery arrives in its original, undamaged packaging.
- Look for proper hazardous material (Hazmat) labeling on the box.
- Make sure the battery temperature is between 65° and 80° Fahrenheit.
- Store batteries unstacked, either on racks or in a single layer on the floor.
- Confirm that the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) is available and easy to find.
- Quarantine any battery that looks damaged, has wrong packaging, or is missing labels. Notify your supervisor or management right away.
- Take photos and write notes if you find any problems. Good records help with recalls and safety reviews.
Alerta: Never use a battery that fails any part of this checklist. Using faulty batteries increases the risk of fire, injury, and future recalls.
By following these steps, you lower your risk of lithium-ion battery recalls and keep your devices running safely.
Charging Safety

Charging lithium polymer batteries safely protects you and your devices from serious hazards. Fires can start quickly if you use the wrong charger or charge in unsafe conditions. You can lower fire risk by following these charging safety tips.
Correct Chargers
You should always use a charger designed for lithium polymer batteries. Chargers from the original manufacturer contain special circuits that balance cells and control temperature. Using a counterfeit or incorrect charger can cause unpredictable battery behavior. This may lead to burns, fires, or even explosions.
- Only use chargers that match your battery’s specifications.
- Avoid aftermarket chargers that do not have safety certifications.
- Never use damaged or modified chargers or batteries.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for battery charging.
| Risk Category | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Sobrecarga | Leads to battery degradation, reduced lifespan, overheating, thermal runaway, fire, and explosion. |
| Safety Mechanism Failure | Protection circuits may fail, causing dangerous overheating or fires when overcharged. |
| Electrical Hazards | Incorrect chargers can cause short circuits, resulting in overheating and potential fires. |
| Charging Protocols | Use only compatible chargers; monitor charging; never leave batteries unattended; avoid overcharging. |
| Manufacturer Guidelines | Follow recommended charging times and procedures; do not rely solely on built-in cutoff features. |
Safe chargers have important features:
- UL approval for strict safety standards.
- Built-in overcharge cutoff to stop charging when full.
- Voltage and temperature monitoring to detect problems.
- Visual indicators, such as LED lights, to show charging status.
- Balance charging to keep all cells at the same voltage.
- Secure connectors to prevent loose connections.
Consejo: Use a LiPo-compatible charger. Non-compatible chargers can cause fires.
Charging Environment
The place where you charge your battery matters. Charging in the wrong environment increases fire risk. Always choose a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. Avoid charging batteries in direct sunlight, near heaters, or inside hot vehicles. High temperatures during charging can damage the battery and lead to fires.
- Charge batteries between 0°C and 40°C (32°F to 104°F).
- Keep batteries away from flammable materials, such as paper or fabric.
- Use fire-retardant bags for small batteries, but remember these bags may not protect larger batteries like those in e-bikes.
- For large batteries, use a metal container lined with fireproof material or charge outdoors.
- Make sure the charging area has good airflow to prevent heat buildup.
Humidity also affects battery safety. High humidity can cause corrosion and weaken battery parts. Low humidity increases static electricity, which can damage battery circuits. Try to keep the relative humidity between 40% and 60%.
Alerta: Never leave batteries unattended while charging. Fires can start quickly and spread before you notice.
Monitoring Charge
You must watch your battery while it charges. Overcharging is a leading cause of battery fires. Chargers with built-in cutoffs help, but you should still monitor the process.
- Charge batteries at a slow rate to reduce heat and stress.
- Use a charger that matches your battery’s capacity.
- Disconnect the battery as soon as it is fully charged.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for voltage and charging rate.
- Avoid charging in extreme temperatures.
Charging in a fireproof container or bag adds another layer of fire prevention. However, some fire-retardant bags may trap heat and increase fire risk, especially with large batteries. Always allow for ventilation.
Nota: Never charge a hot battery. Let it cool before starting battery charging.
By following these charging safety steps, you reduce the risk of fires and protect your devices. Safe charging habits help prevent overcharging, overheating, and other dangers.
Buenas prácticas de almacenamiento
Storage Conditions
You can extend the life of your lithium polymer batteries by following the right storage methods for lithium batteries. Always store your batteries in a cool, dry place. The best temperature range is between 59°F and 77°F. Avoid places with high heat or freezing cold, as both can damage the battery. Keep humidity low and make sure the area has good airflow. This helps prevent corrosion and moisture buildup.
- Store batteries at about Carga 50% for long-term storage.
- Disconnect batteries from devices and chargers before storing.
- Use protective cases to shield batteries from bumps or drops.
- Check your batteries every 3–6 months for swelling, leaks, or corrosion.
- Recharge batteries if the voltage drops below the recommended level.
Before you use a stored battery again, inspect it and do a full charge cycle. This helps keep the battery management system working well.
Fireproof Containers
Fireproof containers add an extra layer of safety to your battery storage. These containers use strong materials and special seals to keep heat and flames inside if a battery fails. Some models even have fire-extinguishing systems and smoke sensors. By using fireproof containers, you protect your home and property from fires caused by battery problems.
- Fireproof containers can hold back fire or explosions for up to 90 minutes.
- They block toxic gases that may escape during a battery fire.
- These containers keep batteries apart, lowering the risk of a big fire.
You should always keep batteries away from metal objects and direct sunlight. Fireproof containers help you follow safe storage methods for lithium batteries.
40-80% SOC Rule
Keeping your batteries at the right state of charge (SOC) is key to long life. Experts recommend storing lithium polymer batteries at 40% to 80% SOC. This range helps prevent stress and slows down battery aging. If you store batteries fully charged or fully empty, they wear out faster.
| Aspecto | Detalles |
|---|---|
| Best SOC for Storage | 40%–80% |
| Average Lifespan (Charge Cycles) | 1500–2000 cycles with best practices |
| Temperature Range | 59°F–77°F (15°C–25°C) |
| Tasa de autodescarga | Less than 1% per month |
By following these battery storage tips, you help your batteries last longer and stay safe.
Disposal and Recycling
When to Dispose
You should know when a lithium polymer battery is no longer safe to use. Damaged batteries can cause fires or leak harmful chemicals. Watch for these warning signs:
- Swelling or bloating of the battery or device
- Cracks, corrosion, or leaking
- Visible burn marks on the battery
- Cracking, bulging, or misalignment of device cases
- Excessive heat or bad smells during charging
- Hissing, popping, or crackling sounds
- Sudden or dramatic loss of charge capacity
If you notice any of these signs, stop using the battery right away. Remove it from your device and prepare it for safe disposal.
Safe Disposal Steps
Proper lithium battery disposal keeps you and the environment safe. Never throw lithium polymer batteries in the trash or regular recycling bins. Follow these steps to dispose of them safely:
- Store the battery in a cool, dry place away from heat and flames.
- Wear protective gloves and avoid crushing or puncturing the battery.
- Place each battery in a separate, non-conductive bag or container.
- Cover the battery terminals with insulating tape.
- Remove the battery from your device following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Store batteries in a fire-resistant container until you can take them to a recycling center.
- Take the battery to an authorized drop-off location or recycling program.
Consejo: Never mix different battery types in the same container. This helps prevent short circuits and fires.
Improper disposal can cause fires at waste facilities, pollute soil and water, and waste valuable metals like lithium and cobalt. Recycling helps recover these materials and protects the environment.
Recycling Centers
You can find certified recycling centers for lithium polymer batteries using online tools like Earth911 or Call2Recycle. Many electronics stores and home improvement centers offer drop-off programs for small batteries. For large batteries, contact the manufacturer or your local hazardous waste program. Always look for recyclers with certifications such as R2 or e-Stewards. These centers follow strict safety and environmental rules. Recycling your batteries helps prevent pollution and supports a cleaner planet.
Emergency Response
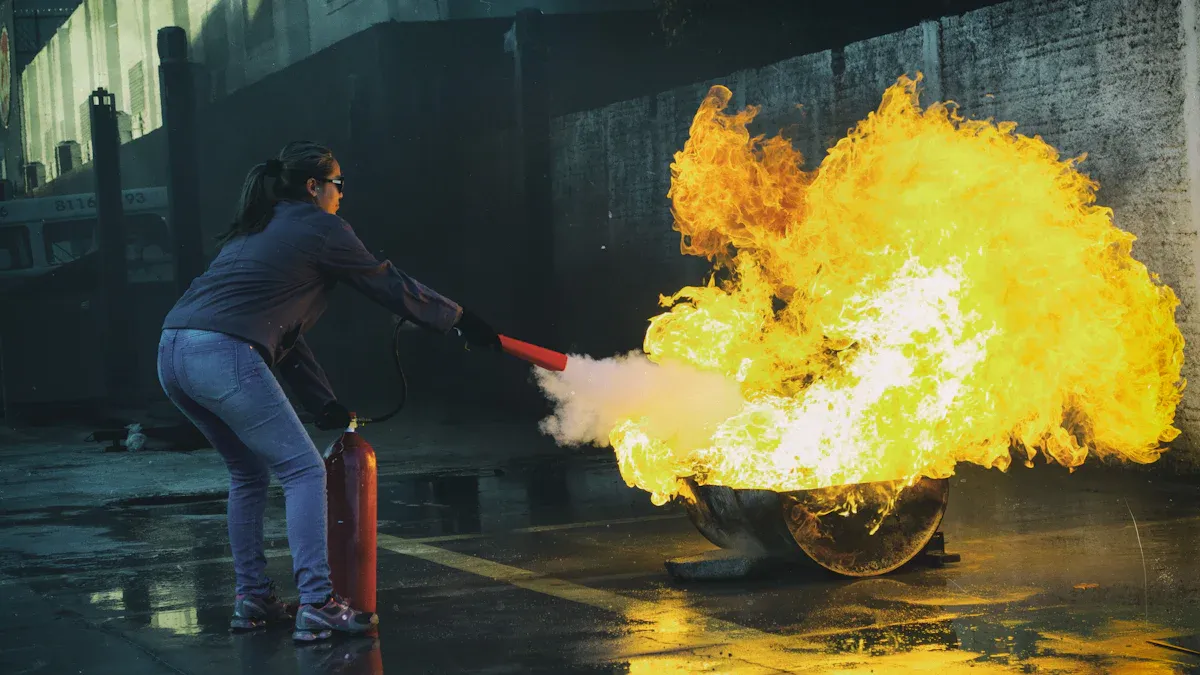

Battery Failure Actions
You must act quickly if you notice swelling, bulging, or a strange odor from your lithium polymer battery. Stop using the battery right away. Shut off your device and move it to a safe, open area. Do not touch the battery with bare hands. Use insulated gloves or tongs to handle it. Place the battery in a fire containment bag made for lithium batteries. Never use water or a regular extinguisher on a battery fire. Water can make the reaction worse.
If you see smoke or hear popping sounds, evacuate the area. Stay at least 5 meters away because toxic gases may escape. Let the battery cool for at least 24 hours. Use pH test strips to check for any leftover hazardous substances. If you find acid, contact professionals for safe disposal. Always store and charge batteries in certified safety bags to help contain any fire.
Fire Safety Steps
If a fire starts, your safety comes first. Evacuate everyone from the area. Alert the fire department and tell them it is a lithium battery fire. Specialized extinguishing agents, like F-500 Encapsulator Agent, work best for these fires. This agent cools the fire and stops the chemical reaction. Never try to put out the fire with water. Use personal protective equipment to avoid chemical exposure. After the fire, monitor the area for reignition. Lithium battery fires can restart even after they seem out.
Set up safety zones to keep people away from danger. Use cooling techniques to manage the heat. Always follow emergency response procedures for electric vehicles or large battery packs. Work with experts and use emergency guides for the safest results. Remember, lithium battery spill cleanup requires special care to avoid further hazards.
Reporting Incidents
After any battery fire or near-miss, report the incident right away. Fill out your workplace’s official incident report form. Include details about the fire, injuries, and actions taken. Take photos and write notes about the scene. Submit your report to the safety office or supervisor. Good records help improve emergency response procedures and prevent future fires.
You can protect yourself and your devices by following lithium polymer battery safety tips.
- Utilice siempre el cargador correcto and avoid damaging the battery.
- Store batteries in cool, dry places and check for warning signs.
- Follow updated safety practices from agencies like the CPSC y IATA.
- Utilice battery management systems and early detection methods to prevent fires.
Stay informed about lithium polymer battery safety by checking trusted resources and new guidelines. This helps you prevent accidents and extend battery life.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
How do you know if a lithium polymer battery is unsafe to use?
You should look for swelling, leaks, strange smells, or heat. If you see smoke or hear popping sounds, stop using the battery right away. These signs mean the battery could be dangerous.
Can you charge a lithium polymer battery overnight?
You should not charge these batteries overnight. Fires can start quickly if something goes wrong. Always watch your battery while it charges and unplug it when it is full.
Consejo: Use a charger with an automatic shutoff for extra safety.
What should you do if a battery gets wet?
Remove the battery from your device. Dry it with a towel. Do not use or charge it. Place it in a fireproof container and take it to a recycling center. Water can cause short circuits and fires.
Is it safe to store lithium polymer batteries in the refrigerator?
No, you should not store these batteries in the refrigerator. Cold temperatures can damage the battery and cause condensation. Store your batteries in a cool, dry place at room temperature.

