
Charge voltage parameters play a critical role in the lifespan and safety of any 18650 battery. Studies show that setting the charge voltage above 4.2 volts leads to rapid battery aging and capacity loss. For example, after only 180 cycles, a 18650 battery charged to 4.4 volts can lose up to one-third of its capacity. Using the correct charge voltage helps a rechargeable battery last longer and work more safely. Industry experts confirm that following recommended charge guidelines protects the battery from overheating and failure. A rechargeable 18650 battery performs best and stays reliable when users respect these charge limits.
Charge Voltage Parameters
Typical Values
Manufacturers set clear charge voltage parameters for every 18650 battery. These values help users get the best performance and longest life from each rechargeable battery. The most common chemistry for 18650 cells is lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2). This type uses a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts. The charging cut-off voltage is 4.2 volts, and the minimum voltage threshold for safe discharging is 2.75 volts. These numbers guide both charging and discharging.
| Química de la batería | Tensión nominal | Charging Limit Voltage | Minimum Discharge Voltage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2) | 3.7 V | 4.2 V | 2.75 V |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | 3.2 V | 3.6 V | 2.0 V |
A typical 18650 battery uses constant current charging at first. The charger supplies a steady charging current for lithium batteries until the cell reaches the charging voltage. Then, the charger switches to constant voltage charging. This method keeps the voltage steady while the current drops. The process stops when the charging current falls below a set value. This approach protects the battery and ensures a full charge.
Chemistry Differences
Not all 18650 batteries use the same chemistry. Different chemistries have different charge voltage parameters and voltage ranges. For example, lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cells have a nominal voltage of 3.2 volts. Their charging voltage should not go above 3.65 volts. The discharge cut-off voltage for LFP is 2.0 volts. Nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) cells, another common type, use a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts. Their charging voltage can reach up to 4.2 volts, and their minimum voltage is about 2.5 volts.
| Parámetro | NMC (18650) | LFP (32650) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensión nominal | 3.7 V | 3.2 V |
| Typical Operating Range | 3.0 V to 4.2 V | 2.5 V to 3.65 V |
| Charge Voltage | Up to 4.2 V (some up to 4.3 V) | Up to 3.65 V |
| Charge C-rate | 0.7–1C | Typically 1C |
NMC cells have a higher nominal voltage and a wider voltage range than LFP cells. LFP cells offer better thermal stability and longer cycle life. Each chemistry needs its own charge voltage parameters and battery management system settings. Using the wrong settings can damage the battery or reduce its lifespan.
Safe Ranges
Safe voltage ranges protect every 18650 battery from harm. The battery management system (BMS) enforces these limits. For a typical NMC 18650 battery, the maximum voltage is 4.2 volts. The minimum voltage is usually 2.5 volts. For LFP cells, the maximum is 3.65 volts, and the minimum is 2.0 volts.
| Química de la batería | Maximum Voltage (Upper Limit) | Minimum Voltage (Lower Limit) | Notas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Li-ion (NMC) 18650 | 4.2 V | ~3.2 V to 3.7 V nominal; cutoff ~2 V | BMS prevents overcharge/discharge; chargers must not exceed 4.2 V |
| LiFePO4 18650 | 3.65 V | 2 V | BMS enforces limits; discharging below 2 V harms battery health |
⚠️ Nota: Exceeding the safe voltage range can cause serious problems. Overcharging above 4.2 volts may lead to battery failure, swelling, or even fire. Discharging below the minimum voltage threshold can cause permanent damage and reduce capacity. Laboratory studies show that overcharging causes lithium dendrite growth, which can short-circuit the cell. Overdischarging leads to copper dissolution and gas buildup, both of which harm the battery.
A healthy 18650 battery stays within the recommended voltage range. Cells that drop below 2.6 volts or rise above 4.2 volts often show signs of stress. These signs include swelling, leakage, or a sweet smell. High internal resistance and low capacity also signal poor health. Cells that remain between 2.6 and 4.2 volts, with normal resistance, last longer and work more safely.
Correct charge voltage parameters, along with proper charging current, help every rechargeable battery deliver safe and reliable power. Users should always follow manufacturer guidelines for charging and discharging. This practice extends battery life and prevents safety risks.
Sobrecarga

Daños en la batería
Charging a 18650 battery above its recommended voltage, usually 4,2 voltios, causes irreversible harm. When the voltage rises past this limit, chemical changes inside the battery begin. The internal structure weakens, and the battery capacity drops. Overcharging stresses the separator and electrodes, which can lead to short circuits. Even a small increase in voltage, such as charging to 4.3 volts, can cut the cycle life in half. Charging to 4.5 volts or higher is unsafe and often results in permanent loss of battery capacity.
Common types of damage include:
- Lithium metal forms on the anode, which can pierce the separator.
- The battery heats up and internal pressure increases.
- The separator and electrodes degrade, raising the risk of short circuits.
- The battery may show a voltage drop below 4.15 volts after resting, which signals capacity loss.
Older 18650 batteries are more likely to suffer heavy damage from overcharging. Newer cells may resist damage for a short time, but repeated overcharging always shortens their lifespan. Some batteries may appear normal at first, but hidden damage can cause problems later.
Riesgos para la seguridad
Overcharging a 18650 battery creates serious safety hazards. As the voltage climbs, the battery heats up and internal resistance increases. This process can trigger embalamiento térmico, a dangerous chain reaction that leads to fire or explosion. Overcharging also causes gas buildup, which makes the battery swell and sometimes vent.
Signs of overcharging include:
- Swelling of the battery pack
- Overheating during or after charging
- Discoloration or melting of the case
- Chemical or burnt odors
- Hissing, popping, or crackling sounds
- Smoke, fire, or even explosion in severe cases
- Rapid loss of charge, unexpected shutdowns, or unusual warmth
Overcharging can cause lithium dendrites to grow, which may puncture the separator and create internal short circuits. The battery’s electrolyte and electrodes become highly reactive at high temperatures. If the separator melts or the safety valve ruptures, flammable gases can escape and ignite. Using a quality charger with overcharge protection helps prevent these risks and keeps the battery safe.
Carga insuficiente
Pérdida de rendimiento
Undercharging a 18650 battery can cause several problems with battery performance. When users do not allow the battery to reach its full charge, the battery cannot deliver its maximum capacity. The device may run for a shorter time before needing another charge. Undercharging also increases the internal resistance of the battery. Higher resistance means the battery cannot provide as much power to the device. This leads to weaker output and less efficient operation.
A 18650 battery that does not receive a full charge will often show signs of reduced power. Devices may shut down earlier than expected. The battery may also struggle to support high-drain devices, such as flashlights or power tools. Users may notice that the battery heats up more quickly during use. These issues all point to a drop in battery performance.
Tip: Always use a charger that matches the recommended voltage for your 18650 battery. This helps maintain strong battery performance and keeps your devices running longer.
Lifespan Impact
Undercharging does not only affect how a battery performs each day. It also shortens the overall lifespan of the 18650 battery. When a battery does not reach its full charge, the chemistry inside the cell becomes stressed. This stress is similar to what happens during overcharging. Over time, the battery loses its ability to hold a charge.
Repeated undercharging can cause the battery to age faster. The battery may lose capacity after fewer cycles. Users may find that the battery needs to be replaced sooner than expected. Proper charging within the recommended voltage range helps prevent this early wear. Matching the charge and discharge rates to the device’s needs also protects the battery.
A healthy 18650 battery receives a full charge and operates within safe voltage limits. This practice supports both long battery life and reliable battery performance.
Optimal Charging Voltage
3.7V Lithium Battery
A 3.7v lithium battery, such as the 18650 battery, works best when users follow the correct charging practices. The fully charged voltage for this type of rechargeable battery is 4.2 volts per cell. This value is known as the full-charge voltage. Charging above this level can cause overheating, loss of capacity, and safety risks. The maximum charging termination voltage should always stay at 4.2 volts to protect the battery.
Charging a 3.7v lithium battery within the recommended range helps maximize its cycle life. Users should avoid letting the voltage drop below 3.0 volts. Deep discharges can damage the battery and reduce its lifespan. Many experts suggest that partial charges, such as keeping the battery between 20% and 80%, help extend battery life. Battery management systems (BMS) monitor and regulate voltage to prevent overcharge and deep discharge.
Tip: Keep the charging temperature between 15°C and 35°C. This range helps prevent fast battery degradation.
A 3.7v lithium battery will last longer and perform better when users follow these charging habits:
- Avoid charging to 100% and discharging to 0% every time.
- Use a charger that matches the battery’s specifications.
- Store the battery at about 50% charge if not in use for a long time.
Manufacturer Guidelines
Manufacturers provide clear instructions for charging a 3.7v lithium battery. The nominal voltage, 3.7 volts, shows the average working voltage, not the charging voltage. The standard full-charge voltage is 4.2 volts per cell. This value is the target for optimal charging. Some special long-life batteries use a lower full-charge voltage, such as 3.92 volts, to extend their lifespan, but this reduces capacity.
Charging follows two main steps. First, the charger uses a constant current until the battery reaches the full-charge voltage. Then, the charger switches to constant voltage mode, holding the voltage steady while the current drops. Charging stops when the current falls below a set level.
Protection circuits play a key role. They cut off charging if the voltage goes above 4.3 volts. This feature prevents damage and keeps the battery safe. Charging above 4.2 volts, even up to 4.3 volts, is considered overcharging. This practice shortens battery life and increases risk.
| Parámetro | Value / Range | Notas |
|---|---|---|
| Tensión nominal | 3.7 V | Average operating voltage of 18650 lithium-ion cells |
| Tensión de carga completa | 4.2 V | Maximum recommended charging voltage; exceeding this risks battery damage |
| Charging Cut-off Voltage | 4.2 V | Voltage at which charging should stop |
| Tensión de corte de descarga | 3.0 V | Minimum safe voltage before battery is considered discharged |
| Charging with Protection Board | 4.8 V to 5.2 V (input) | Protection board allows charging from 5V USB source but regulates cell voltage to 4.2V |
Some users choose a lower charging voltage, such as 4.0 volts, to make the battery last longer. This method reduces the total capacity but increases the number of cycles the battery can handle. The best practice is to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for each 18650 battery.
Tensión de almacenamiento
Storing a 18650 battery at the right voltage helps prevent capacity loss and keeps the battery healthy. Experts recommend storing a 3.7v lithium battery at about 40% to 60% charge, which is around 3.6 to 3.7 volts per cell. Storing at full charge, or 4.2 volts, causes faster capacity loss, especially at high temperatures. Storing at too low a voltage, below 2.5 volts, can damage the battery and cause breakdown.
Manufacturers often store lithium-ion batteries at about 15°C and 40% charge. Smart chargers with storage modes can set the voltage to about 3.7 volts. This feature makes it easy to keep the battery at the best storage voltage.
| Voltage Range (Volts) | State of Charge (%) | Effect on Battery Storage | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.2 (Full charge) | 100% | High stress, faster capacity loss | Avoid storing at full charge |
| 3.6 – 3.7 | 40-60% | Minimizes capacity loss by reducing stress and degradation | Recommended storage voltage |
| 3.3 | ~20-30% | Minimal capacity loss (0% to 0.4% per year) | Best for long-term storage if cautious |
| ~3.0 | Lower than 3.3 | Risk of over-discharge, limited capacity | Use with caution |
Storing batteries in a cool, dry place further reduces capacity loss. The following chart shows how storage voltage and temperature affect battery capacity loss over time:
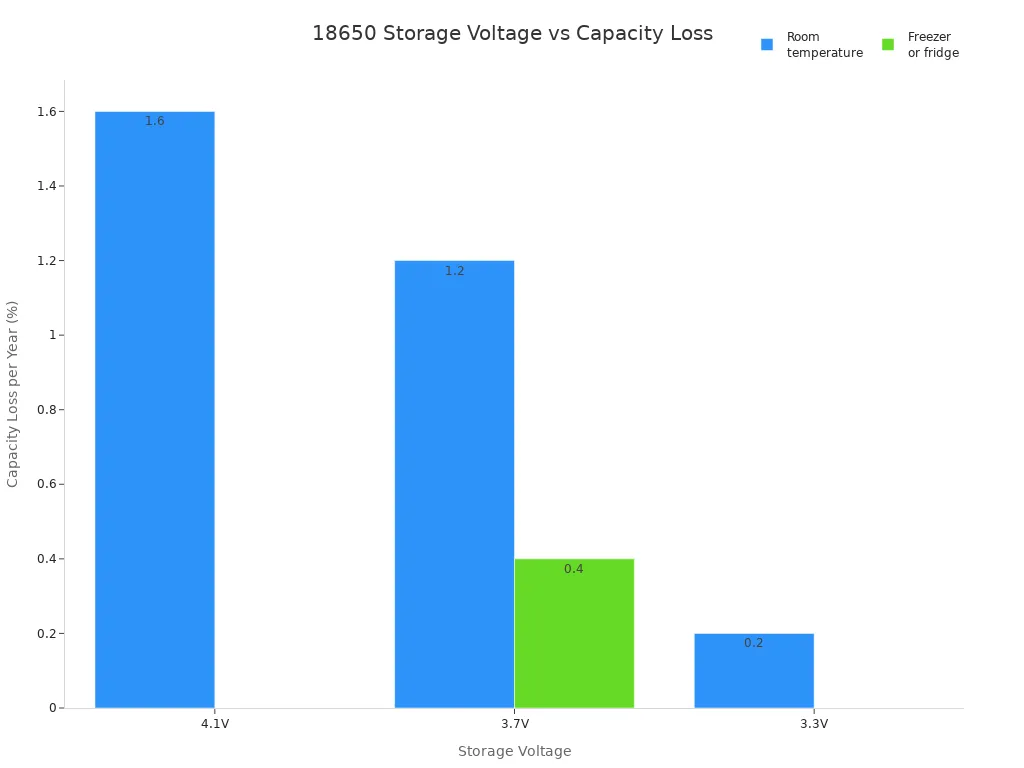
Note: Always avoid storing a 18650 battery at full charge or in hot places. Use a battery case to prevent short circuits and check the voltage every few months during long-term storage.
A 3.7v lithium battery will last longer and stay safer when users store it at the right voltage and temperature. Following these storage tips helps every rechargeable battery deliver reliable power for years.
Setting and Monitoring
Chargers
Selecting the right charger is essential for safe and effective use of any 18650 battery. Modern chargers use constant current charging at the start, then switch to constant voltage charging as the battery nears full capacity. This process keeps the charging current steady and adjusts the voltage to match the battery’s needs. Smart chargers now include features such as overcharge protection, temperature monitoring, and short circuit protection. These features help prevent fires or explosions and keep the battery voltage within safe limits. A good charger will also display the charging current and voltage, making it easier to track the charging process. Users should always choose a charger designed for 18650 batteries. Using the wrong charger can damage the battery or create safety risks.
Tip: Always check that the charger supports the correct charging current for your battery. Too high a charging current can overheat the battery, while too low a current can slow down charging.
Monitoring Tools
Monitoring the voltage of a 18650 battery during charging helps prevent overcharging and deep discharge. Many users rely on dedicated battery testers such as the XTAR VC8 or LiitoKala Lii-500. These testers show real-time voltage and charging current on an LCD screen. They also test capacity and internal resistance, helping users spot weak batteries early. Some advanced systems use voltage dividers with microcontrollers to track voltage and trigger warnings if levels drop too low. Battery management ICs, like those from Texas Instruments, offer precise monitoring for multiple cells and support real-time data access. These tools help users keep batteries healthy and reduce replacement costs.
Note: In series packs, monitoring each cell’s voltage is critical. Without per-cell monitoring, some cells may overcharge while others undercharge. This imbalance can shorten battery life and increase safety risks. A battery management system (BMS) ensures balanced charging and protects every cell.
Consejos de seguridad
Battery safety organizations recommend several steps for setting and monitoring 18650 battery voltage:
- Store batteries at about 50% charge in a cool, dry place.
- Use only chargers made for 18650 batteries and never exceed the recommended charging current.
- Set the maximum charge voltage per cell at 4.2V and keep the minimum above 2.7V.
- Cover battery terminals with insulating material to prevent short circuits.
- Inspect batteries often for swelling, leaks, or unusual odors. Stop using any battery that shows these signs.
- Never mix batteries of different brands, capacities, or charge levels in the same device or storage container.
- Use a BMS or protection circuit module in series packs to monitor per-cell voltage and prevent imbalances.
- Keep a log of voltage readings and maintenance checks to spot problems early.
Following these tips helps every user get the most from their 18650 battery while staying safe.
Charge voltage parameters shape the lifespan and safety of every 18650 battery. Research shows that lower charge voltages slow capacity loss, while higher voltages give more power but speed up wear. Users should always follow recommended voltage ranges and use proper charging equipment. To maximize 18650 battery life and safety, follow these tips:
- Charge at 4.0–4.1 V for daily use
- Use charging currents below 1 A per cell
- Avoid charging below 0°C
- Store at 40–60% charge in a cool place
- Only charge to 4.2 V for long trips
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
What happens if someone charges a 18650 battery above 4.2 volts?
Charging above 4.2 volts causes the battery to heat up and lose capacity. The battery may swell or even catch fire. Always use a charger with overcharge protection.
Can a 18650 battery be charged with any USB charger?
Not every USB charger works safely. Only chargers made for 18650 batteries control the voltage and current. Using the wrong charger can damage the battery or cause safety risks.
How often should users check the voltage of stored 18650 batteries?
Users should check stored batteries every three months. This helps prevent over-discharge. If the voltage drops below 3.0 volts, recharge the battery to the recommended storage level.
Why does storing a 18650 battery at full charge reduce its life?
Storing at full charge puts stress on the battery’s chemistry. The battery loses capacity faster and may age quickly. Store at 40–60% charge for best results.
Is it safe to use different brands of 18650 batteries in one device?
Mixing brands or capacities can cause imbalances. The device may overcharge or over-discharge some cells. Always use matching batteries for safety and longer life.

