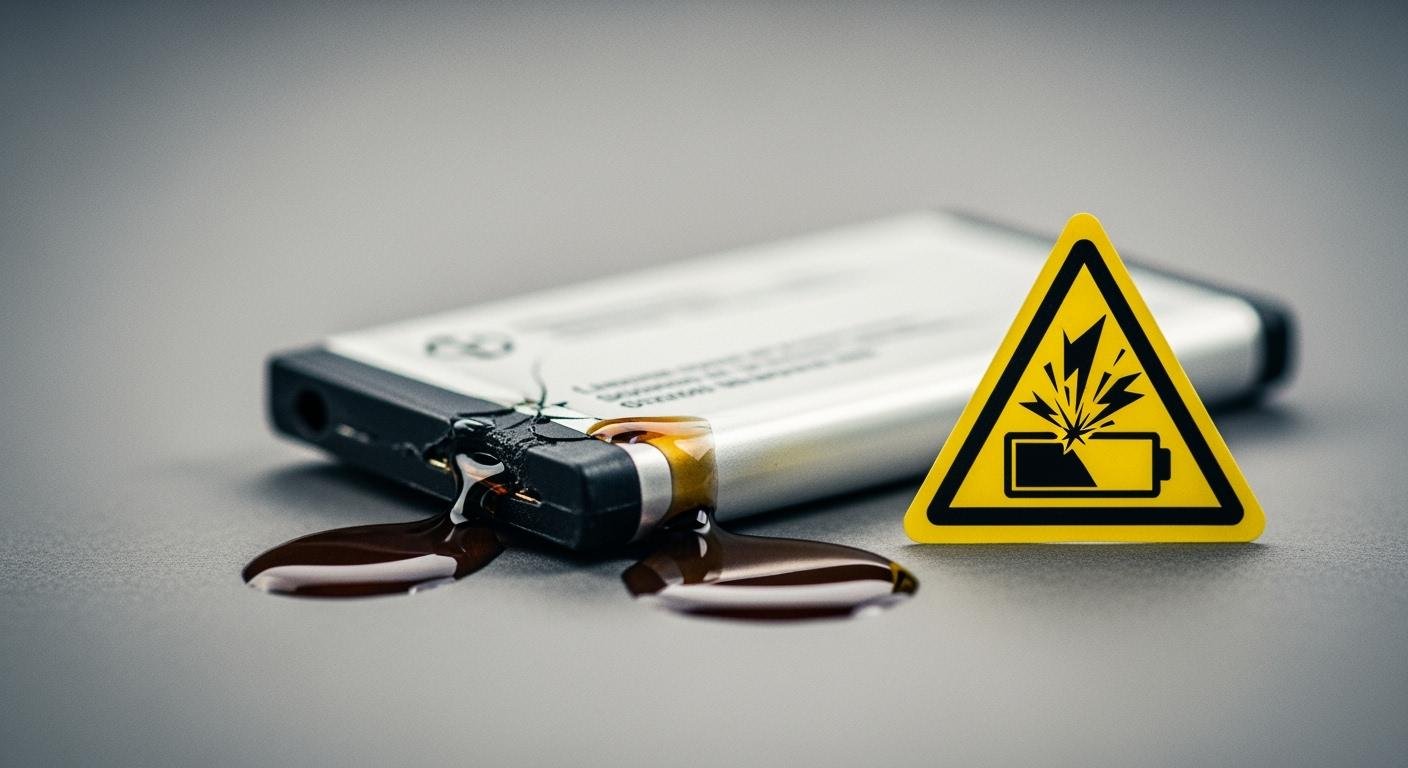

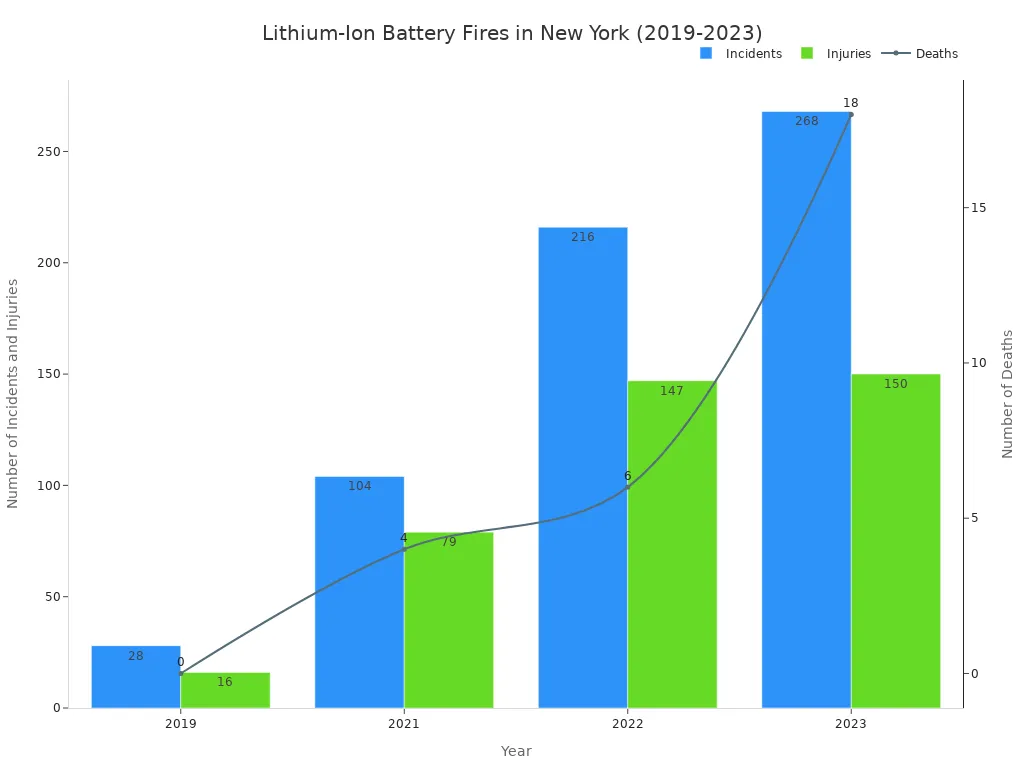
A swollen, leaking, or damaged lithium-ion battery is a serious hazard. It can cause fires, explosions, or chemical burns. If you see signs of lithium-ion battery leaks, you must act fast. Stop using the device and unplug it from any power source. Handle the device with extreme caution. The danger from lithium-ion fires is growing, as shown by recent data from New York.
This guide provides the immediate actions you need to safely manage the situation.
Identifying Lithium-Ion Battery Leaks

You can often spot a failing lithium-ion battery before a dangerous event occurs. Your senses—sight, smell, and hearing—are your best tools for early detection. Knowing the specific signs of a lithium-ion battery leak helps you act quickly to protect yourself and your property.
Visual Signs of Damage
Your first clue is often something you can see. A healthy lithium-ion battery should have a perfectly rectangular and flat shape. You should inspect your devices for any physical changes. These visual signs indicate serious internal problems.
Look for these key indicators of damage:
- Swelling or Bulging: The most common sign is a swollen battery case. Internal gas buildup creates pressure, causing the battery to puff up like a pillow.
- Warped Shape: The battery may look bent, twisted, or otherwise misshapen.
- Pushed-Out Components: In devices like phones or tablets, a swelling lithium-ion battery can push the screen or back cover out of its frame.
- Discoloration: You might notice strange stains or color changes on the battery’s casing.
Telltale Sounds and Smells
Sometimes, you will hear or smell a problem before you see it. These signs signal that a battery failure is actively in progress and requires immediate attention. A strange smell is a clear warning of lithium-ion battery leaks.
Pay close attention to any unusual sounds coming from your device. A hissing noise is a frequent symptom of a failing lithium-ion cell. This sound means you need to get away from the battery right away. Experts describe this sound as a very specific event.
One hint that things might be about to go awry is when the safety valve breaks in a hard battery case to release the pressure caused by a chemical reaction within the unit. NIST described it as “a distinctive click-hiss, a little like the sound of cracking open a bottle of soda.”
You may also notice a distinct chemical odor. This smell comes from the battery’s electrolyte. People often describe it as:
- Sweet and metallic
- Similar to nail polish remover
- A sharp, acrid smell
If you notice these sounds or smells, the situation is urgent.
Feeling for Excessive Heat
A lithium-ion battery getting hot is a major red flag. While it’s normal for batteries to get slightly warm during charging or heavy use, excessive heat is dangerous. High temperatures speed up battery degradation significantly. A battery that feels uncomfortably hot to the touch, even when idle, is a cause for concern.
A continuous temperature around 60°C (140°F) is the maximum for a lithium-ion battery. Anything hotter can cause rapid damage. If you suspect a battery is overheating, you must be very careful. Do not touch it directly if it is extremely hot, smoking, or bulging. If it is safe to do so, feel the device’s casing. If it heats up quickly, its internal temperature may already be high enough to cause damage. Always charge your devices in a cool area away from anything that could catch fire.
The Dangers of a Failing Battery
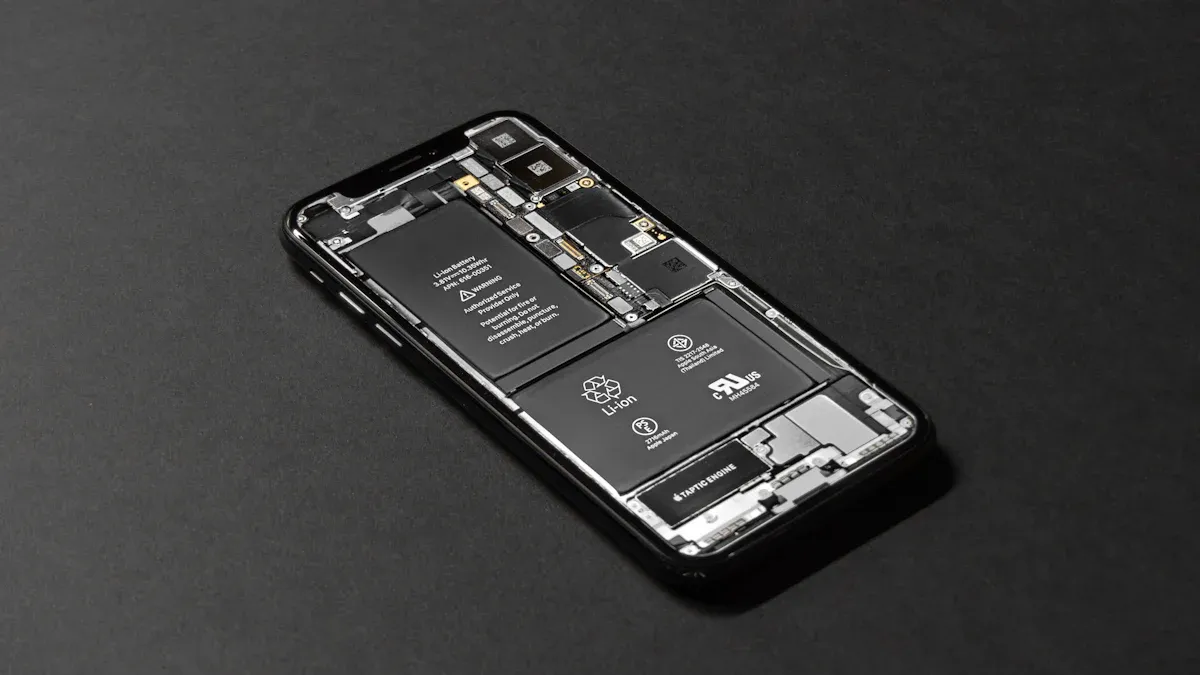

A failing lithium-ion battery presents serious safety risks. You must understand these dangers to protect yourself. The primary concerns involve fire and explosion hazards, chemical exposure, and environmental damage. A battery failure can escalate quickly, so knowledge is your best defense.
Fire and Explosion Risk
The greatest danger from a damaged lithium-ion battery is fire. This happens through a process called thermal runaway. Thermal runaway is a chain reaction inside the battery. It starts when a cell overheats due to damage, a defect, or overcharging. This heat triggers a chemical reaction that creates even more heat. The process becomes a feedback loop, causing temperatures to skyrocket.
This rapid heating can cause the battery to vent flammable gases, catch fire, or even explode. The entire thermal runaway event can happen in minutes.
Thermal runaway is the main failure mechanism for lithium-ion batteries. It can lead to severe fires and explosions. The process is very complex. It is easily influenced by both outside conditions and internal reactions.
Understanding thermal runaway helps you appreciate the urgent need for caution. A single cell failure can quickly become a dangerous fire.
Chemical Health Hazards
A lithium-ion battery leak releases toxic chemicals. These substances pose significant health and environmental hazards. The electrolyte contains organic solvents and lithium salts. Contact with these materials can cause you harm.
- Skin or Eye Contact: The chemicals are corrosive. They can cause severe skin burns and eye damage. If contact occurs, you should immediately flush the area with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical help.
- Inhalation: The vapors can irritate your respiratory system. Inhaling them may lead to dizziness, headaches, and nausea. When the electrolyte meets moisture in the air, it can form highly toxic hydrofluoric acid.
Environmental Contamination
The impact of a failing lithium-ion battery extends to the environment. You should never throw these batteries in the regular trash. Improper disposal leads to serious contamination.
- Land and Water Pollution: When batteries corrode in a landfill, their heavy metals and toxic chemicals leach into the soil and groundwater. This pollution harms ecosystems and can make water unsafe.
- Landfill Fires: Discarded lithium-ion batteries are a leading cause of fires in landfills and recycling centers. These fires are difficult to extinguish and release toxic smoke into the atmosphere, creating a lasting environmental impact.
Your Safety Plan for Damaged Batteries
Discovering a damaged battery is stressful, but having a clear safety action plan helps you stay in control. You must act quickly and methodically to protect yourself and your property. This plan guides you through the essential steps for safely handling, storing, and disposing of a failing lithium-ion battery.
Step 1: Immediate Safety Actions
Your first priority is to create a safe environment. If you suspect a battery is failing, immediately stop using the device and unplug it from any power source. If possible, move the device away from flammable materials. Before you handle the device, you must protect yourself. Safety experts recommend specific personal protective equipment (PPE) to prevent injury.
Your PPE should include:
- Eye Protection: Wear safety eyeglasses to shield your eyes from potential sparks or chemical splashes.
- Hand Protection: You should wear specialty heat-resistant gloves.
- Protective Clothing: Flame-resistant clothing or coveralls are crucial. They protect your skin from heat, sparks, and potential arc flashes if the battery ignites.
⚠️ Important: If the battery is smoking, hissing, or extremely hot, do not touch it. Evacuate the area immediately and call your local fire department.
Step 2: Safe Handling and Storage
Once you have your protective gear on, you can safely handle the device. Move it to a secure, isolated location outdoors if possible. Place it on a non-combustible surface like concrete or dirt, far from buildings, vehicles, and people.
For temporary storage, you need a fireproof container.
- Place the battery in a metal can and cover it completely with sand. The sand helps absorb heat and smother a potential fire.
- Keep the container away from other metal objects to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Another excellent option is a LiPo safe bag. These bags are designed to contain a lithium-ion fire. They are made with multiple layers of flame-retardant materials, like fiberglass and silicone, to reduce airflow and suppress flames.
Some LiPo bags have impressive safety features tested to industry standards.
| Feature | Performance Metric | Test Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Fireproof Performance | Resists 800°C (1472°F) for 60 mins | ASTM E119 |
| Explosion Resistance | Withstands internal pressure of 137.9 kPa (20 psi) | ASTM F2417 |
| Explosion Suppression | Suppresses flame leakage | ASTM F1550 |
Proper storage is a key part of your risk management strategy until you can dispose of the battery.
Step 3: Proper Hazardous Waste Disposal
You must never throw a damaged lithium-ion battery in your regular trash or recycling bin. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) classifies these batteries as hazardous waste. Improper disposal can cause fires in sanitation trucks and waste facilities and pollutes the environment.
Your responsibility is to find a certified disposal facility.
- Find a Collection Site: Use online resources from the EPA or organizations like Call2Recycle to find a local hazardous waste collection site or a retailer that accepts used batteries.
- Follow Instructions: Contact the facility beforehand. They will give you specific instructions for transporting and dropping off the battery safely.
- Consider Reuse: The EPA also promotes the reuse and repurposing of lithium-ion batteries to extend their useful life. However, this option is for healthy batteries, not damaged ones.
Critical ‘What Not to Do’ List
Knowing what not to do is just as important as knowing what to do. A single mistake can have a severe impact. Avoid these actions at all costs:
- Do NOT Use Water on a Fire: Using water on a lithium-ion fire is extremely dangerous. While it might seem to cool the fire, it reacts with the battery’s components to create large amounts of toxic and flammable gases, including hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
- Do NOT Throw the Battery in the Trash: This creates a major fire hazard for sanitation workers and facilities.
- Do NOT Mail or Ship the Battery: Shipping a damaged battery is illegal and dangerous. It puts transportation workers and vehicles at risk.
- Do NOT Try to Fix or Puncture the Battery: Never attempt to repair, open, or puncture a swollen battery. This can trigger an immediate and violent thermal runaway event.
- Do NOT Leave the Battery Unattended: Keep the battery in a safe, isolated location where you can monitor it until you can dispose of it properly.
How to Prevent Lithium-Ion Battery Leaks
The best way to handle a lithium-ion battery leak is to stop it from ever happening. You can prevent lithium-ion battery leaks by adopting safe habits. Your actions directly impact the health and safety of your batteries. Following best practices for charging, storage, and purchasing will significantly reduce your risk.
Smart Charging and Use Habits
How you charge your devices is critical. Always use the charger that came with your device or a certified replacement from the manufacturer. These chargers have built-in safety features to prevent overcharging.
- Automatic Shutoff: Stops charging when the battery is full.
- Temperature Control: Pauses charging if the battery gets too hot.
- Smart Charging: Adjusts voltage and current for optimal battery health.
A quality Battery Management System (BMS) is the brain of your lithium-ion battery. It monitors temperature, voltage, and current to prevent conditions that lead to failure. The BMS is your first line of defense against a potential lithium-ion battery leak.
Proper Storage Guidelines
Proper storage helps you prevent lithium-ion battery leaks and extend battery life. If you need to store a lithium-ion battery for a long time, you should follow two key rules.
Storage Tip: For long-term storage, keep your battery in a cool, dry place around 15°C (59°F). Also, maintain a partial charge of about 40-50%. Storing a fully charged or fully depleted battery causes faster degradation and increases the risk of failure.
Choosing Quality Brands
You should always choose products from reputable brands. Quality manufacturers invest in better materials and safety testing. Look for official certification marks on batteries and chargers. These marks show that the product meets strict safety standards.
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories)
- IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission)
- CE (Conformité Européenne)
These certifications mean the lithium-ion product has passed tests for electrical and fire safety.
Recognizing Manufacturing Defects
Sometimes, a battery is defective from the start. If you suspect a defect, check the manufacturer’s website or the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) website for recalls. If your device has a recalled battery, stop using it immediately. Contact the manufacturer for instructions on how to get a safe replacement. Never try to use a battery you think is defective.
Preventing lithium-ion battery leaks is your best defense. You must know the emergency steps for your personal safety. Your core safety plan is simple.
Safety Mantra: Identify the problem, Isolate the battery, and Dispose of it properly.
You can avoid a lithium-ion battery failure. Prioritize your safety by choosing quality lithium-ion products. Practice safe charging habits. Never ignore the warning signs of a problem.
FAQ
Can I put a damaged battery in the freezer to cool it down?
No, you should never put a damaged battery in the freezer. 🧊 Freezing can cause condensation and moisture buildup. This moisture can short-circuit the battery’s internal components, which increases the risk of a fire or explosion. Keep it in a dry, fireproof container instead.
What if I can’t find a hazardous waste facility nearby?
You can check with major electronics retailers or home improvement stores. Many offer battery take-back programs. You can also contact your local sanitation or public works department. They will provide guidance on the correct disposal options available in your area.
Is a battery that gets a little warm during charging dangerous?
A battery getting slightly warm during charging or use is normal. However, you should worry if it becomes uncomfortably hot to the touch. Excessive heat is a key warning sign of internal failure. Unplug the device immediately if it feels too hot.
Why is a swollen battery so dangerous?
A swollen battery indicates a chemical reaction inside is producing gas. This buildup creates immense pressure. The battery’s casing is not designed to hold this pressure. Any puncture or continued use can cause it to rupture, leak chemicals, or violently catch fire.

