
When you compare nimh vs lithium, lithium batteries usually deliver better performance for most users. In 2024, lithium batteries held over 67% of the global market, showing their popularity in devices like smartphones, electric vehicles, and backup power systems. These batteries offer higher energy density, faster charging, and longer lifespan. NiMH batteries remain a safer and more cost-effective rechargeable power source for some uses. Check out this quick comparison:
| Attribute | NiMH Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 60-120 Wh/kg | 150-200 Wh/kg |
| Lifespan | 500-1000 charge cycles | 500-2000 charge cycles |
| Charging Speed | Slower | 80% charge in about an hour |
| Safety | Stable, low risk | Good with management, some risk |
| Cost | Lower upfront | Higher upfront, better long-term value |
| Best Use Cases | Tools, toys, hybrid cars | Phones, laptops, electric vehicles |
You should choose your rechargeable battery based on your needs for battery performance, safety, and cost.
nimh vs lithium overview
Key Differences
When you look at nimh vs lithium, you see big differences in how these batteries work and what they offer. NiMH batteries use nickel hydroxide and a metal hydride alloy inside. Lithium-ion batteries use lithium oxide and graphite. This difference in battery chemistry changes how each battery stores and releases energy.
| Component | NiMH Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Cathode (Positive) | Nickel hydroxide (Ni(OH)2) | Lithium oxide-based active material |
| Anode (Negative) | Metal hydride alloy (lanthanum, nickel) | Graphite |
| Electrolyte | Alkaline hydroxide solution (20%-40% weight) | Lithium salt-based electrolyte |
| Separator | Non-woven polyolefin | Polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP) |
| Charging Mechanism | Oxidation of Ni(OH)2; hydrogen absorption | Lithium-ion intercalation into graphite anode |
| Discharging Mechanism | Hydrogen desorption and reaction with hydroxyl ions | Lithium ions move from anode to cathode |
| Structural Changes | More significant changes during cycling | Minimal changes due to intercalation compounds |
You will notice that nimh batteries often have more structural changes during charging and discharging. This can make them wear out faster than lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries use a process called intercalation, which keeps their structure more stable over time.
The voltage output also sets these battery types apart. NiMH batteries give you about 1.2 volts per cell. Lithium-ion batteries deliver 3.6 to 3.7 volts per cell. This higher voltage means you can use fewer li-ion cells to power the same device. NiMH batteries tend to be heavier and bulkier for the same amount of energy.
Tip: If you want a lighter device or need more power in a small space, lithium-ion batteries usually work better.
Quick Comparison
You might wonder how nimh vs lithium batteries stack up in real-world use. Here is a quick look at the most important features:
| Characteristic | NiMH Battery | Lithium-ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Voltage Output | 1.2 V per cell | 3.6-3.7 V per cell |
| Average Capacity | Around 2200 mAh | Around 1500 mAh |
| Energy Density | Lower | Higher |
| Self-Discharge Rate | High (up to 50% in first month) | Low |
| Charging Time | 10-12 hours (standard) | 1-3 hours (fast charging possible) |
| Performance in Extreme Temperatures | Voltage drops significantly | Better tolerance |
| Size and Weight | Larger and heavier | Smaller and lighter |
| Safety Considerations | Safer, less risk of thermal runaway | Needs safety circuits, riskier if mishandled |
| Life Cycle | 2-5 years | Around 5 years |
| Suitability | Less suitable for low-load devices | Suitable for low-load devices |
When you compare li-ion vs ni-mh battery, you see that lithium-ion batteries charge much faster. They also hold their charge longer because they have a lower self-discharge rate. NiMH batteries can lose up to 50% of their charge in the first month if you do not use them. Lithium-ion batteries only lose about 1-3% per month.
You also need to think about safety. NiMH batteries are very stable and rarely fail in a dangerous way. Lithium-ion batteries need special circuits to keep them safe. If you damage a li-ion battery or let it get too hot, it can become dangerous.
Here are the main factors you should consider when choosing between li-ion vs ni-mh battery:
| Factor | Lithium-Ion Batteries | NiMH Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Life | Often exceeds 1,000 cycles, longer lifespan | Around 500 cycles, shorter lifespan |
| Self-Discharge Rate | Low (1-3% per month), retains charge well | High (up to 30% per month), loses charge quickly |
| Charging Time | Faster charging, can reach 80% in a couple of hours | Slower charging, prone to overheating |
| Weight and Size | Lighter and more compact for same energy output | Bulkier and heavier |
| Safety | Sensitive to temperature, needs protective circuits | Safer under stress, less prone to failure |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | More affordable |
| Device Compatibility | Higher voltage per cell, may not fit all devices | Lower voltage per cell, fits many basic devices |
You should choose nimh batteries if you want a safer, more affordable option for basic devices. If you need high performance, fast charging, and a lighter battery, lithium-ion batteries are the better choice. The benefits of each battery chemistry depend on your needs. NiMH batteries work well for toys, tools, and some hybrid cars. Lithium-ion batteries power phones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
When you compare li-ion vs ni-mh battery, you see that lithium-ion batteries lead in most performance areas. NiMH batteries still have a place where safety and cost matter most. Both battery types have strengths and weaknesses. You should always match the battery technology to your device and usage.
key differences between li-ion and nimh batteries

Energy Density
When you compare the key differences between li-ion and nimh batteries, energy density stands out as one of the most important factors. Energy density tells you how much energy a battery can store for its weight. If you want a battery that lasts longer and powers your device for more hours, you need to look for high energy density.
Lithium-ion batteries offer much higher energy density than nimh batteries. This means you get more power from a smaller and lighter battery. According to Battery University, lithium-ion battery energy densities depend on the type of lithium chemistry used. For example, lithium iron phosphate batteries have about 90 Wh/kg, while nickel manganese cobalt batteries reach around 170 Wh/kg. Some lithium-ion batteries, like nickel cobalt aluminum, can even go above 200 Wh/kg. In contrast, nimh batteries usually range from 60 to 120 Wh/kg.
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) |
|---|---|
| NiMH | 60 – 120 |
| Lithium-ion (Cobalt) | 150 – 190 |
| Lithium-ion (Manganese) | 100 – 135 |
| Lithium-ion (Phosphate) | 90 – 120 |
You can see that lithium-ion batteries give you more energy for the same weight. This is why you find lithium-ion batteries in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. These devices need high energy density to work well without becoming too heavy or bulky.
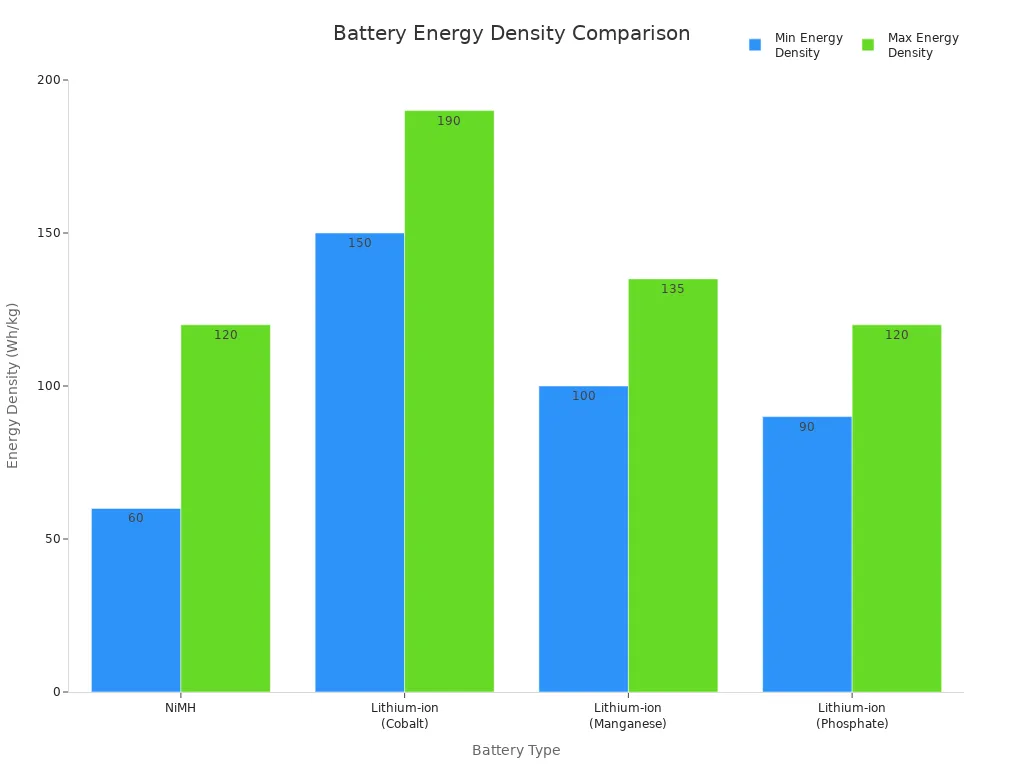
If you use nickel metal hydride battery packs, you will notice they do not last as long as lithium-ion battery packs of the same size. This difference in battery performance makes lithium-ion batteries the top choice for most modern electronics.
Note: High energy density helps you get more use out of your device before you need to recharge.
Weight and Size
Weight and size matter a lot when you choose batteries for portable devices. Another key difference between li-ion and nimh batteries is that lithium-ion batteries are lighter and smaller for the same amount of energy. This makes them perfect for devices where space and weight are important.
Measured data shows that nimh batteries are heavier and bulkier than lithium-ion batteries. For example, a typical AA nimh battery weighs about 27 grams, while a lithium-ion AA cell weighs less. Even though nimh batteries often have a higher average capacity per cell (about 2200 mAh), lithium-ion batteries provide higher energy density, so you need fewer cells to get the same power.
| Cell Size | Diameter (mm) | Length (mm) | NiMH Weight (g) | Lithium-ion Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAA | 10.5 | 44.5 | 13 | Less than NiMH |
| AA | 14.2 | 50 | 27 | Less than NiMH |
| Feature | NiMH | Lithium-ion |
|---|---|---|
| Average Cell Capacity | ~2200 mAh | ~1500 mAh |
| Cell Voltage (V) | 1.2 | 3.6 |
| Specific Energy (Wh/kg) | 1 – 80 | 3 – 100 |
| Energy Density (kWh/m3) | 70 – 100 | 80 – 200 |
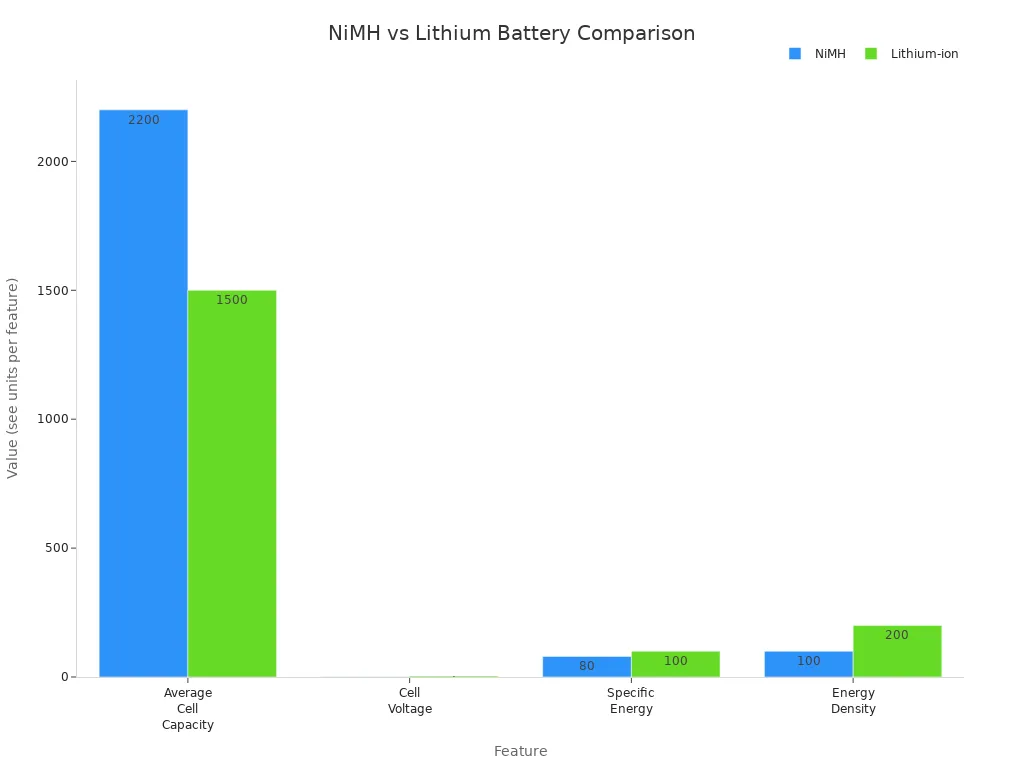
If you use nimh battery packs in your tools or toys, you might notice they feel heavier than devices powered by lithium-ion battery packs. This extra weight can make a big difference if you carry your device all day. Lithium-ion batteries help you keep your devices light and easy to use.
Tip: If you want a lightweight device, always check if it uses lithium-ion batteries.
Self-Discharge
Self-discharge is how quickly a battery loses its charge when you are not using it. This is another important part of battery performance. Nimh batteries have a much higher self-discharge rate than lithium-ion batteries. If you leave a nimh battery unused, it can lose 10–15% of its charge in the first 24 hours. After that, it keeps losing about 10–15% each month.
| Battery Type | Self-Discharge Rate Under Standard Storage Conditions |
|---|---|
| NiMH (Nickel-based) | 10–15% charge lost in first 24 hours; then 10–15% per month |
| Lithium-ion | About 5% lost in first 24 hours; then 1–2% per month plus ~3% per month due to safety circuit |
Lithium-ion batteries lose only about 5% in the first 24 hours, and then about 1–2% per month. The safety circuit in lithium-ion batteries adds a little extra loss, but it is still much lower than nimh batteries. This means you can leave a lithium-ion battery in your device for weeks or months and still have plenty of charge left when you need it.
Nimh batteries are best stored at about 40% charge to reduce capacity loss. They can last 3–5 years in storage, but you may need to prime them if the voltage drops too low. Lithium-ion batteries can last up to 10 years if you store them at around 40% charge and keep them cool. You should never let a lithium-ion battery drop below 2V per cell, or it could get damaged.
If you use nickel metal hydride battery packs in devices you do not use often, you may find them empty when you need them. Lithium-ion batteries hold their charge much better, making them a better choice for backup power and emergency devices.
Callout: For devices you use only sometimes, lithium-ion batteries will be ready when you need them, while nimh batteries may need recharging first.
Lifespan
Cycle Life
When you look at how many times you can recharge a battery before it wears out, you are thinking about cycle life. This is a key part of battery life. NiMH batteries can surprise you with their durability. In some laboratory tests, NiMH batteries have lasted over 12,000 charge and discharge cycles with less than 5% loss in capacity, especially in hybrid electric vehicle conditions. However, the number of cycles you get depends on how you use and charge the battery. Some brands claim up to 2,100 cycles under certain standards, but only 600 cycles under stricter testing. This means the real cycle life can change a lot based on how you treat your battery.
Lithium-ion batteries usually offer between 500 and 2,000 cycles. They often provide a longer-lasting charge per use, but their total number of cycles is usually lower than the best NiMH batteries in special conditions. For most everyday devices, lithium-ion batteries still last several years with regular use.
Tip: If you want a battery that can handle thousands of recharges, NiMH batteries may be the better choice for heavy-duty or hybrid car use.
Shelf Life
Shelf life tells you how well a battery holds up when you store it. NiMH batteries self-discharge faster than lithium-ion batteries. Modern low self-discharge NiMH cells can keep up to 85% of their charge after one year at room temperature. You should store them in a cool, dry place and recharge them at least once a year to prevent leaks or loss of capacity. NiMH batteries do not get damaged if they are fully discharged during storage, and you can recharge them without losing performance.
Lithium-ion batteries keep their charge much better during storage. They need to be stored at a partial charge to avoid damage. If you let a lithium-ion battery fully discharge, it can suffer permanent harm. You should check and recharge both types regularly, but lithium-ion batteries are more sensitive to how you store them.
Note: For backup devices or emergency kits, lithium-ion batteries are often the longer-lasting choice because they hold their charge better over time.
Charging Speed
Fast Charging
Charging speed is a key factor when you choose a battery for your device. You want a battery that charges quickly and safely. NiMH and lithium-ion batteries have different charging methods and speeds. Manufacturers recommend specific charging rates to keep the battery safe and extend its life.
Here is a table showing the maximum recommended charging speeds for NiMH batteries:
| Charging Method | Maximum Recommended Charging Speed (C-rate) | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|
| NiMH Standard Charge | 0.1 C | Charge for 15-16 hours; temperature range 0 to +45°C; timer to prevent overcharge |
| NiMH Accelerated | 0.3 C | Charge for 4 hours; temperature range +10 to +45°C |
| NiMH Fast Charge | 0.5 to 1 C | Requires charge termination by dT/dt or voltage drop; temperature rise rate control recommended |
| NiMH Trickle Charge | 0.01 to 0.03 C | Used to maintain full charge after fast charge; temperature range +10 to +35°C |
You can see that NiMH batteries support fast charging up to 1 C, but you must use special controls to avoid overheating. Most NiMH batteries take longer to charge than lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries often reach 80% charge in about an hour. This fast charging makes lithium-ion batteries a top choice for phones, laptops, and electric vehicles. You save time and get back to using your device sooner.
Tip: Always use the charger recommended for your battery type. This helps you get the best battery performance and keeps your device safe.
Discharge Rate
Discharge rate tells you how quickly a battery can deliver power to your device. This is important for high-drain devices like cameras, power tools, and electric cars. NiMH batteries have low internal resistance. This means they can recharge quickly and handle strong power discharge without a big voltage drop. You get steady performance even when your device needs a lot of power.
Lithium-ion batteries offer even better performance for high-drain devices. They have a higher voltage per cell and greater energy density. You get more power in a smaller, lighter package. Lithium-ion batteries also have a lower self-discharge rate and longer cycle life. These features make them ideal for devices that need strong, steady power.
- Lithium-ion batteries are designed for high discharge rates.
- They deliver consistent power and steady voltage.
- You can use them in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
- Built-in thermal management helps prevent overheating during heavy use.
When you need the best battery performance for demanding devices, lithium-ion batteries stand out. NiMH batteries work well for moderate power needs, but lithium-ion batteries lead in high-performance situations.
Safety
Safety Risks
You need to understand the main safety risks before choosing between nimh and lithium batteries. Both types of batteries can cause problems if you do not handle them correctly. Safety agencies report that lithium batteries have some unique risks. Internal shorts, separator defects, or manufacturing flaws can cause lithium batteries to fail. Sometimes, these failures lead to thermal runaway, which means the battery heats up quickly and can catch fire. Released gases, like hydrogen fluoride, are toxic and corrosive. Fires from lithium batteries are hard to put out, and water can make lithium-metal fires worse. Charging at low temperatures, dropping the battery, or shaking it too much can increase the risk of failure.
Nimh batteries also have safety risks. They can catch fire if the separators age or if you handle them roughly. The heavy metals in nimh batteries can be toxic. The electrolytes can cause burns if they leak. Electrical shorts can start fires in both nimh and lithium batteries.
Here is a table that shows the most common safety risks:
| Battery Type | Common Safety Risks |
|---|---|
| NiMH | Toxic heavy metals, corrosive electrolytes, fire from shorts |
| Lithium | Fire from flammable chemicals, thermal runaway, toxic gas release, cell swelling, hard-to-stop fires |
Always use certified batteries and chargers to lower your safety risks. Look for quality control features like x-ray inspection.
Maintenance
Good maintenance helps you get the best safety and lifespan from your batteries. For nimh batteries, store them between 50°F and 77°F with moderate humidity. Avoid places like cars or basements. Use smart chargers that shut off automatically and monitor temperature. Do not overcharge nimh batteries. Try to do a full charge and discharge every month to prevent memory effect. Recharge nimh batteries before they drop below 20% to avoid deep discharge damage. If you do not use them often, cycle them every three months and store them at 40%-60% charge. Check your batteries every six months for leaks or damage.
Lithium batteries need a different approach. Keep them at room temperature and away from heat. Do not charge or discharge them fully. Try to keep the charge between 20% and 80%. Avoid charging overnight. Protect lithium batteries from moisture. For long-term storage, keep them at 40%-60% charge and recharge them sometimes to prevent deep discharge. Remember, lithium batteries last longer if you use partial cycles and control the temperature.
- Fully charge new nimh batteries before first use.
- Use chargers made for nimh batteries.
- Remove batteries from the charger once full.
- Store all batteries at room temperature and avoid extreme heat or cold.
Regular maintenance and safe storage help you avoid most safety problems with nimh and lithium batteries.
Cost
Upfront Price
When you shop for rechargeable batteries, you will notice a big difference in the upfront price. NiMH batteries usually have a lower cost at the start. This makes them a good choice if you want to save money right away or if you need batteries for low-power devices. You can often buy NiMH batteries for about half the price of lithium-ion batteries. This lower cost helps if you need to buy many batteries at once.
Lithium-ion batteries cost more when you first buy them. The higher price comes from their advanced technology and higher energy density. You might pay between $9 and $90 for a lithium-ion battery, depending on the device. For example, a smartphone battery can cost $10 to $35, while a laptop battery might cost $20 to $90. The extra cost also covers special storage and shipping rules for these batteries.
| Battery Type | Average Upfront Cost |
|---|---|
| NiMH Batteries | About half the cost of lithium-ion batteries; cheaper upfront |
| Lithium-ion Batteries | $9 to $90 depending on device |
Tip: If you want a budget-friendly option for toys, remotes, or flashlights, NiMH batteries can help you save money at the start.
Long-Term Value
You should also think about the total cost over time. NiMH batteries may seem cheaper at first, but they often need to be replaced more often. These batteries last for 500 to 1,000 cycles, so you might need new ones every 18 months if you use them a lot. The cost of recycling NiMH batteries can also add up, with some estimates reaching $2,900 to $3,500 per tonne. This makes the total cost higher over five years, especially if you use many batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries have a higher upfront cost, but they last much longer. Some lithium batteries can last 2,000 to 6,000 cycles. You will spend less on replacements and maintenance. These batteries also keep their performance for years, which saves you money in the long run. For devices like solar panels or e-bikes, lithium batteries give you better value because you do not need to replace them as often.
| Feature | LiFePO₄ Lithium Batteries | NiMH Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Life | 2000–6000 cycles | 500–1000 cycles |
| Upfront Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Maintenance | Lower | Higher |
Note: If you want to save money over several years, lithium-ion batteries are often the smarter choice, even with a higher starting cost.
applications of nimh and li-ion batteries

Everyday Devices
You use batteries every day in many devices. Lithium-ion batteries power most of your mobile computers, smartphones, and notebook computers. You also find them in smartwatches, vape pens, and other small portable gadgets. Their high energy density and low weight make them perfect for these uses. Earbuds like AirPods and Galaxy Buds rely on lithium-ion batteries for long listening times and quick charging. GoPro cameras and drones, such as DJI’s Mini 3, use lithium-ion batteries for lightweight power and long operation.
NiMH batteries still play a role in many everyday devices. You see them in digital cameras, portable music players, and gaming devices. People choose nimh batteries because they are rechargeable and last longer than alkaline batteries. They also have a longer lifespan than nickel-cadmium batteries. Many toys, remote controls, and flashlights use nimh batteries because they are safe and affordable.
Tip: For devices you use often and want to recharge quickly, lithium-ion batteries work best. For basic devices, nimh batteries offer a reliable and cost-effective choice.
High-Drain Electronics
High-drain electronics need batteries that deliver strong, steady power. Lithium-ion batteries are the top choice for modern digital cameras. They are light, have high energy density, and last much longer per charge than nimh batteries. Camera makers like Canon, Nikon, Sony, and Panasonic design special lithium-ion batteries for their models. These batteries give you longer shooting times and consistent performance.
NiMH batteries can also power high-drain devices. They provide more constant energy output than alkaline batteries. Some older cameras and flash units use nimh batteries for this reason. However, most new high-drain electronics use lithium-ion batteries because they are lighter and last longer.
Electric Vehicles
The application of li-ion and ni-mh batteries in electric vehicles shows clear differences. NiMH batteries appear mostly in hybrid cars. They offer good safety and durability but have lower energy density. This means you get less driving range. They also lose more energy when not in use and are sensitive to extreme temperatures.
Lithium-ion batteries dominate full electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids. They store more energy, so you can drive farther on a single charge. They also have a lower self-discharge rate and longer cycle life. However, they cost more and need careful management to stay safe. The table below compares the two:
| Aspect | NiMH Batteries | Lithium-ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Lower | Higher |
| Self-Discharge Rate | Higher | Lower |
| Cycle Life | 500-1000 cycles | Up to 3000 cycles |
| Safety | Safer | Needs management system |
| Typical Use | Hybrids | Full EVs, plug-in hybrids |
Backup Power
Backup power is another important application of li-ion and ni-mh batteries. NiMH batteries have moderate capacity and are environmentally friendly. However, they have a limited cycle life and higher self-discharge. They also need regular maintenance and careful charging. This makes them less ideal for uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
Lithium-ion batteries outperform nimh batteries in backup power systems. They have higher energy density, lower self-discharge, and longer cycle life. Many companies use lithium-ion batteries in mini UPS systems for routers, cameras, and IoT devices. These batteries provide instant backup, last longer, and need less maintenance. They also come with safety features like fire resistance and waterproofing.
Note: For backup power, lithium-ion batteries give you more reliable and efficient performance than nimh batteries.
li-ion vs ni-mh battery drawbacks
NiMH Limitations
When you compare li-ion vs ni-mh battery, you will notice that nimh batteries have several drawbacks that can affect your experience. These batteries do not perform as well as lithium-ion batteries in many ways. Here is a table that shows some of the main factors:
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Charge Cycles | nimh batteries usually last 500 to 1000 cycles. |
| Overcharging/Overdraining | Charging too much or draining too far can cut lifespan by up to 40%. |
| Usage Type | High-power devices wear nimh batteries out faster. |
| Storage Conditions | Heat speeds up aging; cold lowers power. Proper storage helps them last. |
You will also find other limitations when you use nimh batteries:
- nimh batteries have lower energy density than lithium-ion batteries, so your devices run for a shorter time.
- These batteries lose charge quickly when not in use because of a high self-discharge rate.
- nimh batteries can develop a memory effect, which means they lose capacity if you do not fully discharge them before charging again.
- The cycle life is limited, and repeated charging and discharging makes them degrade faster.
- Voltage sag happens under heavy use, causing your device to lose power suddenly.
- nimh batteries are bulkier and heavier than lithium-ion batteries with the same capacity.
Note: If you need long-lasting, lightweight power, nimh batteries may not meet your needs as well as li-ion batteries.
Lithium Limitations
When you look at li-ion vs ni-mh battery, you will see that lithium-ion batteries also have important drawbacks. These batteries can pose safety risks. Internal shorts sometimes cause thermal runaway, which leads to fires that are hard to stop. Even though the failure rate is low, large groups of lithium-ion batteries can still catch fire during storage or transport. You must handle these batteries carefully because harsh conditions or abuse can trigger failures.
- lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to temperature, shock, and overcharging.
- Fast charging can make lithium-ion batteries degrade faster and increase safety risks.
- Newer lithium-ion batteries may have a shorter cycle life and need careful charging, especially in cold weather.
- lithium-ion batteries can be dangerous if you do not follow safety rules. Fires and explosions have happened during air transport.
- Environmental concerns exist because recycling and disposal of lithium-ion batteries are difficult. Fires or explosions can happen during storage or shipping.
- Regulations now limit how you can ship and carry lithium-ion batteries, especially by air.
Callout: Always use approved chargers and follow safety guidelines when you use lithium-ion batteries. This helps prevent accidents and keeps your devices safe.
You should remember that, even with advances in li-ion technology, safety and environmental issues remain a challenge. When you compare li-ion vs ni-mh battery, you must weigh these drawbacks against the benefits for your devices.
choosing a rechargeable battery
Practical Tips
When you pick a rechargeable battery, you want to match it to your device, budget, and safety needs. Here are some tips to help you make the best choice:
- Check your device’s requirements. Make sure the battery type, voltage, and size fit your device.
- Think about how you use your device. High-drain devices like power tools or drones need batteries with high energy density, such as lithium-ion. Low-drain devices like remotes or clocks work well with NiMH batteries.
- Look at your budget. NiMH batteries cost less upfront and do not need complex battery management systems. This makes them a good choice if you want to save money.
- Consider safety. NiMH batteries are safer to transport and handle. Lithium-ion batteries need special chargers and safety features.
- Always use the correct charger for your battery type. This prevents damage and keeps you safe.
- Store and charge batteries in cool, dry places. Avoid charging in extreme temperatures.
Tip: Never mix different battery brands or chemistries in the same device. Replace all batteries at once to keep performance steady.
Use Case Scenarios
You can use this table to decide which rechargeable battery fits your needs:
| Device Type | Best Battery Choice | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| TV Remotes, Clocks | NiMH | Safe, cost-effective, steady voltage |
| Wireless Keyboards | NiMH | Reliable, budget-friendly |
| Power Tools, Drones | Lithium-ion | High energy, lightweight, long runtime |
| Professional Cameras | Lithium-ion | Delivers strong, steady power |
| Emergency Equipment | Lithium-ion | Holds charge longer, better for storage |
| Home Appliances | NiMH | Durable, safe, environmentally friendly |
If you want a rechargeable battery for a device you use every day, lithium-ion batteries give you more power and last longer between charges. For basic devices or when safety and cost matter most, NiMH batteries are a smart pick. Always match the battery to your device’s power needs for the best results.
You now know that choosing between NiMH and lithium batteries depends on your needs. If you want a battery for high-drain devices, long-term use, or compact gadgets, lithium batteries give you better performance, longer cycle life, and stable voltage. For budget-friendly, safe, and steady power in everyday electronics, NiMH batteries work well.
| Situation | Best Choice |
|---|---|
| High-drain, portable | Lithium batteries |
| Budget, low-drain | NiMH batteries |
| Long storage, reliability | Lithium batteries |
| Cold environments | NiMH batteries |
Think about how you use your devices, your budget, and safety. Pay more for lithium batteries when you need long runtime, light weight, or stable power. Choose NiMH batteries for simple, cost-effective solutions.
FAQ
What is the main difference between NiMH and lithium batteries?
You will find that lithium batteries store more energy and weigh less than NiMH batteries. NiMH batteries cost less and offer safer handling. You should choose based on your device’s needs and your budget.
Can you use NiMH and lithium batteries in the same device?
You should never mix NiMH and lithium batteries in the same device. Each battery type has different voltage and charging needs. Mixing them can damage your device or cause safety problems.
How do you store rechargeable batteries safely?
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Keep them away from direct sunlight and heat.
- Charge to about 40–60% before long-term storage.
Tip: Check your batteries every few months for leaks or damage.
Which battery lasts longer between charges?
Lithium batteries usually last longer between charges. They hold their charge better and have higher energy density. You will notice fewer recharges with lithium batteries in most devices.

