Definition in einem Satz
A Battery Management System (BMS) is an electronic system that monitors, manages, and protects rechargeable batteries or battery packs, ensuring their safe operation, optimal performance, and extended lifespan.[1]
Ausführliche Erläuterung
A BMS is essential for any application using lithium-ion or other advanced rechargeable batteries. It continuously tracks key parameters—such as voltage, current, and temperature—across individual cells or modules. By processing this data, the BMS estimates the battery’s State of Charge (SOC) and State of Health (SOH), balances cells, and communicates with external devices. Its primary goals are to prevent unsafe conditions (like overcharging, deep discharging, or overheating), maximize usable capacity, and prolong battery life. Modern BMS solutions also support remote monitoring, data logging, and integration with smart systems.[2]
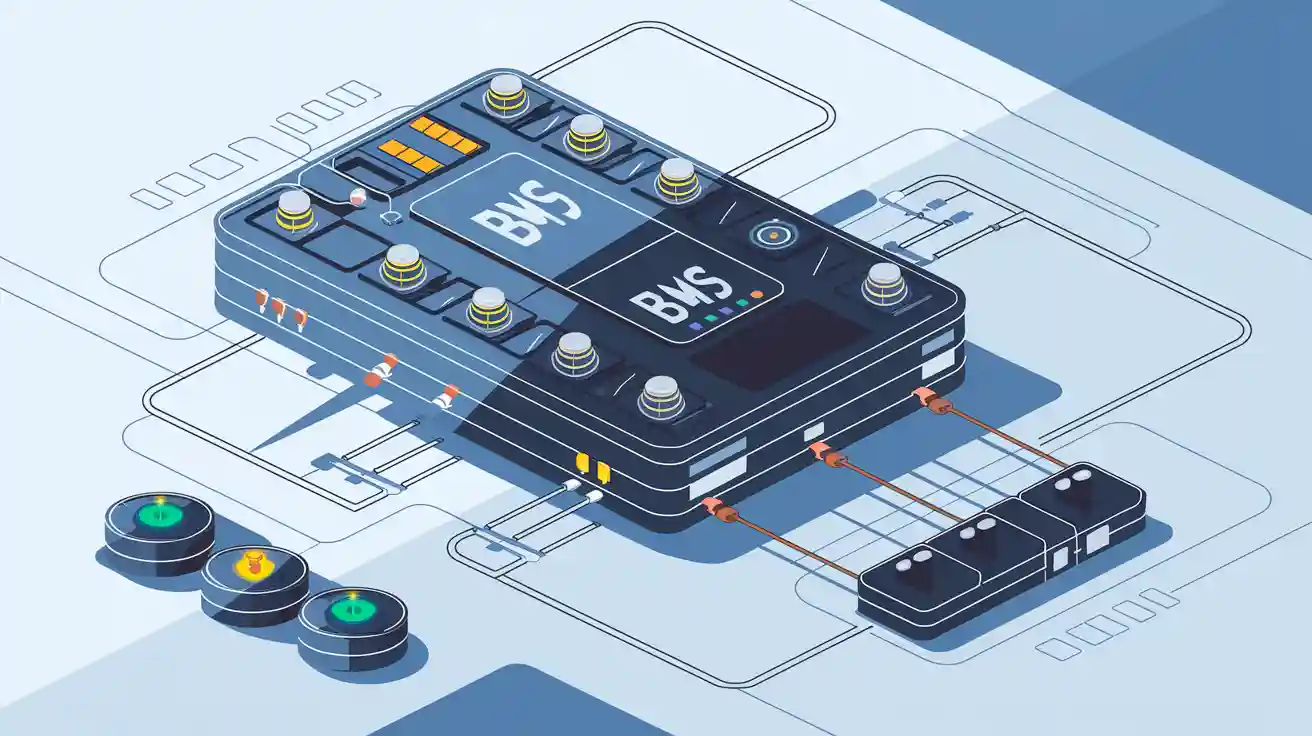
Key Components of a BMS
- Monitoring Module: Continuously measures voltage, current, and temperature of each cell or module.
- Protection Circuitry: Detects and responds to overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, short circuit, and over/under-temperature events.
- Cell Balancing: Ensures all cells maintain similar charge levels, using passive (resistor-based) or active (energy-shuttling) methods.
- State Estimation: Calculates SOC and SOH using advanced algorithms.
- Communication Interface: Connects with external systems via CAN bus, wireless, or other protocols for data exchange and remote diagnostics.
- Control Logic: Executes safety actions, such as disconnecting the battery or adjusting charging rates.
 Figure: BMS (right) offers advanced management, monitoring, and communication compared to basic PCM/PCB protection (left). Source: Grepow
Figure: BMS (right) offers advanced management, monitoring, and communication compared to basic PCM/PCB protection (left). Source: Grepow
Anwendungen in der realen Welt
BMS technology is critical in electric vehicles (EVs), energy storage systems, consumer electronics, smart home devices, and industrial equipment. For example, Yungbang develops custom lithium battery packs for sectors like smart home and industrial automation, integrating advanced BMS solutions to ensure safety, performance, and compliance with international standards (UL, CE, UN38.3, IEC 62133). In high-rate or extreme temperature scenarios, a tailored BMS is vital for reliable operation and longevity. Case studies from companies like Maxwell/ION Energy show how custom BMS designs enable large-scale deployment of e-bikes and industrial batteries across Europe, balancing compactness, safety, and smart features.
Industry Standards and Certification
A robust BMS should comply with international safety and quality standards, such as:
- UL 1642/2054/1998 (United States)
- CE (European Union)
- UN38.3 (Transport safety)
- IEC 62133 (Global battery safety) These certifications ensure the BMS and battery pack meet stringent requirements for electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and environmental protection.[3]
BMS vs. Protection Circuit Board (PCB/PCM)
While a Protection Circuit Board (PCB) or Protection Circuit Module (PCM) provides basic safeguards (overcharge, overdischarge, overcurrent), a BMS offers comprehensive management: real-time monitoring, cell balancing, state estimation, data communication, and smart control. This makes BMS indispensable for complex, high-value, or safety-critical battery applications.[4]
Latest Trends
Modern BMS development is moving toward wireless communication, AI-driven analytics, cloud integration, and enhanced cybersecurity. These advances enable predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and seamless integration with smart grids and IoT platforms.[5]
Verwandte Konzepte
- State of Charge (SOC): The current charge level of a battery relative to its capacity.
- State of Health (SOH): An indicator of battery aging and remaining useful life.
- Cell Balancing: Techniques to equalize charge among cells.
- CAN Bus: A communication protocol widely used in automotive and industrial BMS.
- Smart Battery: A battery pack with integrated BMS and communication features.
Looking for custom lithium battery solutions with advanced BMS? Explore Yungbang’s offerings or contact us for tailored battery packs that meet the highest safety and performance standards.
Referenzen:

