
The right battery powers the “smart” in your smart home devices. Your battery selection is critical for reliable smart home technology. A successful choice for your IoT device balances four key pillars. This ensures your IoT device has the best battery.
- Chemie: The type of battery, such as lithium batteries.
- Power Needs: The energy your IoT battery requires.
- Körperliche Fitness: The size and shape of the IoT battery.
- Safety & Longevity: The safety of the IoT battery.
Key Factors for Lithium Battery Selection
Your first major decision involves choosing between a rechargeable or non-rechargeable battery. This choice directly impacts your IoT device’s cost, maintenance, and user experience. Think of it as picking the right type of athlete for a specific race.
Rechargeable vs. Non-Rechargeable
You can view non-rechargeable (primary) lithium batteries as ‘marathon runners’. They are perfect for low-drain, set-and-forget IoT devices. These long-lasting power sources are ideal for remote sensors or security cameras that need a reliable battery with a long lifespan. A quality primary battery provides steady power for years.
On the other hand, rechargeable (secondary) batteries are ‘sprinters’. You should choose a rechargeable battery for high-drain IoT devices that you use frequently. While the initial cost is higher, a rechargeable battery saves you money over time. You can recharge them hundreds of times, which reduces waste. A key benefit of a rechargeable battery is its consistent high energy output. It maintains a steady voltage, ensuring stable battery performance until the battery is nearly empty. This makes a rechargeable battery an efficient and cost-effective choice for many IoT applications.
Anmerkung: Choosing a rechargeable battery is a great step toward sustainability. Reusing a rechargeable battery many times conserves resources and creates less waste compared to single-use options.
Common Lithium Chemistries
The term “lithium” covers a family of battery types, each with unique strengths. The right chemistry is critical for your IoT battery solutions. Your choice affects the battery’s performance, size, and cost. Understanding the most common options helps you find the best battery solution for your IoT project.
Here is a simple comparison of three popular chemistries for IoT devices:
| Chemie | Ideal Use Case | Relative Cost | Die Energiedichte |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion (Li-ion) | General consumer electronics, portable IoT devices | Mäßig | Hoch |
| Lithium-polymer (LiPo) | Drones, smartphones, devices needing a thin form factor | Moderate-High | Sehr hoch |
| Lithium Thionyl Chloride (LiSOCl₂) | Remote monitoring, utility meters, low-power sensors | Hoch | Highest |
Selecting the correct chemistry ensures your IoT device has a battery with the right power profile and a long lifespan, delivering the quality and reliability you need.
Define Your Power Needs

You must define your device’s energy needs to choose the right battery. Think of this as creating a “power budget.” Like a financial budget, you must account for all energy expenses. For an IoT device, this includes power used during active operation and while in sleep mode. A clear power budget is the foundation for selecting the best IoT battery solutions.
Powering Smart Home Devices
The communication technology in your smart home devices greatly affects battery consumption. Wi-Fi devices, for instance, use significantly more power than Zigbee or Z-Wave alternatives. Zigbee is known for its low power consumption, which helps extend battery life. This focus on energy efficiency is critical for battery-powered IoT sensors. Your choice of protocol will directly influence how often you need to replace or recharge the battery. Better energy efficiency means a longer-lasting battery.
Calculate Capacity (mAh)
To find the right battery capacity, you need to calculate the average power your IoT device uses. Many IoT devices spend most of their time in a low-power sleep mode. You cannot base your calculation only on the active power draw. You must consider both states.
You can find the average consumption with a simple calculation:
Average Current = (Active Current × % Active Time) + (Sleep Current × % Sleep Time)For example, an IoT device might use 200mA for 10% of the time and just 0.01mA for the other 90%. This calculation gives you a true picture of the battery power needed for reliable performance.
Match the Correct Voltage
Matching the battery voltage to your device’s circuit is crucial for safety and battery performance. Using the wrong voltage can lead to overcharging or over-discharging. These conditions damage the battery and shorten its lifespan. Most lithium batteries for smart home devices have a nominal voltage of 3.7V and charge up to a maximum of 4.2V.

Your IoT device’s electronics must be designed to operate within this voltage range. A proper match ensures the battery operates safely and delivers consistent power. This protects both the battery and your IoT device.
Ensure the Right Physical Fit

A battery is useless if it does not fit inside your IoT device. The physical form factor is just as important as the internal chemistry. You must consider the battery’s dimensions, weight, and how it will handle the operating environment of your IoT product. A perfect fit ensures both reliability and a good user experience for your IoT device.
Balance Size, Weight, and Capacity
You must find the right balance between the battery’s capacity, its size, and its weight. Generally, a battery with a higher capacity (more mAh) will be physically larger and heavier. This is because it needs more material inside to store energy. This trade-off directly impacts your IoT device’s final design and how a user handles it. A bulky battery can make a sleek IoT device feel clumsy.
The design of smart home technology needs to tackle the issues that only arise when products are used in ‘real’ home environments… Examples include… a battery that needs replacing regularly.
When designing the housing for your IoT device, avoid these common mistakes:
- Not leaving enough space: A lithium battery can swell slightly over time, especially with heat. You should leave a small amount of extra space to prevent the battery from damaging the case.
- Leaving too much space: If the battery compartment is too large, the battery can rattle. This feels cheap and can damage the battery or its connections over time.
Consider the Operating Temperature
Beyond size, you must consider the environment where your IoT device will operate. Temperature greatly affects battery performance, safety, and lifespan. Lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries have specific temperature ranges for safe charging and discharging.
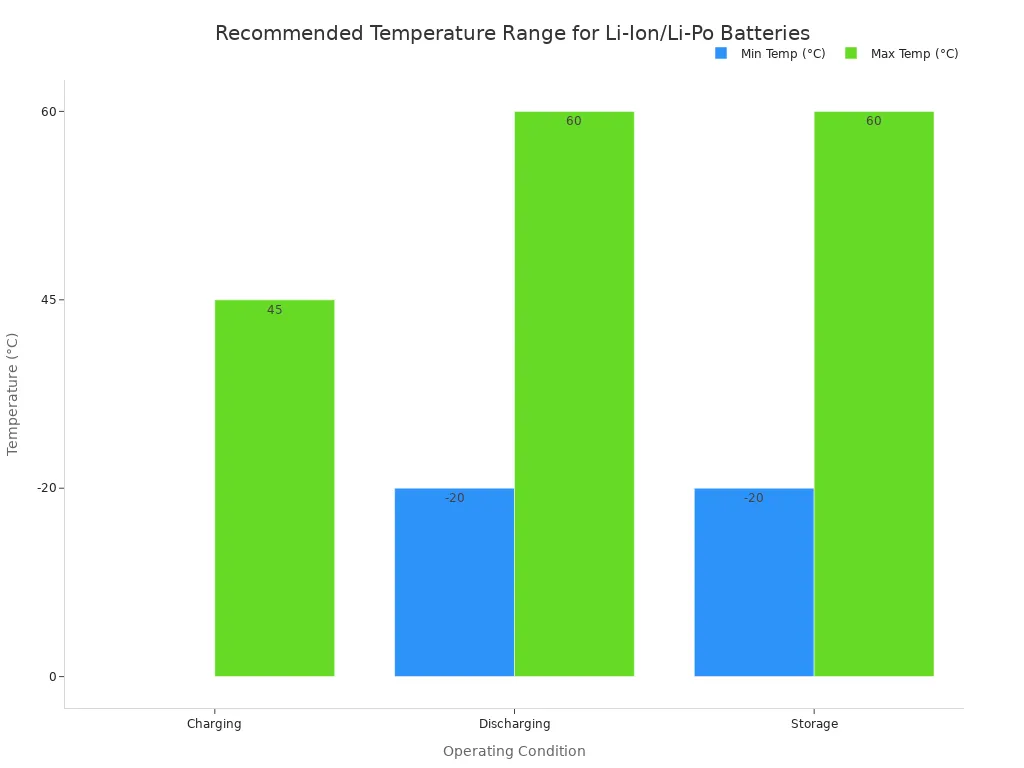
Operating a battery outside these ranges causes problems. In extreme cold, the battery’s internal chemistry slows down, reducing its available capacity. Charging in freezing temperatures can cause permanent damage. High heat causes the battery to age faster and increases safety risks. This is especially important for an outdoor IoT device or for sensors placed in unconditioned spaces. Choosing the right IoT battery solutions means planning for the expected temperature extremes.
Prioritize Safety and Longevity
Choosing a battery goes beyond power and fit. You must prioritize the safety and longevity of your IoT device. A quality battery includes features that protect it from failure. Following best practices ensures you get a reliable, long-lasting power source for your IoT project. This focus on safety and reliability is essential for any successful IoT device.
Verify Built-in Safety Circuits
A quality lithium battery for your IoT device should always include a built-in safety circuit. This is often a Protection Circuit Module (PCM) or a more advanced Battery Management System (BMS). These circuits are the brain of the battery, protecting it from dangerous conditions.
A good safety circuit is non-negotiable for any IoT application. Using an unprotected battery is extremely risky and can lead to device failure or fire.
Key functions of these circuits include:
- Schutz vor Überladung: Prevents the battery voltage from getting too high during charging.
- Schutz vor Überentladung: Stops the battery from draining too low, which can cause permanent damage.
- Short-Circuit Protection: Instantly cuts power if a short circuit occurs, preventing thermal runaway.
A BMS offers even more advanced features for your IoT device, like cell balancing and health monitoring, which contribute to a longer lifespan and better performance.
Best Practices for Charging and Storage
How you charge and store your battery directly impacts its long lifespan. Proper care ensures your IoT device remains reliable. For a long-lasting battery, you should avoid practices that cause unnecessary stress.
When charging your IoT battery, always use a charger designed for lithium chemistry. For optimal health, try not to charge it to 100% every time. Charging to about 80% can significantly extend the battery’s lifespan. For long-term storage, you should not leave the battery fully charged or completely empty.
Pro Tip: Store your lithium battery at a 40-60% state of charge in a cool, dry place. This simple step minimizes degradation and keeps your IoT battery ready for future use.
Look for Safety Certifications
Certifications from independent labs are a great sign of a quality product. These marks show that the battery has passed rigorous tests for safety. When selecting your iot battery solutions, look for these common certifications on the product datasheet.
- UN/DOT 38.3: Ensures the battery is safe for transportation.
- IEC 62133: A key international standard for battery safety.
- UL 2054 / UL 1642: A demanding U.S. standard that signals a very reliable and safe product for your IoT device.
Choosing a certified battery gives you confidence in its construction and safety, which is critical for any consumer-facing IoT product.
Choosing the best IoT battery requires balancing chemistry, power, fit, and safety. Your choice ensures your IoT device has a reliable, long-lasting battery. Investing time in selecting a quality battery guarantees the long lifespan and reliable performance of your smart home devices. A quality IoT battery is key for a quality IoT product. This ensures your IoT project has a battery with a great lifespan.
Before committing, always buy a small batch of lithium batteries to test. Real-world testing in your actual IoT device and environment is the ultimate confirmation of your choice for your IoT battery.
FAQ
What is the main difference between Li-ion and LiPo?
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries use a liquid electrolyte inside a rigid metal case. Lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries use a gel-like electrolyte in a flexible pouch. This allows LiPo batteries to be made in thinner, more custom shapes for your devices.
Can I use any USB charger for my lithium battery?
No, you should not use just any charger. You must use a charger specifically designed for lithium chemistry. Using the wrong charger can lead to overcharging. This damages the battery and creates a significant safety risk for your IoT device.
Why did my lithium battery swell up?
A swollen battery is a sign of internal failure. This can happen from overcharging, physical damage, or simply old age. The swelling is caused by gas buildup inside the battery cell.
Safety Alert ⚠️: You must stop using a swollen battery immediately. Safely dispose of it according to your local regulations for hazardous waste.
How long does a rechargeable lithium battery last?
A battery’s lifespan is measured in charge cycles. Most last between 300 to 500 full cycles. Your usage habits, charging practices, and the operating temperature all affect how long the battery will perform well. Proper care extends its life.

