
You may feel frustrated with your GPS tracking device. Its battery life seems too short. This rapid battery drain is a common issue. Frequent gps tracking updates quickly use the battery. Extreme temperatures and poor gps signal also shorten battery life. Your device’s age can cause battery failure. You can improve the battery life of your gps tracking device. This helps your gps tracking, gps tracking, and gps tracking stay active. A healthy battery is key for your gps, gps, gps, gps, gps, gps, and gps tracking.
Common Causes of GPS Tracker Battery Failure
You want your gps tracking device to be reliable. A dead battery makes it useless. Understanding why a battery fails is the first step to preventing it. Several factors drain your battery’s power. These common gps tracking device problems often have simple explanations. Let’s explore the main reasons for poor battery life.
Frequent Location Updates (Pings)
Your gps tracking device sends its location to you in updates, or “pings.” Each ping uses a small amount of power. More frequent pings provide more detailed gps tracking, but they also drain the battery much faster. The device’s battery capacity is measured in milliampere-hours (mAh). A higher mAh rating means the battery can store more energy. However, even a large battery will drain quickly with constant gps tracking updates.
Think of it this way: real-time gps tracking every few seconds is like sprinting. Periodic updates every few minutes are like walking. Sprinting uses far more energy. Optimizing your ping frequency can extend your battery life by up to 30%. This is one of the most common gps tracking device problems. The difference in battery life can be huge.
💡 Tip: Adjusting the update interval is a powerful way to conserve battery power. If you do not need constant monitoring, setting longer intervals between gps pings will significantly preserve your battery charge.
See how changing the update frequency impacts two different device models.
| Device Model | 10-Second Interval | 5-Minute Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Spark Nano | Approximately 8 days | Approximately 21 days |
| EON | Approximately 40 days | Approximately 140 days |
Extreme Hot and Cold Temperatures
Lithium-ion batteries, found in most gps trackers, have an ideal temperature range. Extreme heat and cold can cause serious issues and are common gps tracking device problems.
- Hot Temperatures: Heat above 95°F (35°C) makes the battery work harder. This accelerates chemical reactions inside the battery, causing it to degrade faster and permanently lose capacity. Leaving your gps tracking device in a hot car is a major cause of reduced battery life.
- Cold Temperatures: Cold weather slows down the chemical processes inside the battery. This reduces its ability to deliver power. You will notice the battery drains much faster in freezing conditions. Charging a very cold battery can also cause permanent damage.
- High Humidity: Moisture is another enemy. While many devices can handle up to 75% relative humidity, very damp environments can allow moisture to seep inside. This can corrode internal components and battery contacts, leading to poor battery performance and potential failure.
The table below shows how temperature affects a battery’s ability to hold a charge. A capacity loss of 25% at 14°F means your battery will only last 75% as long as it normally would.
| Temperature | Charge Rate | Cycles | Capacity Loss |
|---|---|---|---|
| -10°C (14°F) | 0.5C | 40 | 25% |
| 0°C (32°F) | 1C | 1 | 3.6% |
Poor GPS or Cellular Signal
Your gps tracking device needs two signals to work: a gps signal to find its location and a cellular signal to send that location to you. When either signal is weak, the device must boost its power to search for a connection. This constant searching is a massive power drain and one of the most common gps tracking device problems.
Your device struggles to get a gps fix indoors, in underground parking garages, or in “urban canyons” between tall buildings. Many building materials also block cellular signals. A loss of just -3 decibels (dB) cuts the signal strength in half.
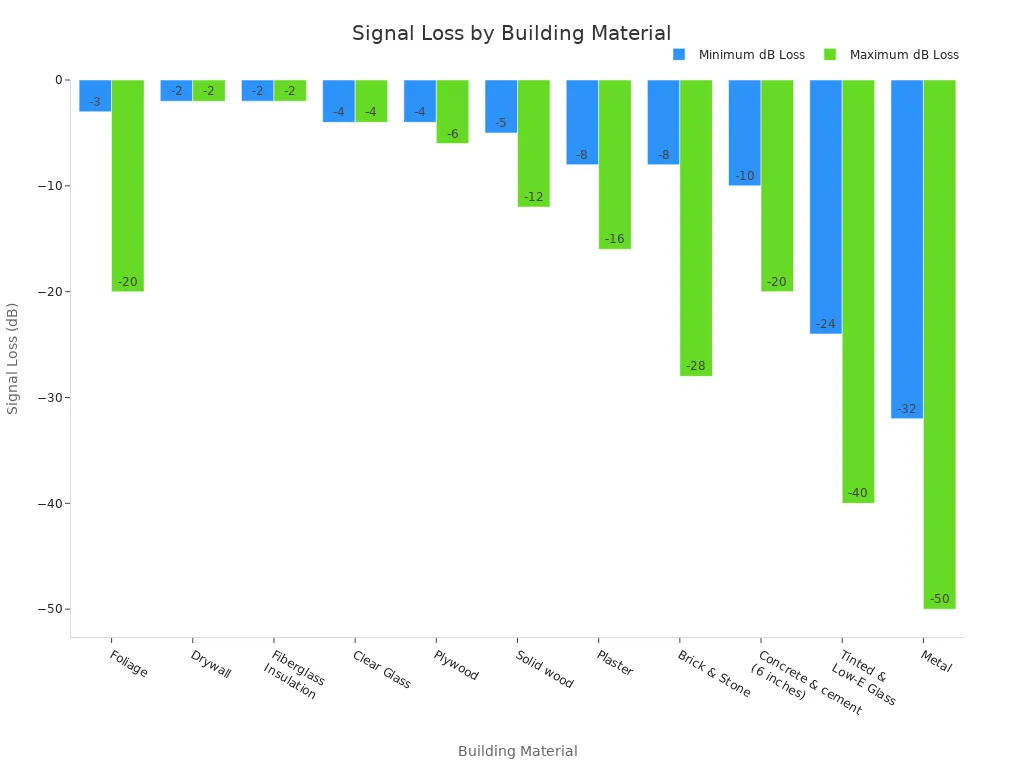
Common materials that block gps and cellular signals include:
- Metal: The worst offender, causing signal loss of -32 to -50 dB.
- Concrete & Brick: Dense materials that can block -8 to -28 dB of signal.
- Low-E or Tinted Glass: Often contains metal particles, blocking -24 to -40 dB.
- Plywood and Drywall: Cause less interference but still weaken the signal.
When your device is in a weak signal area, it uses 5 to 10 times more power trying to connect. This constant struggle for a gps signal is a primary cause of rapid battery drain.
Battery Age and Health Degradation
Like all rechargeable batteries, the battery in your gps tracking device has a limited lifespan. Each time you charge and discharge it, it loses a tiny bit of its total capacity. Over hundreds of cycles, this degradation adds up. An older battery simply cannot hold as much power as a new one. This is a natural process.
Leaving the battery uncharged for a long time also causes damage. This is one of the most overlooked common gps tracking device problems. Here is what happens:
- Self-Discharge: A lithium-ion battery slowly loses its charge even when turned off.
- Deep Discharge: If the battery self-discharges completely, its voltage can drop too low. This can make the battery “dormant,” meaning it can no longer accept a charge. This leads to permanent battery failure.
- Chemical Aging: Internal chemical reactions continue even when the device is idle. These reactions break down the battery’s components over time, reducing its ability to store power.
A healthy battery is crucial for effective gps tracking. An old or neglected battery will give you poor battery life and unreliable gps tracking.
Incorrect Charging Habits
How you charge your gps tracking device directly impacts its long-term health. Bad habits can shorten your battery life and even create safety risks.
Warning: Never use a cheap or unverified charger. These chargers often lack safety features to prevent overheating. Overcharging a lithium-ion battery can cause it to expand, generate extreme heat, and create a fire risk.
Using the wrong charger is a serious problem. For example, using a charger with the incorrect voltage can overcharge the battery, causing it to release hazardous gases. This is dangerous in enclosed spaces.
Treating your device like a smartphone is a great habit. A daily charging routine ensures the battery is always ready for gps tracking when you need it most. Lithium-ion batteries perform best with frequent, partial charging instead of being fully drained each time. This simple habit prevents deep discharge and extends the overall life of your battery. Consistent charging eliminates anxiety about your battery level and keeps your gps tracking active.
Solutions to Extend Battery Life

You can take control of your GPS tracker’s performance. Simple changes to your settings and habits can dramatically improve its battery life. These gps tracking solutions help you get the most out of your device. You will ensure your gps tracking is always active when you need it. Let’s explore the best ways to boost your battery life.
Optimizing GPS Tracking Settings
Your device’s settings are the first place to look for power savings. You have direct control over how much power the gps tracker uses. Adjusting these settings is a key part of effective power management. You can balance detailed gps tracking with longer battery life.
Consider changing these common settings in your gps tracking app:
- GPS Update Frequency: You can increase the time between location pings. If you do not need second-by-second updates, changing the interval to every 5 or 10 minutes will significantly extend your battery life.
- Sleep Modes: You can configure the device to enter a low-power sleep mode when it is not moving. It will wake up and resume gps tracking once it detects motion.
- Geofencing: You can set up virtual boundaries. The device will only send location updates when it enters or leaves these specific areas. This stops constant gps tracking when the asset is in a known, safe location.
- Screen Settings: You should set a short screen timeout on devices with screens. Dimming the brightness also helps conserve the battery.
Protecting from Extreme Weather
You must protect your gps tracking device from extreme temperatures and moisture. Heat, cold, and humidity all reduce your battery’s capacity and lifespan. Proper protection is a simple way to ensure reliable gps tracking.
Many devices offer protective cases. For example, you can get a waterproof case for the Family1st GPS Tracker or a weatherproof M2 case for the Spytec GPS GL300. Models like the LandAirSea 54, Spark Nano, and EON Odyssey have rugged, water-resistant designs built to handle harsh weather. These enclosures shield the internal components and battery from damage.
🚗 Vehicle Tip: When placing a gps tracker in a car, choose a cool, shady spot. You should avoid placing it near the engine, under the hood, or by heating elements. These areas get very hot and can damage the battery.
Ensuring Strong Signal Reception
Your device uses a lot of power when it struggles to find a gps or cellular signal. You can improve battery life by placing the tracker where it has a clear view of the sky. Metal and dense building materials block signals, forcing the battery to work harder.
Here are some of the best placement locations in a vehicle for strong gps signal:
- On the Dashboard or Rear Shelf: These spots offer great signal strength. Only glass blocks the gps signal.
- Under the Car: A magnetic case lets you attach the device to the vehicle’s frame. The gps signal bounces off the road, providing a strong connection.
- Inside a Plastic Bumper: This is a good hidden location. The gps signal can easily pass through plastic or fiberglass.
You should avoid placing the device in the trunk or glove box. These enclosed metal spaces can severely weaken the signal and drain your battery. A strong signal means less work for the device and better battery life for your gps tracking.
Adopting Proper Charging Practices
Your charging habits directly affect your battery’s health and longevity. Good power management starts with using the right tools. You should always use the charger that came with your gps tracking device. Unverified chargers can damage the battery or create a fire hazard.
You can develop a consistent charging routine. Treating your gps tracker like a smartphone is a great idea. Charging it regularly prevents the battery from draining completely. This practice avoids deep discharge, which can permanently damage the battery. A full battery gives you peace of mind and reliable gps tracking.
🚚 For Fleet Managers: If you have hardwired gps trackers in vehicles that are not used often, a trickle charger is an excellent power management tool. It provides a slow, steady stream of power to the vehicle’s battery. This ensures both the vehicle and the hardwired gps tracker always have power, extending the battery life of the unit. You can also set up low-voltage alerts to notify you when a vehicle’s battery is running low.
Using Power-Saving Modes
Most modern gps trackers offer special power-saving modes. These features are designed to maximize battery life by intelligently managing the device’s functions. Understanding these modes helps you choose the best power management setting for your needs.
Here is how some common modes work to save power:
- GPS Sleep Mode: The device turns off the gps module when it is stationary for a set period. The cellular module stays on. It wakes up instantly when it detects movement. This mode offers good power savings.
- Deep Sleep Mode: This mode turns off both the gps and cellular modules when the device is stationary. This provides very low power consumption. The device still wakes up when it detects movement.
- Online Deep Sleep Mode: This mode is similar to Deep Sleep, but the device briefly turns on its cellular module to send a periodic update. This lets you check on the device without fully waking it. It offers a great balance between power savings and connectivity.
Activating a power-saving mode is one of the most effective ways to get more battery life from your gps device.
Troubleshooting Your GPS Tracking Device
Sometimes, even with the best habits, your gps tracking device may act up. You can troubleshoot common issues to find the source of the problem. These steps help you identify if the issue is a simple connection, a software glitch, or a hardware failure. Learning to troubleshoot common issues will save you time and restore your gps tracking.
Checking Power and Connections
You should first check the device’s power source. The steps differ for battery-operated and hardwired trackers.
- Battery-Operated Trackers: You can ensure the battery is correctly inserted. You should also check that the charging port is clean and free of debris. A loose battery can interrupt power.
- Hardwired Trackers: A poor connection is a common cause of power loss. You can check these key areas for your gps tracking device:
- Inspect the vehicle’s fuse box and any in-line fuse for the gps tracker. Replace any blown fuses.
- Perform a “wiggle-test” on all wiring to find loose connections that might cut power.
- Examine the ground wire. A bad ground connection is a frequent cause of gps tracking problems.
Performing a Hard Reset
A hard reset can often resolve software issues that affect gps tracking. This process reboots the gps tracking device without erasing your settings. If your gps tracker shows a “Last Known” position, it may be stuck.
💡 Note: A reset forces the device to re-establish its gps and cellular connections. This can fix many temporary gps tracking glitches and improve battery life.
You can typically perform a reset from your gps tracking app. The device will attempt to get a “Current” position status. This simple step can restore your gps tracking and power.
When to Replace the Battery
An old battery cannot hold a charge effectively. This leads to poor battery life and unreliable gps tracking. You should replace the battery if you notice these signs of battery failure:
- The device shuts down suddenly, even after a full charge.
- The battery looks swollen or feels hot when charging.
- The battery no longer accepts a charge at all.
A healthy battery is essential for your gps. Experts recommend replacing the battery when its maximum capacity drops below 80%. A new battery will restore your device’s battery life and gps tracking performance. This is a clear sign of battery failure.
When to Replace the Entire Unit
Sometimes, the problem is not the battery. The entire gps tracking device may be failing. You might need a new unit if you experience these issues:
- The device reports inaccurate gps locations or shows erratic movement.
- You see frequent error messages like “GPS signal lost.”
- The unit often appears “offline” or has long delays in gps updates.
A failing unit compromises your gps tracking. Replacing the device ensures you have reliable power and accurate gps data.
You can control your gps tracking device’s battery life. Your gps tracking needs a healthy battery. You can improve your gps battery life with three key actions. First, adjust your gps settings for better gps tracking. Second, protect your gps from extreme weather and ensure a good gps signal. This helps the battery. Third, use proper charging habits for your gps battery. These steps give you reliable gps tracking and a longer battery life.
Your gps tracking and gps battery performance are in your hands. You now have the knowledge to ensure your gps is always ready.
FAQ
How long should my GPS tracker battery last?
Your tracker’s battery life varies. It depends on the device model, your settings, and signal strength. Some batteries last a few days, while others can last for months. You can check your device’s specifications for an estimate.
Can I use any USB charger for my GPS tracker?
You should only use the charger that came with your device. Using a different or unverified charger can damage the battery. It might also create a safety risk, like overheating or a fire.
Why does my tracker’s battery drain so fast in my car?
Your car can get very hot, which makes the battery work harder. The car’s metal frame can also block GPS and cellular signals. This forces the device to use more power searching for a connection, draining the battery quickly.
Does turning the tracker off save the battery?
Yes, turning the device off saves significant power. The battery will still self-discharge slowly over time. You should not leave it uncharged for long periods, as this can cause permanent battery failure.

