
You can read a 3.7V lithium battery state of charge chart by matching the battery’s voltage to its charge level. The chart shows you how the voltage relates to the charge in a lithium-ion battery. This helps you know when the battery is full, half, or almost empty. Accurate reading of the state of charge helps you protect battery health. Research shows that understanding the voltage and state of charge lets you make better choices for battery use and safety. Good habits extend battery life and keep your lithium battery working well.
Lithium Battery State of Charge

SOC Chart Basics
You can use a state of charge chart to understand how much energy remains in your lithium-ion battery. The chart shows the link between the battery’s voltage and its charge level. When you check the voltage, you can estimate the battery capacity left. This helps you avoid overcharging or deep discharging, which can damage the battery and shorten battery life.
A 3.7V lithium-ion battery changes voltage as it charges and discharges. When the battery is full, the voltage is high. As you use the battery, the voltage drops. The state of charge chart helps you see this change and manage your battery safely. Good soc management means you keep your battery within safe voltage limits. This protects battery life and keeps your device working longer.
Tip: Always use a state of charge chart made for your battery type. Different lithium battery chemistries can have different voltage ranges.
Voltage and Charge Levels
The voltage of a lithium-ion battery tells you its state of charge. You can use the chart below to match voltage to battery status and battery capacity. This helps you know when to charge your battery or stop discharging it.
| Voltage Parameter | Typical Voltage Range / Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 3.6V to 3.7V | Average voltage during discharge cycle; most of the battery’s life is spent here |
| Full Charge Voltage | 4.2V | Maximum safe charging voltage; do not exceed this value |
| Discharge Cut-off Voltage | 3.0V to 2.8V | Minimum safe voltage; avoid going below this to protect battery life |
| Open Circuit Voltage to Start Charging | Below 3.6V | Start charging when voltage drops below this point |
| Charging Voltage (No Protection Board) | 4.2V max | Monitor charging to avoid overcharging |
| Charging Voltage (With Protection Board) | 4.8V to 5.2V | Charging circuit controls voltage for safety |
The state of charge chart for a 3.7V lithium-ion battery shows how voltage matches with battery capacity and charge level:
| Voltage Range (V per Cell) | Approximate SOC (%) | Battery Status |
|---|---|---|
| Around 4.2 V | 100% | Fully charged |
| 3.8 V to 4.1 V | 80% to 99% | High charge level |
| 3.5 V to 3.7 V | 50% to 79% | Medium charge level |
| 3.3 V to 3.4 V | 20% to 49% | Low charge level |
| Around 3.0 V | 0% to 19% | Nearly depleted/empty |
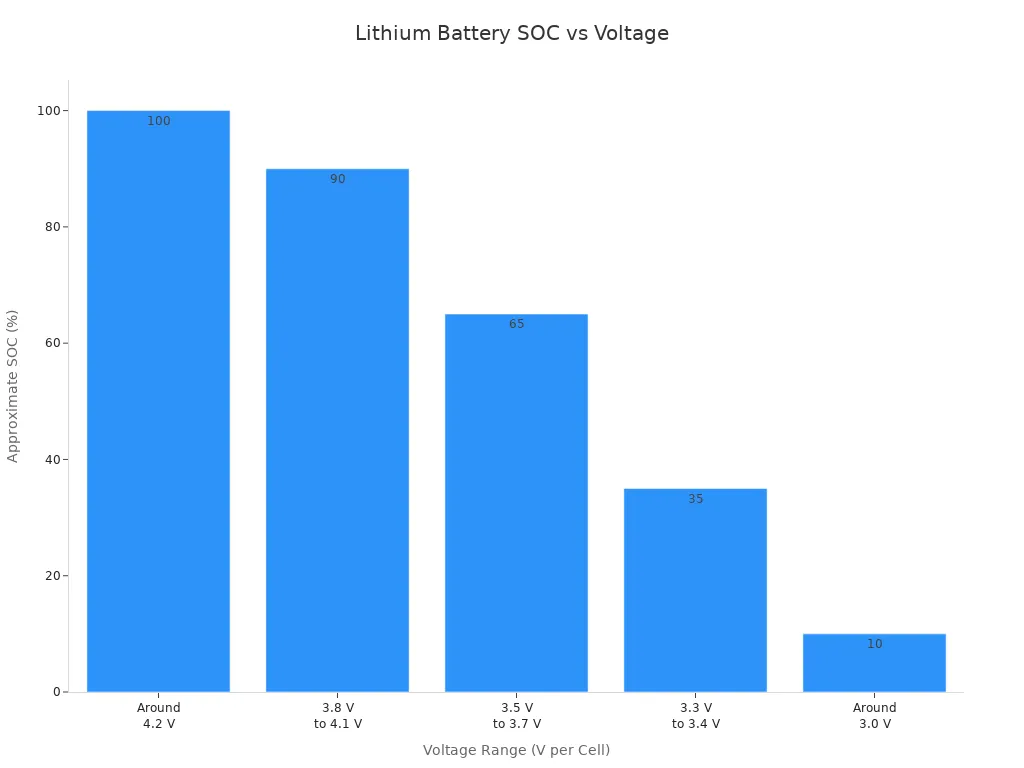
When your lithium battery voltage is near 4.2V, the battery is fully charged. This means the battery capacity is at its highest. If the voltage drops to around 3.7V, the battery is at its nominal or average charge level. Most of the battery’s life happens in this range. When the voltage falls to 3.0V, the battery is almost empty. Discharging below this point can damage the battery and reduce battery life.
You should avoid charging above 4.2V or discharging below 3.0V. Staying within these limits helps you get the most out of your lithium-ion battery. Good soc management means you check the voltage often and keep the battery in the safe range. This protects battery capacity and extends battery life.
Note: Battery management systems (BMS) help monitor voltage and prevent overcharging or deep discharging. This keeps your lithium battery safe and healthy.
You can use the state of charge chart to plan when to charge your battery and when to stop discharging. This helps you avoid problems like overheating, swelling, or loss of battery capacity. By following the chart, you make sure your lithium-ion battery lasts longer and works better.
Using the SOC Chart
Measuring Battery Voltage
To get an accurate state of charge reading, you need to measure your battery voltage correctly. The best way to do this is by using the open-circuit voltage method. This method gives you a clear picture of your battery’s charge level when the battery is not connected to any device or charger.
Here are some important points to remember when measuring open-circuit voltage:
- Always let your lithium-ion battery rest after use or charging. Wait at least 30 minutes before taking readings. This allows the voltage to stabilize.
- Use a digital voltmeter or multimeter with a range that covers your battery voltage. Make sure the tool is calibrated for accurate readings.
- Disconnect the battery from any circuit or device. This prevents false readings caused by current flow.
- Connect the red probe to the positive terminal and the black probe to the negative terminal.
- Read the voltage displayed on the meter. Write down the value for comparison.
Tip: Temperature can affect your readings. Try to measure your battery voltage at room temperature. Extreme heat or cold can change the voltage and give you the wrong state of charge.
You should also know that battery aging can change how voltage matches with the state of charge. Over time, the same voltage may not mean the same battery capacity. Regular calibration and temperature compensation help keep your readings accurate. For real-time battery monitoring in dynamic systems, experts recommend combining open-circuit voltage with other methods, like coulomb counting and model-based tools. This approach improves accuracy, especially when the battery is in use.
Matching Voltage to SOC
Once you have measured your battery voltage, you can use the state of charge chart to find out how much charge remains. Follow these steps to match your readings to the correct state of charge:
- Select a voltmeter or multimeter that matches your battery’s voltage range.
- Disconnect your battery from any device or charger.
- Attach the probes: red to positive, black to negative.
- Read the voltage on the display. Make sure you use the correct setting on your meter.
- Compare your measured voltage to the state of charge chart for your lithium-ion battery.
For example, if your reading is close to 4.2V, your battery is fully charged. If you see around 3.7V, your battery is about halfway charged. A reading near 3.0V means your battery is almost empty and needs charging soon. This process helps you with soc management and keeps your battery within safe limits.
Note: Always use the correct chart for your battery type. Different lithium-ion batteries can have slightly different voltage-to-charge level relationships.
Monitoring battery levels with regular readings helps you avoid overcharging or deep discharging. This practice supports best practices for soc management and extends battery life. Using soc monitoring tools, like a battery management system, can make readings easier and more reliable. These tools help with soc optimization and real-time monitoring, especially if you use your battery in demanding applications.
By following these steps and using the right tools, you can improve your soc readings and protect your battery capacity. Good soc management and best practices for soc management will help you get the most from your lithium-ion battery and your battery charger. Accurate readings and careful monitoring lead to better optimization and longer battery life.
Battery Maintenance

Charging Best Practices
You can extend battery life by following best practices for charging lithium-ion batteries. Charging lithium-ion batteries to the full 4.2V gives you maximum battery capacity, but research shows this can shorten battery longevity. To get the most cycles from your battery, use your battery charger to stop charging at 4.0V or 4.1V. Many experts recommend keeping your charge between 20% and 80%. This range reduces stress on the battery and helps with soc optimization. Avoid deep discharges below 3.0V. If you let your battery voltage drop too low, you risk permanent damage and a big loss in battery life. Always use a battery management system or a smart battery charger to monitor voltage and prevent overcharging or deep discharge.
Charging lithium-ion batteries in shallow cycles and not letting them reach full charge or deep discharge will help you get longer battery life and better battery performance.
Storage Guidelines
Proper storage is a key part of battery care. If you plan to store your lithium-ion battery for a long time, charge it to about 40%. This means your battery voltage should be around 3.7V. Storing batteries at this level helps you keep more battery capacity over time. Batteries stored fully charged lose up to 20% of their capacity each year, but those stored at 40% charge lose only about 4%. Store your battery at room temperature, between 15°C and 25°C, to slow down aging and keep battery longevity high.
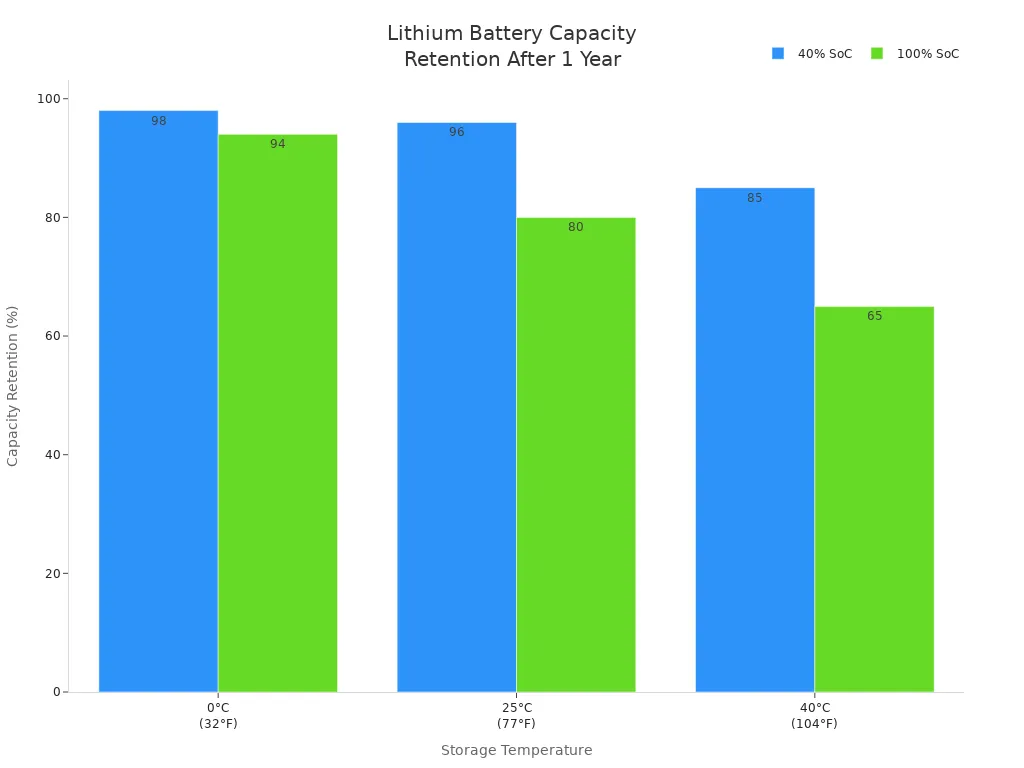
Check your battery every month. Use your battery charger to top up if the voltage drops. This routine supports battery maintenance and battery care.
Temperature and Safety
Charging lithium-ion batteries at the right temperature keeps your battery safe and healthy. Only charge your battery between 0°C and 45°C. Charging outside this range can cause dangerous chemical changes and lower battery life. Store your battery between 10°C and 25°C for best results. Battery management systems help you track temperature and voltage. They protect your battery from overheating and overcharging. You should recalibrate your battery management system every few months to keep your state of charge readings accurate. This step helps you maintain battery performance and battery longevity.
Troubleshooting
Inaccurate Readings
You may sometimes notice that your soc readings do not match your expectations. Several common issues can cause inaccurate voltage readings when you check your battery. The table below shows some of the most frequent problems and their effects:
| Condition | Effect on Voltage Reading | Explanation / Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Poor probe connection | Fluctuating or erratic readings | Loose or shaky probe contact during testing |
| Incorrect multimeter settings | Incorrect or unstable readings | Using wrong range or mode on the multimeter |
| Temperature effects | Voltage readings vary or drop | Battery voltage affected by ambient temperature |
| Battery internal damage/aging | Erratic or low voltage readings | High internal resistance or physical damage |
To improve your soc readings, follow these tips:
- Make sure your probes have a stable and secure connection.
- Always use the correct settings on your multimeter.
- Test your battery in a room with a steady temperature.
- Stop testing if your battery feels warm, as this can signal damage.
Temperature changes can affect your voltage readings. Cold weather can make the voltage drop, which may cause you to overestimate the charge. Hot weather can also change the voltage and make your readings less reliable. For the best results, measure the open-circuit voltage after your battery rests. Using a battery management system helps you get more accurate results by adjusting for temperature and current flow. This approach supports real-time battery monitoring and helps you with monitoring battery levels.
Battery Aging
As your battery gets older, you may notice changes in battery life and soc readings. Aging happens faster if you store your battery fully charged or at high temperatures. Storing your battery at about 40-50% charge and in a cool place helps slow down aging and keeps your battery life longer.
Signs of battery aging include:
- Loss of battery life and lower battery capacity.
- Voltage drops faster than before.
- The battery heats up more during charge or use.
Aging causes the battery’s internal resistance to rise. This makes voltage a less reliable way to check the charge. The link between voltage and charge changes as the battery ages. You may see that the same voltage now means less battery life than before. To keep your soc readings accurate, use a battery management system and calibrate your battery by doing a full charge and discharge cycle sometimes. Real-time monitoring with a battery management system helps you spot these changes early and adjust your charging habits.
You can read a 3.7V lithium battery SOC chart by following a few simple steps:
- Measure the open-circuit voltage after your battery rests.
- Match the voltage to the chart to find the charge level.
- Keep your battery between 20% and 80% charge for longer battery life.
- Never let the voltage drop below 3.0V to avoid damage.
- Store your battery at about 3.7V and in a safe place.
Using these steps helps you protect your battery and keep it working well.
FAQ
How often should you check the state of charge on your lithium battery?
You should check the state of charge every few weeks. Regular monitoring battery levels helps you catch problems early. This habit supports battery maintenance and improves battery longevity.
What is the safest way to store a lithium-ion battery for long periods?
Store your lithium-ion battery at about 40% charge. Keep it at room temperature. This practice protects battery capacity and supports battery care. You help prevent damage and extend battery life.
Why does temperature affect SOC readings?
Temperature changes the chemical reactions inside your battery. Cold or hot conditions can make SOC readings less accurate. For best results, measure at room temperature. Battery management systems can help adjust for temperature and improve real-time battery monitoring.
Can you use any SOC chart for all lithium batteries?
No, you should use a state of charge chart made for your battery type. Different lithium battery chemistries have different voltage ranges. Using the correct chart helps with soc optimization and best practices for soc management.
How do battery management systems help with battery maintenance?
A battery management system tracks voltage, temperature, and charge level. It prevents overcharging and deep discharging. This system supports battery health, battery performance, and real-time monitoring. You get better soc management and longer battery life.

