
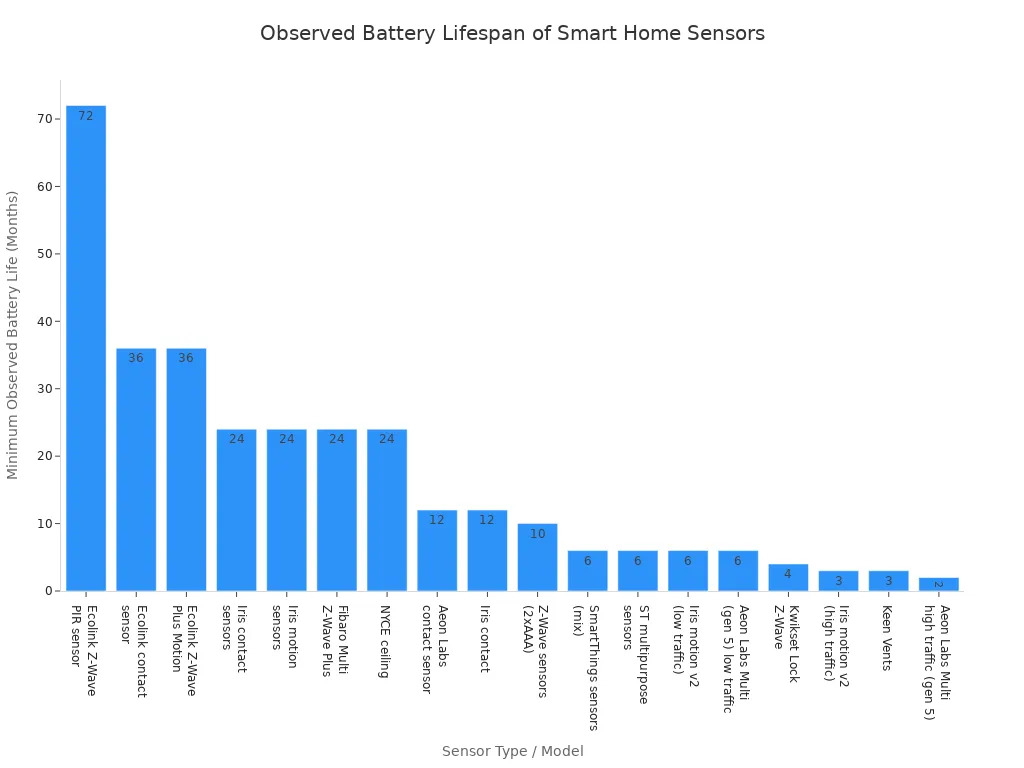
You can improve battery life for your smart home devices through simple setting adjustments. The battery life of smart home sensors varies greatly, as some devices drain their battery in months while others last for years. This chart shows just how wide that range can be depending on the sensor.
You can boost efficiency and save energy by adjusting communication frequency, sensor sensitivity, feature management, and power management modes.
These tweaks reduce maintenance, ensuring your energy-efficient devices have a longer life and operate reliably when you need them most.
Adjust Communication Frequency
One of the biggest drains on a battery is communication. Your smart home devices wake up from a low-power sleep mode to send updates to your hub. You can extend battery life by telling your sensor to report less often. This adjustment reduces energy consumption significantly.
Understanding Reporting Intervals
A “reporting interval” or “polling rate” is the schedule your sensor follows to wake up and send data. Each time a sensor node wakes from its sleep mode, it uses energy. A shorter interval means more frequent updates but also higher power consumption. A longer interval saves battery power but provides less frequent data. The goal is to find a balance that works for your needs. Each time a sensor node wakes from its sleep mode, it uses a small amount of battery.
Find and Change App Settings
You can usually find these settings within your smart home app. Navigate to the specific sensor you want to adjust. Look for an “Advanced” or “Device Configuration” menu. Some apps, like Hubitat, allow direct changes to the reporting interval. For other platforms, you might need to install a custom driver to access these controls. The sensor node will then adopt the new sleep mode schedule.
Recommended Intervals for Sensors
The right interval depends on the sensor’s job. For high-traffic areas, a shorter “cool-off” time is better. For low-traffic zones, you can extend the time to save your battery.
| Traffic Area | Recommended Cool-off Time |
|---|---|
| High-traffic (e.g., hallways) | 10 seconds |
| Low-traffic (e.g., garages) | 1 minute |
For temperature or humidity sensors, a fast reporting interval is often unnecessary. An interval of 15 to 30 minutes is usually enough to balance data accuracy and extend battery life. The sensor node will wake from its sleep mode less often, extending its life.
Communication Protocol Impact
The communication technology your smart home devices use also affects battery consumption.
- Wi-Fi: These devices are power-hungry. You should use them only when they can be plugged into an outlet.
- Zigbee and Z-Wave: These protocols are designed for low-power devices like a battery-operated sensor. They use a mesh network, which helps a sensor node maintain a stable connection from its sleep mode. Both offer excellent battery life, though performance can vary based on the specific product’s design. A longer life for your devices is the result. The sensor node will have a better sleep mode.
Optimize Sensor Sensitivity
Every time your sensor detects an event, it wakes up and uses its battery. A highly sensitive sensor wakes up for small, unimportant events. This constant activity drains the battery much faster. You can improve battery life by fine-tuning these sensitivity settings on your smart home devices. This simple optimization ensures your devices only report what truly matters.
Why High Sensitivity Drains Your Battery
A sensor with high sensitivity is like a person who is easily startled. It reacts to everything. A passing car’s headlights, a curtain moving in a breeze, or a small temperature shift can trigger a report. Each report uses a small amount of energy. When these reports happen frequently, the cumulative energy consumption adds up, shortening the battery life of the sensor node.
Your goal is to make your sensor less “jumpy.” This reduces unnecessary wake-ups and lowers the overall power consumption of the sensor node.
Adjusting Motion Sensor Sensitivity
You can adjust the sensitivity settings on your motion sensors to reduce these unnecessary triggers. This is very useful in areas with frequent background movement that would otherwise cause the sensor to activate too often. Lowering the sensitivity prevents the sensor node from waking up for minor events, which extends the life of your battery.
Common causes of false triggers include:
- Pets walking around
- Robot vacuums
- Ceiling fans or air vents
- Sunlight changes
Adjusting this setting in your app tells the sensor to ignore these small movements, saving precious battery power.
Setting Temperature and Light Thresholds
This same principle applies to other sensors, like those for temperature, humidity, or light (Lux). These devices report when a measured value changes by a specific amount, or “threshold.” A smaller threshold causes more frequent reports. You can reduce this data transmission and save energy.
| Sensor Type | High-Consumption Setting | Battery-Saving Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Temperatur | Report on every 0.5°F change | Report on every 2°F change |
| Light (Lux) | Report on every 10 Lux change | Report on every 100 Lux change |
Setting a wider threshold means the sensor node sends fewer updates, reducing battery consumption and extending the life of your smart home devices.
Extend Sensor Battery Life via Optimization
This fine-tuning is a key part of smart home optimization. By carefully adjusting sensitivity and thresholds, you tell your devices what is important. This simple action reduces the number of times the sensor node needs to wake up and transmit data. The result is a longer life for your battery and more reliable performance from your sensors.
Core Settings for Smart Home Devices

Many smart home devices come with extra features that you might not need. These features often run in the background, quietly using energy and shortening your battery life. You can improve the battery life of your smart home devices by turning off these non-essential functions. This simple step reduces the overall power consumption of each sensor.
Turning Off LED Status Indicators
That small blinking light on your sensor serves a purpose, but it also draws power. An LED indicator constantly uses a small amount of energy to show the device’s status. While one LED won’t drain a battery overnight, this continuous use adds up over the life of the battery. You can often disable these lights in the device settings. This is an easy way to save a little extra energy and extend the life of your sensor.
Disabling Secondary Sensor Functions
Some smart home devices are multi-talented. For example, a motion sensor might also include a temperature or light sensor. If you only need the motion-detecting feature, the other functions are using your battery for no reason. Check your app settings to see if you can disable any secondary sensor functions. This tells the sensor node to stop monitoring and reporting on data you do not use, which directly saves battery power. Each disabled feature reduces the workload on the sensor node.
Managing Tamper and Other Alerts
Frequent notifications can be a major drain on your battery. Alerts for things like tampering or low battery are useful, but constant notifications create “notification noise” that uses energy. Each alert wakes the sensor node, uses data to communicate, and can even light up your phone screen. This process significantly drains the battery. One user found that frequent push notifications used a large amount of cellular data, which quickly killed their battery.
You can optimize your settings to reduce these unnecessary alerts. This prevents the sensor node from waking up too often and keeps your devices running longer.
- Disable push notifications for alerts you do not need.
- Review your app settings to reduce the frequency of non-critical alerts.
How Unused Features Drain Your Battery
Every feature on a sensor requires energy to operate. When you leave unused functions active, the sensor node must still power them. This includes LEDs, secondary sensors, and frequent alert systems. These small power draws accumulate, shortening the total life of your battery. By disabling what you don’t need, you streamline the sensor’s job. The sensor node then focuses only on its main task, resulting in a much longer battery life for your smart home devices.
Effective Power Management Strategies

Effective power management is one of the best ways to get more life from your battery. Many smart home devices include built-in settings designed to reduce energy use. You can activate these features to significantly lower power consumption. This smart power management ensures your sensor operates efficiently.
Finding and Using Power-Saving Modes
You can find power-saving options in your device’s settings menu or smart home app. Some devices, like smart displays or appliances, offer automatic power-down modes. You can use scheduling timers to put a sensor into a low-power sleep mode during specific times. Activating these modes is a simple step toward better power management.
Understanding Sleep and Eco Modes
Your devices might offer different types of low-power states, such as a sleep mode or an “eco mode.” These two modes serve different purposes.
Sleep Mode: This mode focuses on comfort and quiet operation, often for nighttime. It might make small adjustments to save some energy without shutting down completely. The sensor node remains in a light sleep mode. Eco Mode: This mode prioritizes maximum energy savings. It aggressively reduces functions and is best used when you are away from home. The sensor node enters a deeper sleep mode.
Understanding the difference helps you choose the right power management setting. A sensor in the correct sleep mode uses less battery.
When to Use Power–Saving Features
You should enable power-saving features based on your daily routines. For example, you can use them in these situations:
- When you are away: Set your sensor to enter a deep sleep mode when the house is empty.
- Based on a schedule: Program your devices to use a low-power sleep mode overnight.
Using a sleep mode during periods of inactivity is a core power management strategy. The sensor node will wake up less, extending battery life.
The Role of Deep Sleep States
A deep sleep mode is the ultimate battery-saving feature. In this state, the sensor node shuts down most of its components, including its radio. It uses almost no power but remains registered to your network. When the sensor node needs to send an update, it can wake up without having to reconnect completely. While waking up uses a bit of energy, the long periods in a deep sleep mode result in massive battery savings over time.
Strengthen Your Network Connection
A weak network signal forces your smart home devices to work harder. This extra effort drains the battery much faster. You can improve battery life by ensuring your devices have a strong, stable connection to your smart hub. A better signal means less energy is needed for communication.
Why a Strong Signal Boosts Battery Life
A device with a poor connection uses more power to send and receive signals. This increased power consumption shortens the life of the battery. Think of it like your cell phone in an area with bad reception; the battery drains quickly as it constantly searches for a signal. Your sensor does the same thing.
- A weak signal forces a device to work harder to stay connected.
- This increased effort leads to higher energy consumption.
- The device continuously searches for a stronger signal, which is an intensive process.
Optimizing Smart Hub Placement
You can improve your network signal by moving your smart hub to a better location. The ideal spot is central to your home. This helps the signal reach all your devices more easily.
Place your hub in an open, elevated space, like on a shelf. Avoid putting it on the floor, inside cabinets, or near large metal objects like refrigerators. Keep it away from other electronics that can cause interference, such as microwaves or TVs.
Using Signal Repeaters and Mesh Networks
If your home is large, you may need to extend your network’s reach. You can use signal repeaters oder mesh network nodes to strengthen the signal for a distant sensor. Many plugged-in smart devices, like smart plugs or light bulbs, can act as repeaters for Zigbee and Z-Wave networks. Adding one of these between your hub and a far-away sensor can dramatically improve its connection and extend its battery life.
Running Network Optimization Tools
Some smart home platforms offer tools to help you manage your network. Z-Wave and Zigbee systems often have a “network heal” or “repair” function. Running this tool helps your devices find the most efficient communication paths. This optimization reduces the energy needed for data transmission and can extend the life of your battery.
You can improve battery life with these simple setting adjustments. Studies show adaptive settings can dramatically increase battery duration, boosting efficiency. To get the most life from your battery, focus on these key actions:
- Reduce reporting frequency
- Lower sensor sensitivity
- Disable unused LEDs
- Enable power-saving modes
These tweaks help you improve battery life and create a more efficient smart home, extending the life of your battery. This approach ensures a longer battery life for your devices.
FAQ
What is the fastest way to save battery? 🔋
You can save the most battery by reducing the reporting frequency. This setting tells your sensor to send updates less often. Fewer updates mean the device wakes up less, which directly extends battery life. It is a very effective change.
Do smart plugs use battery power?
No, smart plugs do not use batteries. You plug them directly into a wall outlet for power. They can, however, act as signal repeaters for your Zigbee or Z-Wave network. This helps other battery-powered devices save energy.
How often should I check my device batteries?
You should check battery levels in your smart home app about once a month. Many apps also send you a low-battery notification. This regular check helps you avoid unexpected device failures and keeps your smart home running smoothly.
Why does my new battery drain so fast?
A new battery can drain quickly if the device settings are too aggressive. High sensitivity or frequent reporting intervals cause the sensor to work constantly. You should check these settings first to optimize power consumption and improve battery life.

