Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries have become the standard for drones, RC vehicles, robotics, and many high-performance applications. Understanding LiPo charging voltage—and how cell count, safety thresholds, and charger settings interact—is critical for maximizing battery life and avoiding catastrophic failures.
What is LiPo Charging Voltage?
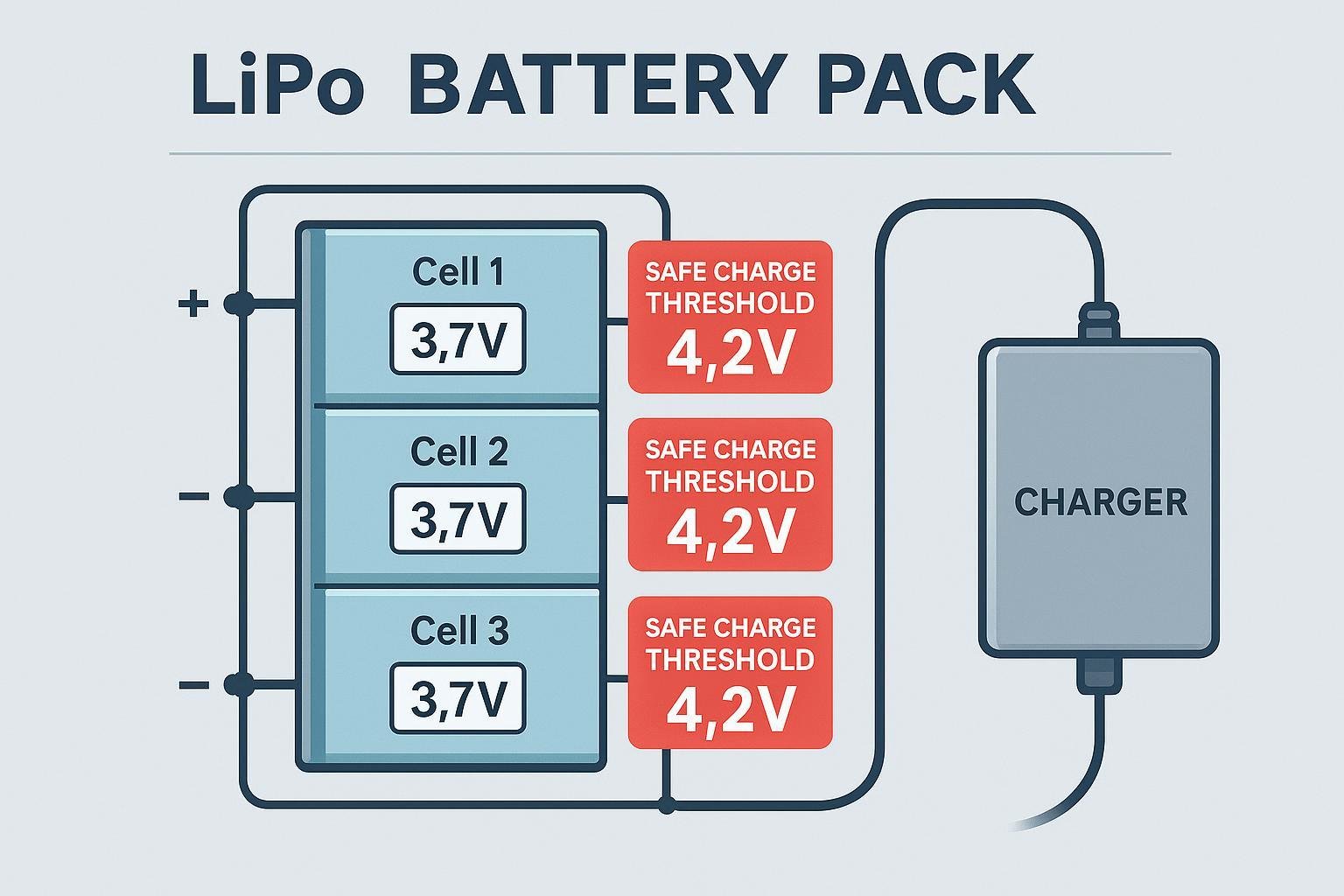
A LiPo battery is made up of one or more cells, each designed with a specific nominal voltage (typically 3.7V per cell) and a maximum safe charging voltage of 4.2V per cell. Charging beyond this value can cause cell swelling, fire, or permanent capacity loss (Batterie-Universität).
Understanding Cell Count: The Basis of Pack Voltage
“Cell count” refers to the number of cells connected in series (denoted as 1S, 2S, 3S, etc.). The total pack voltage is the sum of each cell’s voltage. For safety and optimal performance, you must set your charger to match the exact cell count of your battery pack. Here’s a handy reference:
| Zellzahl (S) | Full Charge Voltage (per cell 4.2V) | Total Pack Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| 1S | 4.2V | 4.2V |
| 2S | 4.2V | 8.4V |
| 3S | 4.2V | 12.6V |
| 4S | 4.2V | 16.8V |
| 6S | 4.2V | 25.2V |
If you incorrectly set the charger for the wrong cell count—say, charging a 3S pack as 4S—you risk overcharging and potential battery failure (Rogers Hobby Center).
Safety Thresholds: Why 4.2V Per Cell Matters
The industry-standard maximum charging voltage for each LiPo cell is 4.2V. This threshold is based on the internal chemistry: Exceeding it can lead to electrolyte breakdown, overheating, swelling, and—at worst—fire or explosion. Real-world incidents (especially in hobbyist drones) usually stem from:
- Overcharging a cell above 4.2V
- Unbalanced charging (cells drift apart in voltage)
- Leaving packs unattended on cheap/unverified chargers
Regulatory standards like UL2054 and IEC62133 exist to guide manufacturers and users toward safer designs and usage, but individual vigilance is crucial.
Charger Settings & Practical Tips
- Select the correct cell count (S number) on your charger. Always double-check—never guess.
- Choose the recommended charge current (usually 1C, where C = pack capacity in Ah).
- Enable the balancing function if your charger supports it—this ensures each cell stops at exactly 4.2V.
- Never leave charging LiPo packs unattended.
- If a cell swells or the pack feels hot, STOP charging immediately.
For added protection, advanced battery packs include a Batterie-Management-System (BMS), but many hobby-grade LiPo packs do not.
Related Concepts & Further Reading
- Batterie-Management-System (BMS)
- Series vs. Parallel Battery Packs
- Li-ion vs. LiPo Batteries: Differences & Safety
Schlussfolgerung
Correct understanding and application of LiPo charging voltage, cell count, and charger settings underpin both battery performance and user safety. Always reference your device’s manual, use quality equipment, and supervise every charging session. Safe charging keeps your equipment—and you—protected.
Referenzen:

