
Overcharging lithium batteries can damage your devices, even if they have built-in protection. You might think lithium-ion batteries stay safe, but protection systems sometimes fail. Overcharging creates several risks:
- Batteries can overheat and swell.
- Fires or explosions may happen if thermal runaway starts.
- You may see bulging, leaks, or hear popping sounds.
- Your device’s lifespan drops with repeated overcharging.
You need to watch for these signs and understand the risks to protect your safety and your tech.
Overcharging Lithium-Ion Batteries

When you hear about overcharging lithium batteries, you might wonder what it really means. Overcharging happens when you keep charging lithium-ion batteries after they reach their maximum voltage. This can occur if the battery management system fails or if you use a faulty charger. Overcharging lithium batteries is one of the most dangerous situations for your devices. It can lead to permanent damage, safety hazards, and even fire or explosion.
Battery Damage
Overcharging lithium-ion batteries causes several types of damage. At first, the battery enters a normal charging phase. If you continue charging past the safe voltage, the battery moves into a severe overcharge stage. Here’s what happens step by step:
- In the early stage, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode without side effects.
- As voltage rises, the cathode metal starts to oxidize, and lithium begins to plate on the anode. This thickens the SEI (solid electrolyte interface) layer and increases internal resistance.
- If you keep charging, lithium plating continues, and metallic dendrites form. These dendrites can pierce the separator, causing internal short circuits and pressure buildup.
Overcharging leads to chemical and physical changes inside the battery. The cathode material breaks down, and the structure becomes unstable. Lithium dendrites grow on the anode, which can cause internal shorts and rapid capacity loss. The battery swells as gases like CO2 and H2 build up. You might notice the battery casing bulging or even popping.
| Phenomenon | Description | Impact on Battery Capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Phase transformation | Cathode materials change structure due to high voltage. | Causes irreversible capacity fade. |
| Mechanical damage | Cracks form in the cathode, letting electrolyte in. | Accelerates internal degradation. |
| Lithium dendrite formation | Lithium metal plates and grows into dendrites. | Leads to short circuits and capacity loss. |
| Thermal effects | High voltage causes electrolyte breakdown and gas production. | Can trigger thermal runaway and degradation. |
| Local charge heterogeneity | Uneven overcharging causes localized damage. | Increases risk of capacity loss. |
Permanent damage from overcharging lithium batteries means you lose battery capacity and shorten the number of charging cycles. Even a few overcharge events can cause irreversible degradation, making your device unreliable.
Safety Hazards
The dangers of overcharging go far beyond just battery damage. Overcharging lithium-ion batteries can trigger thermal runaway, a chain reaction where the battery heats up uncontrollably. This process can cause fire, explosion, and severe property damage. The electrolyte inside lithium-ion batteries is flammable, and overcharging increases the risk of ignition.
Note: Thermal runaway is the main safety hazard in overcharged lithium-ion batteries. It starts with overheating, then chemical reactions speed up, leading to fire or explosion.
Physical signs of overcharge include swelling, venting of gases, smoke, and sometimes flames. In pouch cells, pressure can build up quickly, causing the battery to burst. If one cell overheats, it can affect nearby cells, spreading the hazard.
Here are some common hazards you might face:
- Overheating and thermal runaway incidents
- Internal short circuits from dendrite growth
- Fire and explosion, especially if the battery casing ruptures
- Severe burns, smoke inhalation, and property damage
Statistical data shows that fire incidents from overcharging lithium batteries are not rare. From December 2023 to May 2025, 23 fires were reported in campus buildings, with 78% happening inside. Most incidents involved devices like scooters, e-bikes, and skateboards. About 43% of these devices were charging at the time of the incident.
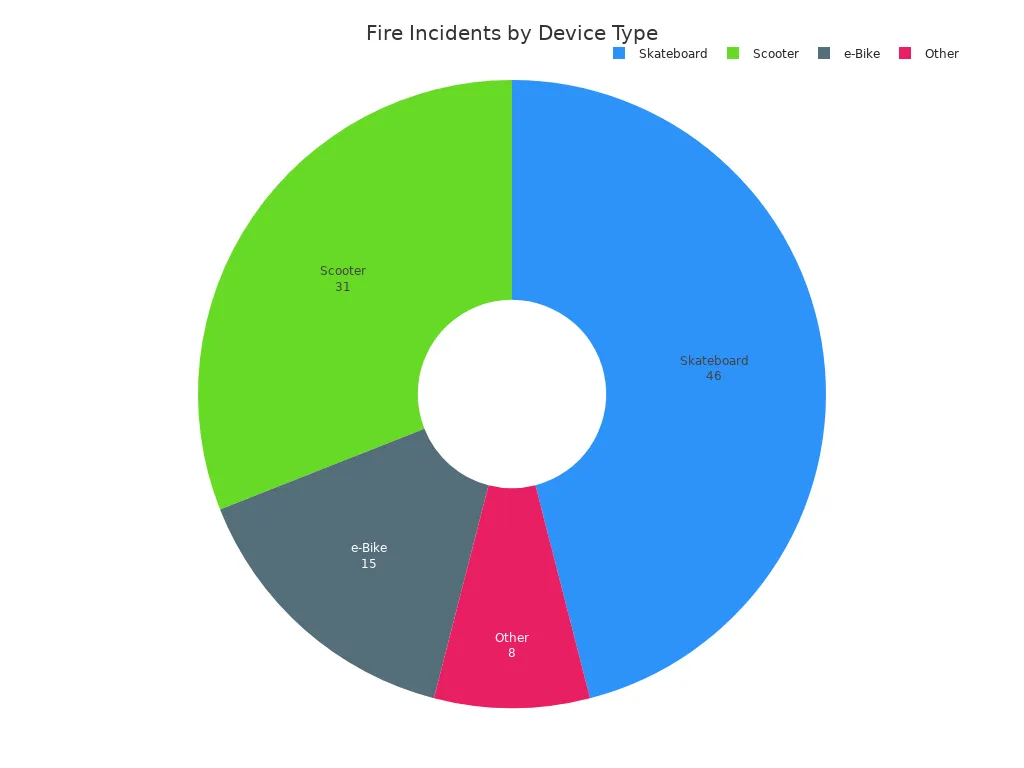
The hazards of overcharging are serious. You risk not only permanent damage to your device but also your own safety.
Performance Loss
Overcharging lithium-ion batteries does not just cause immediate damage. It also leads to long-term performance loss. Each time you overcharge, you reduce the number of charging cycles the battery can handle. The battery loses capacity faster, and its internal resistance increases. This means your device will not last as long on a single charge.
Technical problems like electrolyte breakdown and dendrite formation play a big role in performance loss. Dendrites cause internal short circuits and increase the risk of thermal runaway. The SEI layer becomes uneven and porous, raising impedance and lowering efficiency. Over time, these changes make the battery less reliable and more dangerous.
You might notice your device heats up more during charging, or the battery drains quickly. These are signs of permanent damage from overcharging. Even if you stop overcharging, the damage is often irreversible. The battery will continue to degrade, and the risk of fire or explosion remains high.
Tip: Always use the correct charger and avoid leaving your device plugged in after it reaches full voltage. This simple habit can prevent most hazards and extend your battery’s life.
Overcharging lithium batteries is a serious risk. It causes battery damage, creates safety hazards, and leads to performance loss. By understanding the dangers of overcharging and how voltage affects your battery, you can protect your devices and yourself from permanent damage and thermal runaway.
Built-In Protections
Battery Management Systems
You rely on built-in protections to keep your lithium batteries safe. The battery protection system, also called a battery management system (BMS), acts as the main defense against overcharge and failure. This system works by constantly checking the voltage, current, and temperature of each cell. When the voltage gets close to the safe limit, the battery protection system reduces or stops the charging current. This prevents the battery from going past its designed voltage and keeps you safe.
Here’s how a battery protection system helps prevent overcharge and failure:
- It monitors each cell’s voltage, current, and temperature to keep batteries within safe limits.
- It provides overcharge protection by cutting off charging when voltage or current gets too high.
- It manages heat, making sure batteries do not get too hot during charging.
- It balances the charge between cells, so no single cell gets overcharged.
- It collects real-time data and makes quick adjustments to avoid damage.
A strong battery protection system can stop most overcharge problems before they start. Scientific studies show that when the battery protection system works well, it cuts off charging within milliseconds if voltage goes too high. This quick action lowers the risk of thermal runaway and other safety hazards.
Protection Failures
Even with a battery protection system, failures can still happen. The most common causes of lithium battery overcharging include faulty chargers, damaged circuits, and battery aging. If you use a charger that does not match your device, the battery protection system may not work as it should. This can lead to overcharge, swelling, or even fire.
Other reasons for protection failure include:
- Physical damage, like dropping your device, can break the battery protection system.
- Extreme temperatures can make batteries overheat or lose capacity.
- Manufacturing defects or contamination inside the battery can cause short circuits and failure.
- Overcharging or over-discharging can weaken the battery protection system over time.
You can lower your risk by using manufacturer-approved chargers, keeping batteries at safe temperatures, and not leaving devices plugged in after they reach full voltage. Remember, the battery protection system is your best defense, but it is not perfect. Always watch for signs of overcharge or failure to keep your devices and yourself safe.
Signs of Lithium Battery Overcharge

Physical Changes
You can spot early signs of lithium battery overcharge by looking for changes in your device’s battery. Watch for these physical warning signs:
- Swelling or deformation of the battery. This means internal pressure has built up from overcharging.
- Discoloration or corrosion on the battery casing. This shows chemical reactions have started inside.
- The battery feels much hotter than usual during charging.
- Leakage of chemicals. If you see any liquid or smell something strange, stop using the device right away.
These changes signal that your battery has suffered damage. Swelling and leaks can lead to more serious problems, including fire or explosion. Always check your device for these signs, especially if you charge it often.
Device Warnings
Modern devices use sensors to help you avoid lithium battery overcharge. Your device may show warnings if it detects unsafe conditions. Here are some common warning signs:
| Warning Type | What You Might Notice |
|---|---|
| Voltage Alerts | Sudden spikes or drops in battery percentage |
| Temperature Warnings | Device feels hot or displays a high-temperature alert |
| Pressure Changes | Battery compartment feels tight or hard to close |
Your device’s battery management system tracks voltage, temperature, and pressure. If any value goes outside the safe range, you may see a pop-up or hear an alarm. These warnings help you act before serious damage happens.
Tip: Never ignore device warnings. They protect you from sudden thermal runaway, which can happen without clear signs.
Reduced Battery Life
Overcharging shortens your battery’s lifespan. Each time you overcharge, you lose more charging cycles. The battery heats up, which causes chemical breakdown and wears out the inside. You may notice your device does not last as long between charges or shuts down unexpectedly.
- Overcharging causes heat, which speeds up internal wear and chemical damage.
- The number of effective cycles drops, so you need to replace the battery sooner.
- The damage from lithium battery overcharge is usually permanent.
If you see your device’s battery life dropping fast, overcharging may be the cause. Protect your device by following safe charging habits and watching for these signs.
Prevent Overcharging
Safe Charging Habits
You can prevent overcharging by following safe charging habits every time you use your device. Battery manufacturers recommend these steps:
- Use chargers made for your battery type to match voltage and current.
- Monitor your device while charging. Do not leave it plugged in for long periods.
- Charge lithium batteries correctly by keeping them at room temperature.
- Unplug your device once it reaches full charge.
- Use smart chargers that stop charging when the battery is full.
- Charge in a cool, dry place to avoid heat and moisture.
- Do not keep batteries at 100% for too long.
- Recharge when the battery drops to about 20% instead of letting it drain completely.
- Always use manufacturer-approved chargers.
- If your battery gets hot during charging, unplug it right away.
Tip: Charging safety starts with you. Always check cables and connectors for damage before use.
Certified Chargers
Certified chargers help prevent overcharging and protect your device. Always use the charger that came with your device or one approved by the manufacturer. Certified chargers match the correct voltage and current for your battery. Using the wrong charger can cause overcharging, overheating, or even fire. Inspect your charger and cables often. Replace them if you see any damage.
| Charger Type | Safety Level | Voltage Match | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer-Approved | High | Yes | Always |
| Certified Third-Party | Medium | Yes | If original is lost |
| Uncertified/Counterfeit | Low | No | Never |
Avoid Overnight Charging
Leaving your device plugged in overnight increases the risk of overcharging. Studies show that overnight charging can cause battery degradation and heat buildup. This can lead to fire hazards, especially with larger batteries like e-bikes. The Fire Safety Research Institute recommends charging away from sleeping areas and unplugging devices once they reach full charge. Avoid charging on beds or near flammable materials. Monitor your device for swelling, heat, or strange smells during charging.
- Do not charge overnight.
- Unplug once the battery is full.
- Charge on flat, non-flammable surfaces.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
Device makers provide clear instructions to help you prevent overcharging. Always read and follow these guidelines. Use only the charger designed for your device. Unplug your device when it reaches full charge. Keep the battery between 20% and 80% for the best lifespan. Never ignore warning signs like swelling, heat, or sudden drops in battery percentage. Following these safety protocols helps you avoid voltage problems and keeps your device safe.
Note: Manufacturer guidelines exist to protect you and your device. Following them is the best way to prevent overcharging and extend battery life.
Preventing overcharging protects your device and keeps you safe. You can make your battery last longer and avoid dangerous incidents by following these steps:
- Keep your battery between 20% and 80% charge.
- Use only manufacturer-approved chargers.
- Charge in cool, dry places and unplug when full.
- Watch for swelling, heat, or strange smells.
Safe charging habits lead to fewer replacements, lower costs, and less waste. Stay alert to warning signs and always follow best practices for a safer, longer-lasting device.
FAQ
Can you leave your phone plugged in overnight?
You should avoid leaving your phone plugged in overnight. Charging for too long can heat the battery and cause damage over time. Unplug your phone once it reaches 100% to keep the battery healthy.
What happens if a lithium battery swells?
A swollen battery means gas has built up inside. This can lead to leaks, fire, or even an explosion. Stop using the device right away. Replace the battery as soon as possible.
How do you know if your charger is safe?
Always use chargers from the device’s manufacturer or certified brands. Check for safety labels like UL or CE. Avoid using damaged or cheap chargers. Unsafe chargers can cause overcharging and fires.
Does fast charging damage lithium batteries?
Fast charging can heat up the battery more than normal charging. This extra heat may shorten battery life if used often. Use fast charging only when needed to help your battery last longer.

