
If you want a battery that lasts long, stays safe in tough weather, and gives you reliable power, lithium iron phosphate batteries stand out over many traditional choices. These batteries now hold a leading spot in the global market:
| Metric | Value (End of 2022) |
|---|---|
| Global market share of LFP batteries | 60% |
| Installed capacity share (LFP) | 69.3% |
When you compare battery types, you should look at key factors:
- Lifespan and durability, with some lasting over 2,000 cycles
- Safety, since stable chemistry lowers risks of overheating
- Performance in both hot and cold climates
- Cost over time, not just the upfront price
- Impact on the environment and supply chain
Choosing the right battery matters because it affects how well your energy system works, how much you spend, and even your impact on the planet.
Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries: Quick Overview

What Is a Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery?
You may hear people call these batteries by their chemical name or by the abbreviation lifepo4. A lithium iron phosphate battery uses lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material. This chemistry gives the battery a strong structure and makes it safer than many other types. You can see the difference in the table below:
| Feature | Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) |
|---|---|---|
| Cathode Material | Lithium Iron Phosphate | Nickel, Manganese, Cobalt |
| Energy Density | 160-180 Wh/kg | 200-250 Wh/kg |
| Thermal Stability | High (ignition at 270°C) | Lower (ignition at 210°C) |
| Cycle Life | 3,000 – 7,000 cycles | 1,000 – 2,000 cycles |
| Safety | High resistance to thermal runaway | Lower resistance |
You get a battery that resists overheating and lasts for thousands of cycles. Lifepo4 batteries often work for 10-15 years with daily use. This long lifespan means you do not need to replace them as often as other batteries.
Tip: Lifepo4 batteries are safer under stress, such as high temperatures or physical damage. You can use them in places where safety matters most.
How Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries Work
A lithium iron phosphate battery stores energy by moving lithium ions between the cathode and anode. When you charge the battery, lithium ions travel from the iron phosphate cathode to the graphite anode. When you use the battery, the ions move back, releasing energy for your devices.
You will notice that lifepo4 batteries have a lower energy density than some other lithium-ion batteries. However, they make up for this with a much longer cycle life and better safety. High voltage lfp batteries also offer stable performance, even in tough conditions.
- Lifepo4 batteries can reach 3,000 to 7,000 cycles with little loss of capacity.
- Standard lithium-ion batteries usually last only 1,000 to 2,000 cycles.
- High voltage lfp batteries resist thermal runaway, which lowers fire risk.
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion | 150-200 | 500-1,000 |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | 90-120 | Up to 10,000 |
High voltage lfp batteries give you reliable power and safety. You can trust them for solar systems, RVs, and backup power.
Lithium Iron Phosphate vs. Lead-Acid Batteries

Safety and Reliability
You want a battery that keeps you safe and works reliably. Lithium iron phosphate batteries offer strong thermal and chemical stability. This means you do not have to worry about overheating or dangerous chemical leaks. Lead-acid batteries, on the other hand, can spill acid and release hydrogen gas. These risks make lead-acid batteries less safe, especially if you use them in homes, vehicles, or places with children.
| Battery Type | Safety Risks | Safety Features |
|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid Batteries | Risk of acid exposure and hydrogen gas release during maintenance. | Requires acid-resistant PPE for protection. |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate | No acid exposure; maintenance-free with constant monitoring of battery health. | Safety backups prevent thermal runaway and high temperature shutdown. |
- Lead-acid batteries pose risks of acid spills and hydrogen gas release.
- Lithium iron phosphate batteries are thermally and chemically stable, reducing the risk of environmental contamination.
Note: You do not need special protective gear when you handle a lithium iron phosphate battery. This makes it easier and safer for everyday use.
Lifespan and Cycle Life
You want your battery to last as long as possible. Lifepo4 batteries can achieve over 2,000 cycles at 80% depth of discharge. Lead-acid batteries usually last less than 300 cycles under the same conditions. This means you will replace lead-acid batteries much more often.
| Battery Type | Average Cycle Life (80% DoD) |
|---|---|
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) | Over 2000 cycles |
| Lead-Acid | Less than 300 cycles |
- Lithium iron phosphate batteries can last over 12 to 15 years.
- Lead-acid batteries typically last about 1 to 3 years.
If you use high voltage lfp batteries, you get even more cycles and longer life. Over a decade, you may only need one lifepo4 battery, while you might replace lead-acid batteries six or more times.
Energy Density and Weight
Energy density tells you how much power a battery stores for its size and weight. Lithium iron phosphate batteries have much higher energy density than lead-acid batteries. This means you get more power in a smaller, lighter package.
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) |
|---|---|
| Lead Acid | 30-50 |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | 100-135 |
- Lithium iron phosphate batteries weigh about one-third of equivalent lead-acid batteries.
- Lifepo4 batteries have two to three times higher energy density than lead-acid batteries.
- The compact size and lighter weight of lifepo4 batteries make them ideal for RVs, boats, and electric vehicles.
Tip: If you need a battery for mobile use, such as in an RV or boat, choose high voltage lfp batteries for easier installation and better performance.
Cost and Value
You may think lead-acid batteries cost less at first. However, you need to look at the total cost over time. Lithium iron phosphate batteries last much longer and need less maintenance. This saves you money in the long run.
| Battery Type | Cost per usable KWh per cycle |
|---|---|
| Lead-Acid AGM | 0.42€ / usable kWh |
| Lithium-Ion | 0.15€ / usable kWh |
- Lifepo4 and AGM/Gel batteries are maintenance-free.
- Flooded lead-acid batteries require regular maintenance, which increases total cost of ownership.
- Lithium iron phosphate batteries typically last over 10 years, while lead-acid batteries last only 3-5 years.
- Over a 10-year period, you may only need one lifepo4 battery, compared to 6-11 replacements for lead-acid batteries.
Fast charging is another advantage of lithium iron phosphate batteries. You spend less time waiting and more time using your devices.
Environmental Impact
You care about the environment. Lithium iron phosphate batteries and lead-acid batteries both have environmental impacts, but they differ in important ways.
| Aspect | Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) | Lead-Acid |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Extraction | Mining lithium, cobalt, nickel, etc. can lead to land clearing and water contamination. | Mining lead can also cause environmental degradation. |
| Energy Consumption | More energy-intensive due to complex materials and high-temperature processes. | Generally less energy-intensive. |
| End-of-Life Management | Recycling systems are less established, leading to potential soil and groundwater contamination. | Established recycling system with lower overall environmental impact. |
| CO2 Emissions | Approximately 120 lb CO2-equivalent per kWh. | Lower emissions due to recycling efficiency. |
| Lifespan | Longer lifespan, tolerates deeper discharges. | Shorter lifespan, sensitive to discharge levels. |
- Lead-acid batteries have a recycling rate of nearly 99% in the U.S.
- The recycling process for lead-acid is energy-intensive and emits harmful substances.
- Lithium iron phosphate batteries are gaining attention for greener disposal methods.
Note: Lead-acid batteries are recycled at a rate of 99% in the USA. Lithium ion batteries have a global recycling rate of only 2%–47%.
Common Uses
You need to know which battery fits your needs. Here is a performance comparison of common applications:
| Battery Type | Common Applications |
|---|---|
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) | – Solar energy storage systems – Electric powertrains for vehicles and marine vessels – Off-grid power installations – Industrial equipment requiring daily power |
| Lead-Acid | – Backup power systems for emergency lighting – Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) – Starting engines in automobiles and generators |
- Lithium iron phosphate batteries work best for solar energy storage, electric vehicles, and off-grid power.
- Lead-acid batteries are common in backup power, UPS systems, and engine starting.
If you want reliable energy storage for daily use, lifepo4 batteries and high voltage lfp batteries give you the best results. You get longer life, better safety, and easier maintenance.
Lithium Iron Phosphate vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Safety and Thermal Stability
You want a battery that keeps you safe, even when things get hot. Lithium iron phosphate battery technology stands out for its safety. The unique structure of this battery, with strong P-O bonds, gives it a much higher thermal runaway onset temperature than other lithium ion batteries. This means it can handle more heat before any risk of fire or explosion.
| Battery Chemistry | Approximate Thermal Runaway Onset Temperature |
|---|---|
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | 270°C / 518°F |
| Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) | 210°C / 410°F |
| Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO) | 150°C / 302°F |
A lithium iron phosphate battery does not release oxygen during decomposition. This lowers the chance of combustion. You can use lifepo4 batteries in places where safety matters most, like homes, schools, and electric vehicles. Studies show that lifepo4 batteries rarely fail due to overheating, even when overcharged or exposed to high temperatures. This makes them a top choice for reliable energy storage.
Tip: If you want peace of mind, choose high voltage lfp batteries for their strong safety record.
Lifespan and Performance
You want your battery to last as long as possible. Lifepo4 batteries give you a much longer cycle life than most other lithium ion batteries. You can expect 2,000 to 4,000 cycles, and some models reach up to 6,000 cycles. In comparison, NMC and NCA batteries usually last only 500 to 1,500 cycles.
| Battery Type | Cycle Life (Cycles) | Service Life (Years) |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | 2,000–4,000 (up to 6,000 for some models) | 7–8 |
| NMC/NCA | 500–1,500 | N/A |
Lifepo4 batteries also perform well in high-drain applications. You can use them for electric motors, solar systems, and backup power. They deliver strong bursts of current and keep working for years. High voltage lfp batteries offer stable performance, even when you use them every day.
- Lifepo4 batteries have a higher discharge rate, which is great for devices that need a lot of power fast.
- Standard lithium ion batteries store more energy per kilogram, but they do not last as long.
- Lifepo4 batteries give you both safety and a long service life.
Energy Density and Voltage
Energy density tells you how much energy a battery can store for its weight. Lithium iron phosphate batteries have a lower energy density than other lithium ion batteries. This means they are a bit heavier for the same amount of power.
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Voltage Range (V) |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) | > 90 (up to 160) | 2.0-3.65 |
| Other Lithium-Ion Chemistries | 150-200 | 3.6 |
If you need a lightweight battery for a phone or laptop, standard lithium ion batteries may work better. If you need a battery for solar storage, RVs, or electric buses, high voltage lfp batteries give you the right balance of safety and performance. You get a battery that can handle deep discharges and still last for years.
Note: High voltage lfp batteries keep a steady voltage during use, which helps protect your devices.
Cost Comparison
You want to get the most value for your money. In 2024, lithium iron phosphate batteries cost less than most other lithium ion batteries. The average price for a lithium iron phosphate battery is just under $60 per kWh. NMC and NCA batteries cost about $95 per kWh.
| Battery Type | Average Price per kWh (2024) |
|---|---|
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) | Just under $60 |
| Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) | USD 95 |
| Nickel Cobalt Aluminum (NCA) | USD 95 |
LFP batteries are over 20% cheaper than NMC batteries. When you look at the total cost over the battery’s life, lifepo4 batteries save you even more money. They last longer, so you do not need to replace them as often.
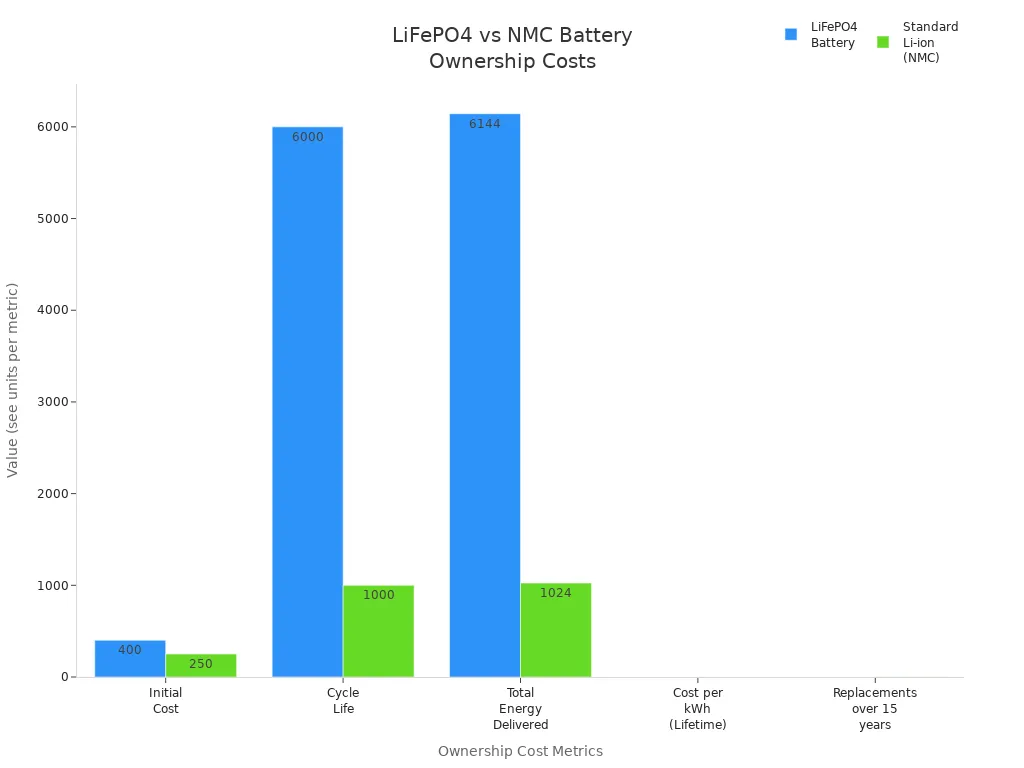
| Metric | LiFePO4 Battery | Standard Li-ion (NMC) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost (Example) | $400 | $250 |
| Cycle Life (at 80% DoD) | ~6,000 cycles | ~1,000 cycles |
| Total Energy Delivered | ~6,144 kWh | ~1,024 kWh |
| Cost per kWh (Lifetime) | ~$0.065 | ~$0.244 |
| Replacements over 15 years | 0 | 3-4 |
Fast charging is another benefit of high voltage lfp batteries. You spend less time waiting and more time using your devices.
Environmental Factors
You care about the planet. Lithium iron phosphate batteries have some clear environmental advantages. They do not use cobalt or nickel, which are linked to harmful mining practices. The materials in a lithium iron phosphate battery are more common and less toxic.
- Efficient recycling strategies for spent lithium iron phosphate batteries help reduce environmental impact.
- LFP batteries use materials that are easier to recycle and less energy-intensive.
- Recent improvements in LFP technology have boosted energy density while keeping environmental benefits.
If you want a greener choice, high voltage lfp batteries are a smart pick.
Best Applications
You want to know where each battery works best. Here is a quick performance comparison:
- Lithium iron phosphate batteries work well in electric buses, solar energy systems, and places where you need a long cycle life.
- Standard lithium ion batteries are better for portable electronics, like phones and laptops, where size and weight matter most.
- Lifepo4 batteries are ideal for reliable energy storage in homes, RVs, and off-grid systems.
If you need a battery that lasts, stays safe, and works in tough conditions, choose high voltage lfp batteries. For lightweight gadgets, standard lithium ion batteries may be the better fit.
Lithium Iron Phosphate vs. Nickel-Based Batteries
Safety and Maintenance
You want a battery that keeps you safe and is easy to care for. A lithium iron phosphate battery gives you strong safety features. It resists overheating and does not leak harmful chemicals. Nickel-based batteries, like nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride, can overheat if you charge them too quickly. They also need more maintenance. You may need to check for leaks or replace them more often. With a lithium iron phosphate battery, you get a safer and more hands-off experience.
Tip: If you want less maintenance and more peace of mind, lifepo4 batteries are a smart choice.
Lifespan and Power Output
You want your battery to last and deliver steady power. Lithium iron phosphate batteries have a much longer cycle life than nickel-based batteries. They keep a steady voltage as they discharge, so your devices work well until the battery is empty.
| Battery Type | Typical Lifespan (Cycles) | Power Output Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium Iron Phosphate | 2000-3000 cycles | Maintains consistent voltage output throughout discharge |
| Nickel-Metal Hydride | 500-1000 cycles | Experiences faster capacity degradation over time |
You can see that a lithium iron phosphate battery lasts two to three times longer. This means fewer replacements and less waste.
Energy Density and Availability
Energy density tells you how much energy a battery can store for its size. Nickel-based batteries have higher energy density, so they are smaller and lighter for the same power. Lithium iron phosphate batteries are bigger, but they make up for it with longer life and better safety. High voltage lfp batteries give you reliable energy storage for larger systems, even if they take up more space.
Cost and Environmental Concerns
You want a battery that is affordable and good for the planet. Lithium iron phosphate batteries cost less to make because they use common materials. Nickel-based batteries cost more because they use nickel and cobalt. These metals are harder to get and can harm the environment.
| Aspect | Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) | Nickel-based Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Production Costs | Lower due to abundant materials | Higher due to cobalt and nickel |
| Environmental Impact | Fewer emissions, less energy | Higher emissions, more energy |
| Lifespan | Longer, reduces waste | Shorter, increases waste |
| Energy Density | Lower, larger packs required | Higher, smaller packs possible |
| Recycling | Easier, more viable | More complex due to cobalt |
You help the environment by choosing a battery that lasts longer and is easier to recycle.
Typical Applications
You should pick the right battery for your needs. Lithium iron phosphate batteries work best for solar storage, electric vehicles, and backup power. They give you fast charging and long life. Nickel-based batteries still work well in power tools, medical devices, and some older electronics. If you need a battery for reliable energy storage, a lithium iron phosphate battery is the better choice.
Note: Nickel-based batteries may still be preferred in small devices where size and weight matter most.
Choosing the Right Energy Storage Solution
Key Factors to Consider
When you choose a battery for your energy storage solutions, you need to look at several important factors. Each factor helps you decide which battery fits your needs best.
- Energy needs: Think about how much power you use every day. Some batteries work better for high energy demands.
- Battery types: You can pick from lithium iron phosphate, lead-acid, lithium-ion, or nickel-based batteries. Each type has strengths and weaknesses.
- Cost: Look at both the upfront price and the long-term value. Some batteries cost more at first but save you money over time.
- Safety: Choose a battery with strong thermal stability and chemical safety. This lowers the risk of overheating or leaks.
- Top brands: Reliable brands offer better warranties and support.
You should also consider how the battery handles temperature changes. Lithium iron phosphate batteries give you greater thermal stability and higher tolerance to temperature variations. You get longer cycle life and enhanced chemical stability. These features make them a strong choice for many energy storage technologies.
Tip: LiFePO4 batteries can last between 3,000 and 10,000 full charge and discharge cycles. This long lifespan means you spend less on replacements and enjoy reliable energy storage for years.
You see clear differences between lithium iron phosphate batteries and traditional choices. The table below highlights key strengths and weaknesses:
| Battery Type | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| LiFePO4 (LFP) | Superior safety, longevity, thermal stability | Lower energy density |
| Traditional Li-ion | Higher energy density | Trade-offs in safety and cycle life |
- Choose LiFePO4 batteries for safety and long-term use.
- Pick lithium-ion batteries for small devices needing high energy.
- Think about your needs before you decide.
- Ask an expert if your situation is complex.
FAQ
What makes lithium iron phosphate batteries safer than other types?
You get safer performance because lithium iron phosphate batteries resist overheating and do not leak harmful chemicals. Their stable chemistry lowers fire risk. You can use them in homes, schools, and vehicles with confidence.
How do lithium iron phosphate batteries compare to lithium-ion batteries?
You will notice lithium iron phosphate batteries last longer and offer better safety. Lithium-ion batteries have higher energy density, so they work well in small devices. You should choose based on your needs.
Can I use lithium iron phosphate batteries in cold weather?
Yes, you can use these batteries in cold weather. They deliver steady power even when temperatures drop. You may see a slight reduction in capacity, but performance remains reliable.
Are lithium iron phosphate batteries better for the environment?
You help the environment by choosing lithium iron phosphate batteries. They use common, less toxic materials and last longer. Recycling options continue to improve, making disposal easier.
What is lithium iron cobalt oxide, and how does it differ from lithium iron phosphate?
Lithium iron cobalt oxide is another battery material. It stores more energy in a smaller space. You get higher energy density, but safety and lifespan are lower than with lithium iron phosphate batteries.

