
The life expectancy of a 18650 battery depends on several conditions. A typical 18650 battery offers a certain number of charge cycles. Users can generally expect a lifespan for their 18650 rechargeable battery based on these figures:
- Charge Cycles: 300 to 500 cycles
- Years: 2 to 4 years
Some high-quality 18650 models can achieve a long lifespan. This rechargeable battery might even exceed 1000 cycles with proper care. The overall life expectancy for any 18650 battery is not fixed. User habits greatly affect how long the battery lasts.
Understanding the Life Expectancy of a 18650 Battery

The life expectancy of a 18650 battery is not a single, fixed number. It depends on a mix of chemical processes and user habits. A battery degrades in two ways. Cycle aging happens from charging and discharging. Calendar aging happens over time, even when the battery is not in use. For devices like laptops or electric vehicles that are idle most of the time, calendar aging can be the main cause of degradation. Understanding these factors helps users extend the life of their 18650 cells.
Key Factors in 18650 Life Expectancy
Several key factors determine the lifespan of an 18650 rechargeable battery. Inside every battery, chemical reactions occur. These reactions cause slow, irreversible changes. For example, a layer called the Solid Electrolyte Interphase (SEI) grows on the electrodes. This growth consumes active lithium and increases internal resistance, which reduces the battery’s capacity.
The main factors that speed up this degradation are:
- Battery Quality: Reputable brands produce cells with better materials and fewer manufacturing defects.
- Depth of Discharge (DoD): How much capacity a user drains before recharging.
- Charging Rate: The speed at which the battery is charged.
- Temperature: Both high and low temperatures affect battery health.
Charge Cycles and Usage Frequency
A “charge cycle” describes one full discharge and recharge. While a typical 18650 is rated for 300-500 charge cycles, this number can be misleading. The depth of each cycle matters more than the number of cycles. Shallow discharges and recharges are much less stressful on a battery than full ones.
For instance, NASA tests on Sony 18650 batteries showed they could last over 75,000 cycles over eight years. This was possible because they were only discharged to about 30% of their capacity in each cycle. This shows that frequent, shallow charging can lead to a much longer overall life expectancy. A battery does not have a “memory effect,” so partial charges are beneficial.
Depth of Discharge (DoD)
Depth of Discharge (DoD) refers to the percentage of the battery’s capacity that has been used. A 100% DoD means the battery is completely drained, while a 30% DoD means it still has 70% charge left.
Pro Tip: To maximize the life of your 18650, try to keep its charge between 20% and 80%. Regularly draining the battery to 0% causes significant stress and shortens its lifespan. Maintaining a partial charge can double the number of effective cycles you get from the battery.
Charging Rate and Voltage
The speed and voltage of charging directly impact the life expectancy of a 18650 battery. The charging rate is measured in “C,” where 1C is the rate that would fully charge the battery in one hour.
- Charging Rate: A slower charging rate is always better for battery health. The ideal rate is between 0.3C and 0.5C. For a 3000mAh 18650 battery, this means charging at 1.5 amps or less. Fast charging at 1C or higher generates extra heat and accelerates degradation.
- Charging Voltage: Standard 18650 cells are charged to 4.2V. However, stopping the charge at a lower voltage can dramatically increase lifespan. Charging to just 4.1V can double the cycles, while charging to 4.0V can quadruple them. This is why some electric vehicle manufacturers recommend charging to 80% for daily use.
High discharge rates also shorten battery life. Drawing a lot of power quickly generates heat and puts stress on the cell’s internal components.
| Discharge Rate | Capacity Loss (after 300 cycles) |
|---|---|
| 1C | 9.5% |
| 3C | 16.9% |
Operating and Storage Temperature
Temperature is one of the most critical factors for a rechargeable battery. Extreme heat or cold can cause permanent damage. High temperatures speed up the chemical reactions that cause degradation, like SEI growth and electrolyte decomposition. Storing a battery at 60°C (140°F) can cause it to lose 20% of its capacity in just a few months.
| Battery Type | Operating Temperature | Charging Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| 18650 Rechargeable | -20°C to 60°C | 0°C to 45°C |
The ideal operating temperature is between 20-25°C (68-77°F). Never charge an 18650 below freezing, as this can cause lithium plating on the anode, creating a risk of a short circuit.
Battery Quality and Chemistry
Not all 18650 cells are created equal. The quality of manufacturing and the specific chemistry used play a huge role.
Chemistry: Different lithium-ion chemistries offer different benefits. For example, LiFePO4 (IFR) batteries are known for their excellent safety and very long cycle life, often reaching 1000-2000 cycles. They are a great choice for applications where longevity is the top priority.
Quality: High-quality cells from brands like DNK, Sony, Samsung, LG, and Panasonic have strict manufacturing controls. Low-quality or counterfeit cells often have dangerous defects, such as poor internal alignment, which increases the risk of short circuits and fires. These cells also have wildly inflated capacity ratings. A high-quality 18650 will have realistic specifications and a clean, professional appearance.
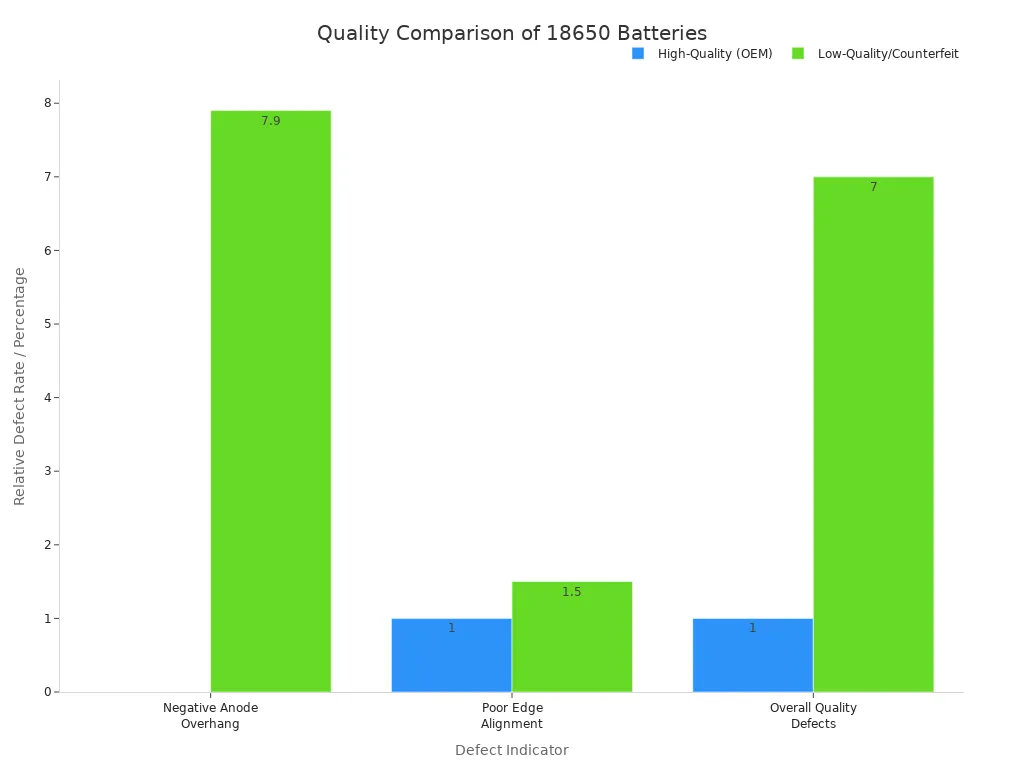
Choosing a high-quality 18650 from a reputable source is the first step toward ensuring a long and safe operational life.
How to Maximize 18650 Battery Lifespan
Users can take several practical steps to extend the operational life of their 18650 cells. Proper care not only improves performance but also ensures safety. Following best practices for charging, storage, and general use can significantly increase the number of cycles a battery provides.
Optimal Charging Practices
Correct charging habits are the most effective way to improve the life expectancy of an 18650 battery. Users should avoid fully draining or fully charging the battery whenever possible. Keeping the charge level between 20% and 80% minimizes stress on the cell’s chemistry.
A slow and steady charge is always better. A charging rate of 0.5C (or half the battery’s capacity in amps) is ideal. For a 3000mAh 18650, this means charging at 1.5 amps. Users should also avoid leaving a battery on the charger after it reaches 100%. While a smart charger will stop, keeping the battery at its peak voltage of 4.2V accelerates degradation.
Why You Shouldn’t “Trickle Charge” a Full 18650
Leaving a fully charged 18650 on a charger is not recommended. This practice keeps the battery at a high voltage, which speeds up aging.
- Manufacturers design chargers to stop when the current drops below a certain level (e.g., 50-100mA).
- Holding a battery at 4.2V for long periods accelerates chemical decay.
- This high-voltage state can lead to metallic lithium plating, a process that permanently damages the battery.
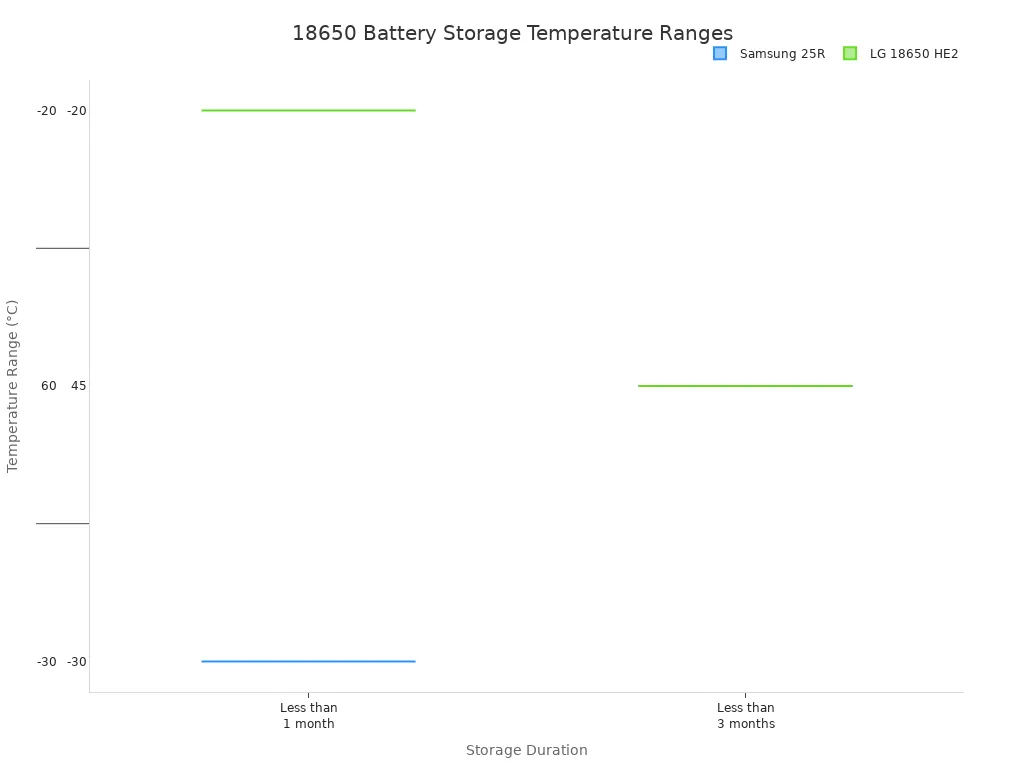
Proper Storage Guidelines
Proper storage is essential for preserving a rechargeable battery. Users should never store an 18650 battery when it is fully charged or completely empty. The ideal state of charge for long-term storage is between 40% and 60%. This level provides enough energy to account for self-discharge without stressing the cell.
| State of Charge (%) | Approximate Voltage (V) |
|---|---|
| 40% | 3.5V |
| 50% | 3.6V |
| 60% | 3.7V |
The storage environment is just as important. A cool, dry place is best. The ideal temperature is around 20-25°C (68-77°F). High temperatures are extremely harmful. Storing a battery in a hot car, for example, can cause rapid and irreversible capacity loss. The acceptable temperature range narrows for longer storage periods.
Safe Usage Habits
Safe handling protects both the user and the 18650 battery. Users must regularly inspect their cells for any physical damage. The thin PVC wrapper on an 18650 is a critical safety feature.
A torn or missing wrapper exposes the metal can of the battery. The entire can is the negative terminal. If a metal object like keys or coins touches the exposed can and the positive top, it will cause a dangerous short circuit.
- Never use an 18650 with a damaged wrapper or insulator ring.
- A short circuit can cause the battery to explode, burn, or start a fire.
- Users should immediately rewrap any 18650 with a damaged wrapper using a new 18650 wrap and a heat source.
Additionally, users should only use an 18650 in devices designed for it. Drawing too much current from a battery not rated for high-drain applications can cause it to overheat and fail.
Choosing a Quality Smart Charger
A high-quality smart charger is a necessary investment for any 18650 user. These chargers do more than just supply power. They actively manage the charging process to protect the rechargeable battery.
One of the most important functions is chemistry identification. A smart charger can detect the type of battery inserted and apply the correct charging algorithm. For a lithium-ion 18650, it uses a specific voltage-limited process. Applying the wrong charging method can cause permanent damage or even thermal runaway.
Smart chargers also include several key features that protect the battery:
- Temperature Monitoring: Prevents the battery from overheating during a charge cycle.
- Overcharge Protection: Automatically stops the charge when the battery reaches 4.2V.
- Automatic Shutoff: Ends the charging process completely once the battery is full, preventing harmful trickle charging.
Using a dedicated smart charger ensures each 18650 is charged safely and efficiently, helping it reach its maximum potential lifespan.
Signs Your 18650 is Degrading
Every rechargeable battery eventually wears out. Recognizing the signs of degradation helps users know when to replace their 18650 cells for safety and performance. Paying attention to these indicators is crucial for any 18650 battery user.
Reduced Capacity and Runtime
The most obvious sign of a degrading 18650 is a noticeable drop in runtime. A battery that once powered a device for hours may now last only a fraction of that time. This happens because the battery can no longer hold its original charge. Users can measure the true capacity of a battery to confirm its health.
A common testing method involves these steps:
- Fully charge the 18650 to 4.2V.
- Let the battery rest for one hour to stabilize.
- Discharge the battery at a constant, low current (e.g., 0.5A) until it reaches its cutoff voltage, usually around 2.75V.
- The total time it takes to discharge reveals the battery’s actual capacity in milliampere-hours (mAh).
Increased Self-Discharge Rate
A healthy 18650 holds its charge well when not in use. A degrading battery will lose its charge much faster.
- New Battery: A new battery typically self-discharges at a rate of 1-2% per month.
- Degrading Battery: An older battery may lose a significant amount of charge in just a few days due to internal chemical changes.
If a fully charged 18650 is nearly empty after sitting on a shelf for a week, its internal components are likely breaking down.
Physical Damage or Swelling
Physical changes are a serious warning sign. Users should regularly inspect their cells for damage. A swollen or bulging 18650 is extremely dangerous. Swelling occurs when the electrolyte inside the battery decomposes and releases gas, increasing internal pressure. This can be caused by overcharging, overheating, or simple aging.
⚠️ Safety First: Handling a Damaged Battery If a battery is swollen, leaking, or has a torn wrapper, users must stop using it immediately. Place the damaged battery in a safe, isolated location away from flammable materials. Never attempt to charge or use a physically damaged cell.
Overheating During Use or Charging
It is normal for a battery to get slightly warm during charging or heavy use. However, excessive heat is a clear sign of a problem. As a battery ages, its internal resistance increases. This resistance causes the battery to generate more heat as it works. An unreliable cell can overheat, vent flammable gas, and even catch fire. If an 18650 becomes too hot to touch comfortably, it is failing and should be replaced.
The life expectancy of a 18650 battery is not a set number. A rechargeable battery can last from 300 to over 1000 charge cycles. Users can extend the life expectancy of their 18650 battery. Proper care significantly increases the number of cycles a battery delivers. This includes managing charging, controlling temperature, and avoiding deep discharges. Safety is the top priority for any 18650.
⚠️ Safety and Disposal Users must always inspect their battery. A swollen or damaged battery is unsafe. Stop using the battery immediately. Responsibly replace the rechargeable battery. Find a local recycling facility, as this type of battery is often considered hazardous waste.
FAQ
How many years does a 18650 battery last?
A typical 18650 battery lasts for two to four years. This lifespan depends on usage habits and care. High-quality cells can last longer with proper charging and storage. Frequent heavy use or exposure to extreme temperatures will shorten the battery’s operational life.
Can you revive a dead 18650 battery?
Users should not try to revive a dead 18650 battery. A battery discharged below its safe voltage (around 2.5V) may have permanent internal damage. Attempting to recharge it is dangerous and creates a risk of fire or explosion. Always replace over-discharged cells.
Is it safe to use different 18650 brands together?
No, users must never mix different brands or models of 18650 batteries in the same device. Cells have different capacities and internal resistance. Mixing them can cause one battery to overcharge or over-discharge, creating a serious safety hazard. Always use identical, matched cells.
Does fast charging ruin a 18650 battery?
Fast charging does not immediately ruin a battery, but it shortens its total lifespan. The process generates extra heat and puts more stress on the battery’s internal chemistry. For a longer life, users should charge their 18650 cells at a slower rate, such as 0.5C.

